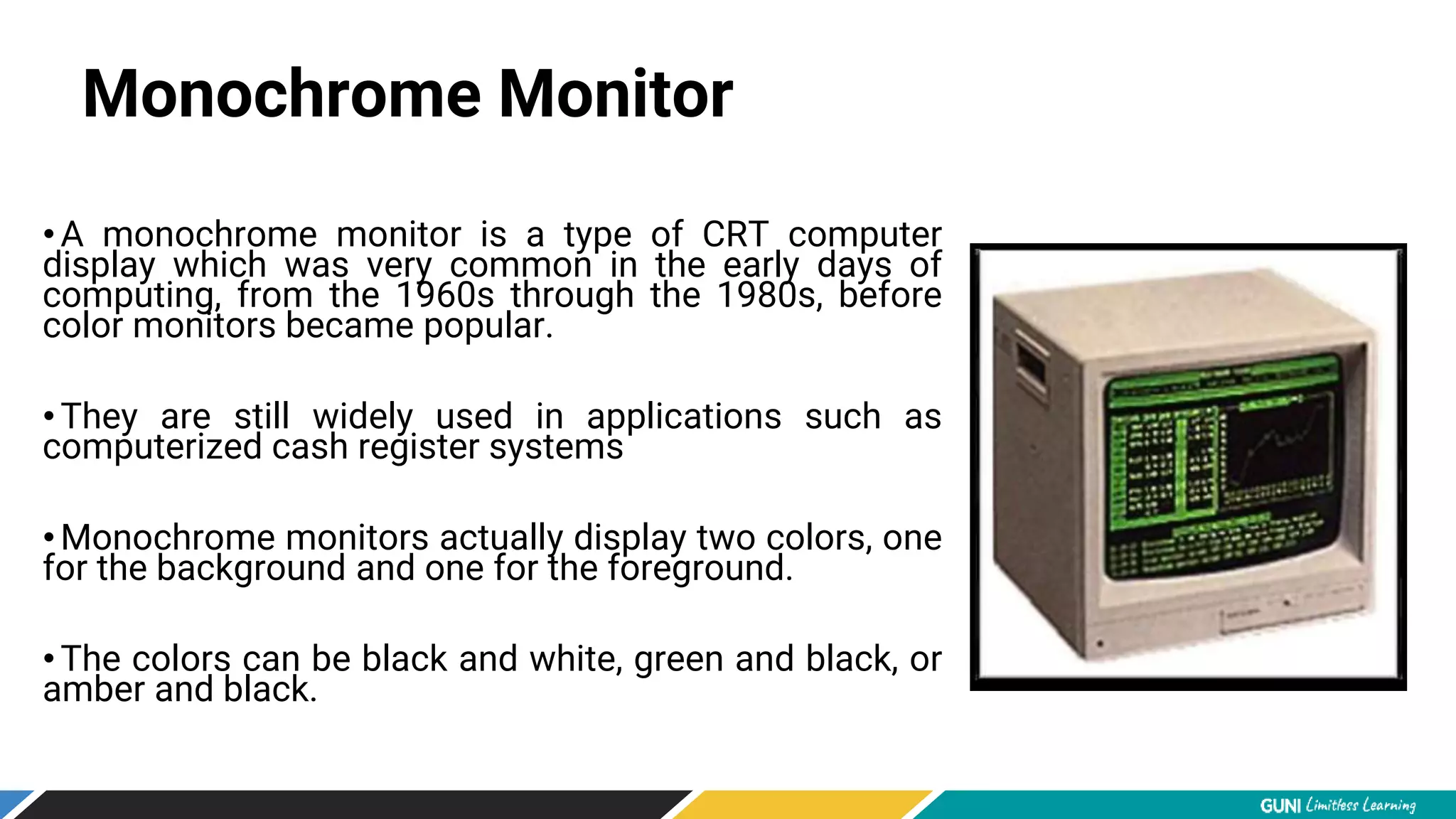
The document discusses different types of computer monitors including monochrome monitors, color monitors, CRT monitors, LCD monitors, and LED monitors. It describes key monitor features such as screen size, aspect ratio, display resolution, refresh rate, and color depth. Monitors display computer output through the video card and are similar to televisions but with higher display resolutions.