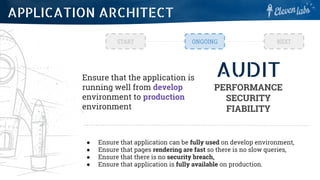
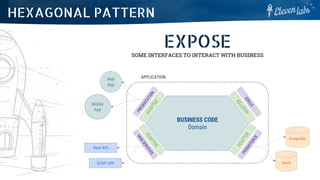
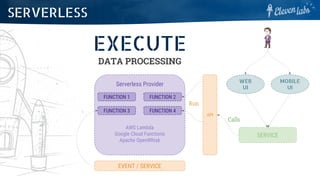
The document outlines the roles and responsibilities of various types of architects in software development, including application architects, solution architects, and enterprise architects. It describes their tasks related to project structure, technology organization, and ensuring application performance and security. Additionally, it discusses architectural patterns such as microservices and event-driven designs, highlighting their pros and cons.