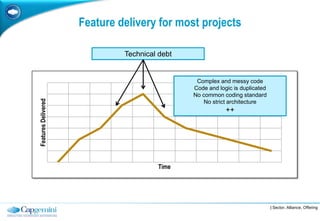
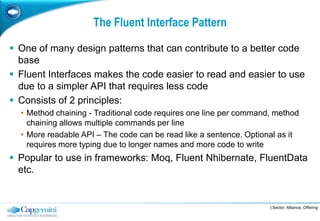
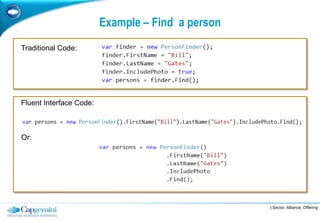
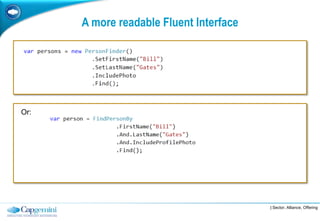
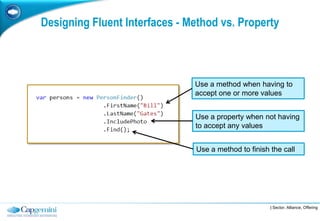
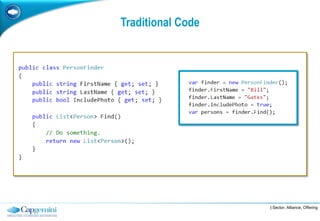
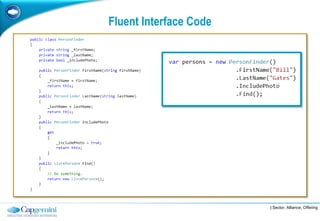
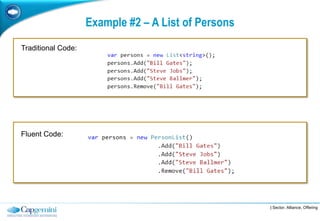
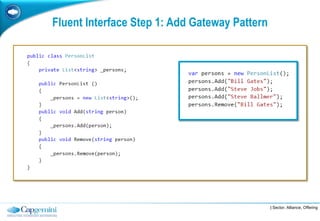
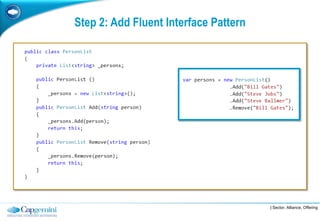
The Fluent Interface Pattern makes code easier to read and use by allowing method chaining and a more readable API. It consists of two principles: method chaining which allows multiple commands per line, and a more readable API that reads like a sentence. Popular frameworks like Moq and FluentData use this pattern. The pattern is useful anywhere code readability can be improved, especially for frequently called methods. It can be used with the Gateway Pattern to hide complex code.