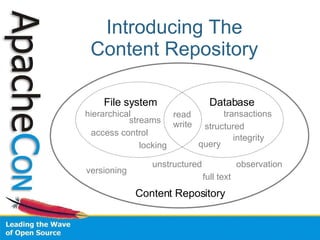
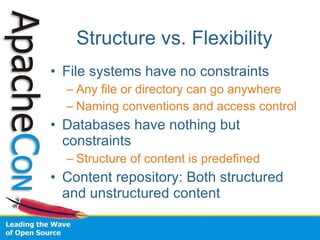
This document introduces the Java Content Repository (JCR), which provides a standardized API for storing and managing content. It discusses how JCR addresses limitations of traditional storage methods like file systems and databases by providing features like a flexible content model, full text search, transactions, versioning, and observation capabilities. The document also introduces Apache Jackrabbit, an open source JCR implementation, and outlines its goals and upcoming releases.