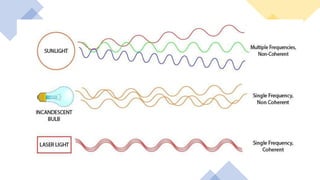
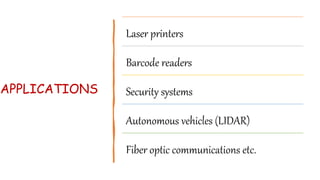
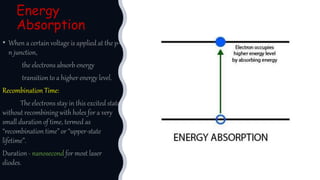
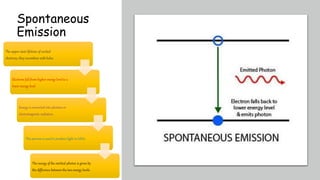
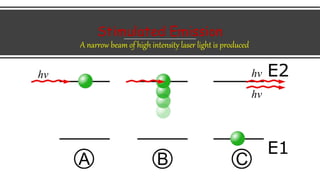
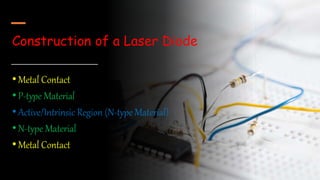
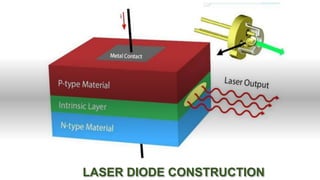
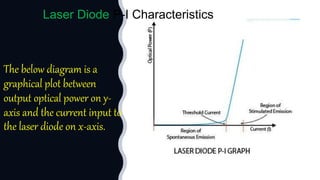
Laser diodes emit coherent light in which all waves are at the same frequency and phase. They use a p-n junction to produce a narrow beam of high intensity laser light via the processes of energy absorption, spontaneous emission, and stimulated emission. Laser diodes have applications in consumer electronics, medical devices, autonomous vehicles, scientific instruments, and industry due to their simple construction, small size, long operating life, high efficiency, and low power consumption.