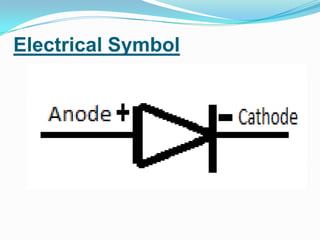
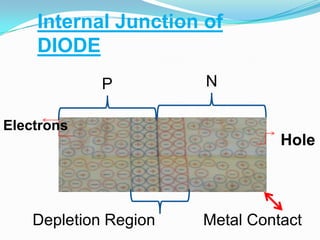
Diodes are electronic components that allow current to flow in only one direction. They have two terminals called an anode and a cathode. Diodes have many applications including rectifying AC to DC current, over-voltage protection, logic gates, radiation detection, temperature measurement, and current steering. Common types of diodes include light emitting diodes (LEDs), avalanche diodes, laser diodes, Zener diodes, and rectifier diodes.