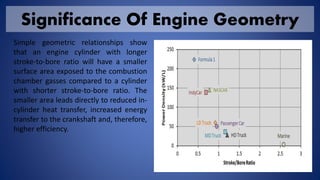
Large bore engines refer to engines with larger cylinder diameters. These engines have certain geometric advantages like reduced heat transfer and higher efficiency due to a smaller surface area exposed to combustion gases. There are two main types - large bore natural gas engines and large bore diesel engines. In some large bore engines, the piston is connected to the crankshaft via a piston rod and crosshead bearing rather than a direct connecting rod. Piston rings play an important role in sealing the combustion chamber and managing heat transfer and lubrication. Large bore engines find applications in marine propulsion systems and power plants.