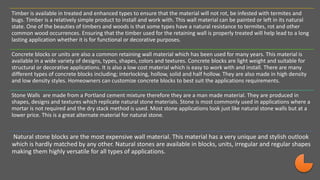
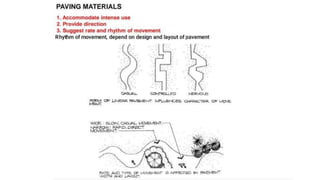
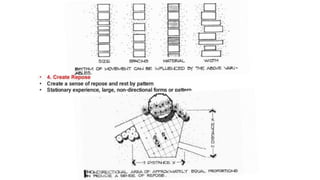
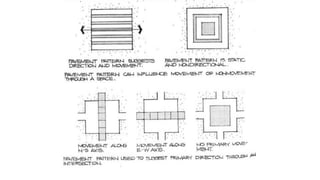
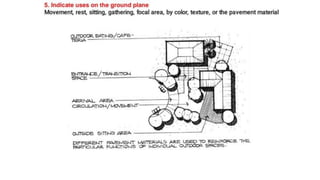
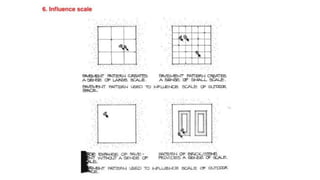
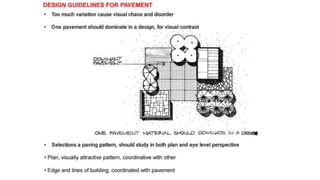
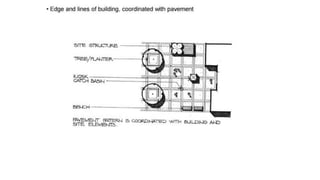
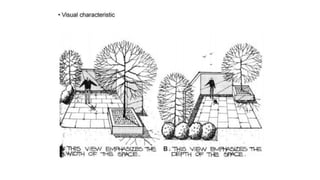
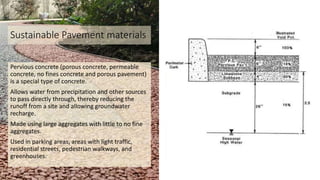
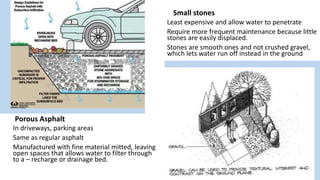
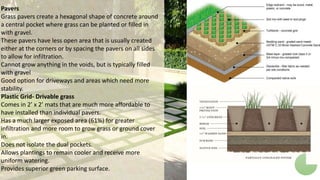
Hardscaping refers to permanent landscape elements made from hard materials like stone, concrete, wood, and metal. It includes features like driveways, walkways, retaining walls, stairs, and planters. Hardscaping is used to provide structure, separate different areas, and enhance the beauty of the natural landscape. There are many options for hardscaping materials with considerations including durability, maintenance needs, and aesthetic qualities. Proper planning is needed to incorporate hardscaping elements that meet the functional needs of the space.