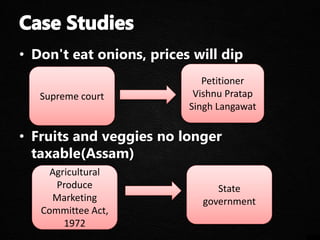
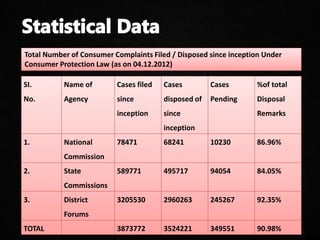
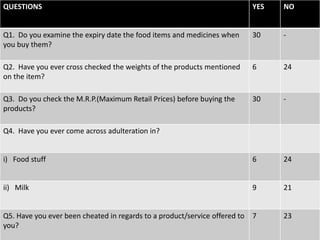
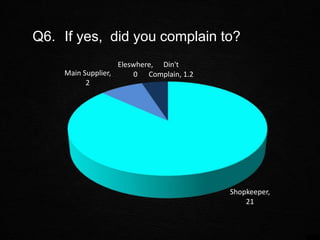
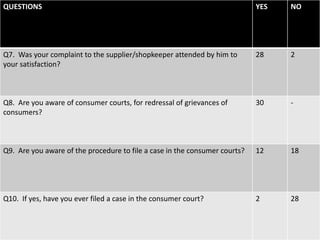
The document discusses various aspects of consumer protection laws and rights in India. It provides definitions of key terms like consumer, complaint, trader, etc. It outlines objectives to protect consumer rights, educate consumers, and provide redressal mechanisms. It describes the three-tier structure of consumer dispute resolution councils at district, state and national levels. It also discusses international examples of consumer protection laws and the importance of consumer awareness and education.