1. The law of variable proportions examines production with one variable input while keeping other inputs fixed.
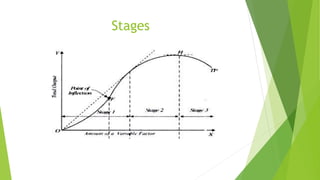
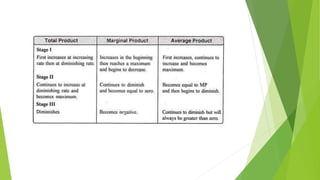
2. It describes three stages: initially increasing marginal returns, then diminishing marginal returns, and finally negative marginal returns.
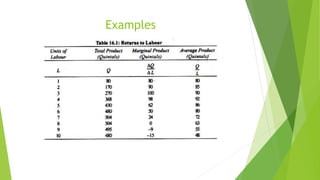
3. An example is given of a farmer using increasing amounts of labor on a fixed amount of land, showing total product first rising at an increasing rate, then a diminishing rate, and eventually falling as marginal returns become negative.




![Definition
[G. Stigler]
As equal increments of one input are added the inputs of
other productive services being held constant, beyond a
certain point the resulting increments of product will
decrease. i.e. the marginal products will diminish
[F. Benham]
As the proportion of one factor in a combination of factors is
increased, after a point first the marginal and then the
average product of that factor will diminish](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lawofvariableproportion-200909072527/85/Law-of-variable-proportion-5-320.jpg)