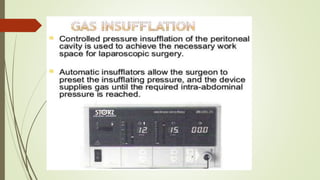
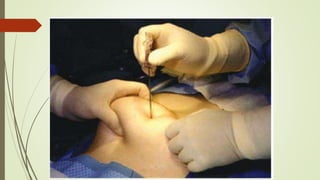
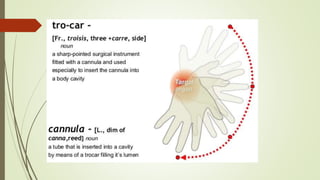
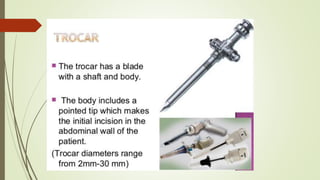
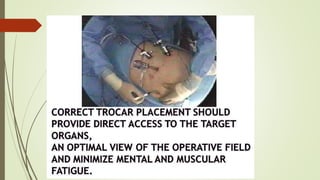
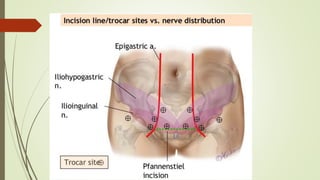
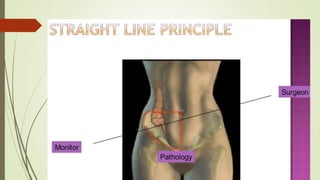
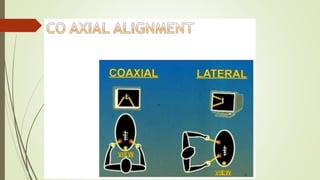
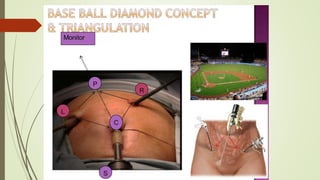
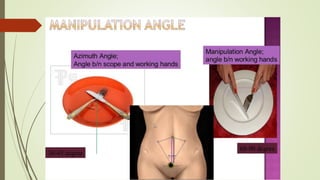
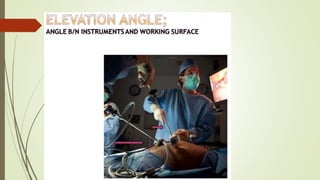
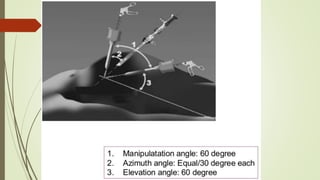
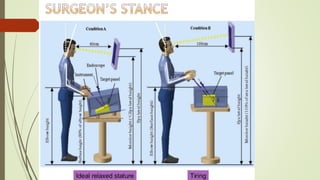
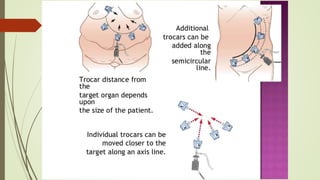
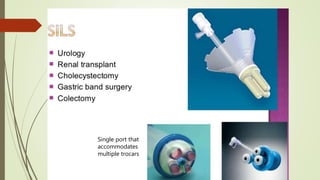
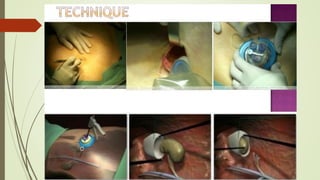
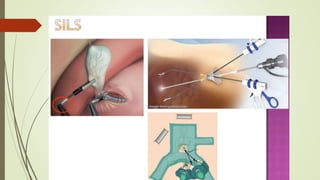
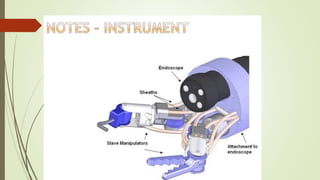
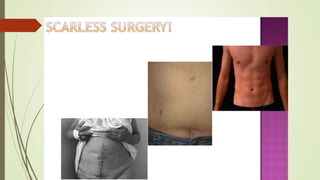
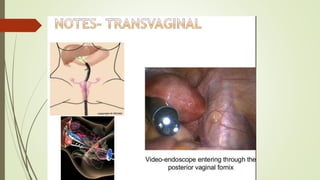
Laparoscopy, also known as keyhole surgery, allows surgeons to examine the abdominal organs through small incisions using a laparoscope. It was developed in the early 1900s and is now commonly used to diagnose and treat conditions of the appendix, gallbladder, intestines, and other abdominal organs. The key advantages of laparoscopy over open surgery are reduced pain, scarring, and recovery time for patients. However, it requires more technical skill from surgeons due to limited movement and vision within the abdominal cavity. Complications can include injuries from trocar insertion or electrical burns, but the risks of laparoscopy are generally low when performed by an experienced surgeon.