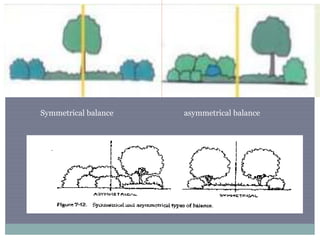
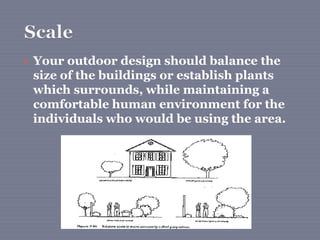
The document discusses landscape architecture, focusing on the design of outdoor environments like parks and gardens to achieve aesthetic harmony with surrounding structures. It distinguishes between natural and manmade landscapes, detailing elements such as color, balance, and texture that influence design. Examples such as the Butchart Garden and typical urban planning components highlight practical applications of these design principles.