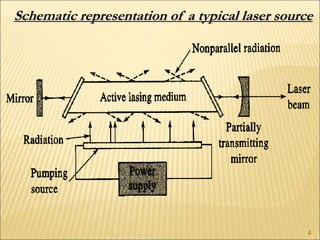
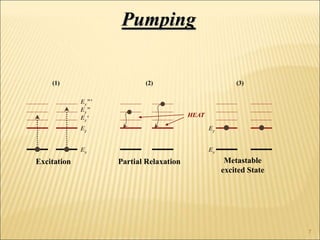
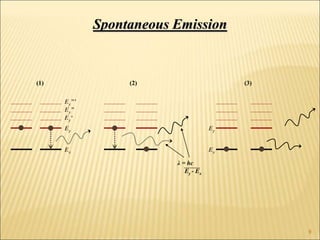
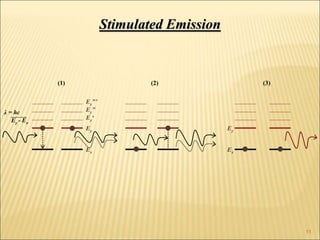
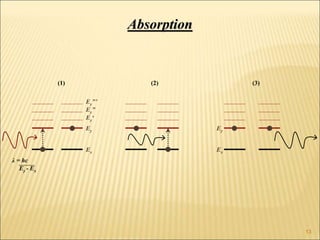
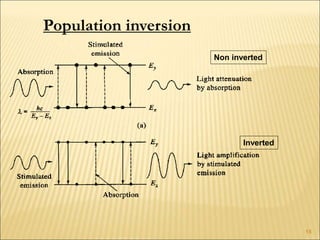
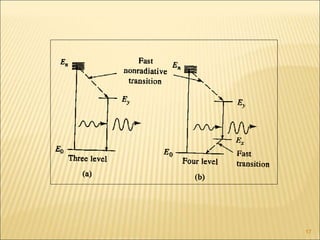
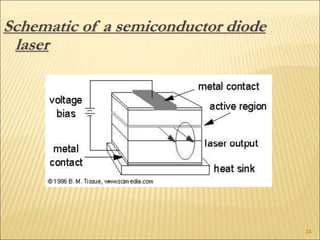
Lasers provide a highly useful light source for analytical instrumentation due to their high intensities, narrow band widths, and coherent outputs. Laser spectroscopy utilizes lasers as light sources. The three main components of a laser are the lasing medium, the energy pump source, and the resonator cavity. Laser action occurs through the processes of pumping, spontaneous emission, stimulated emission, and absorption, which can create population inversion necessary for light amplification. Common types of lasers include gas lasers, dye lasers, solid state lasers, and semiconductor lasers. Laser spectroscopy has wide applications in fields such as chemistry, environmental research, biology, and medicine.