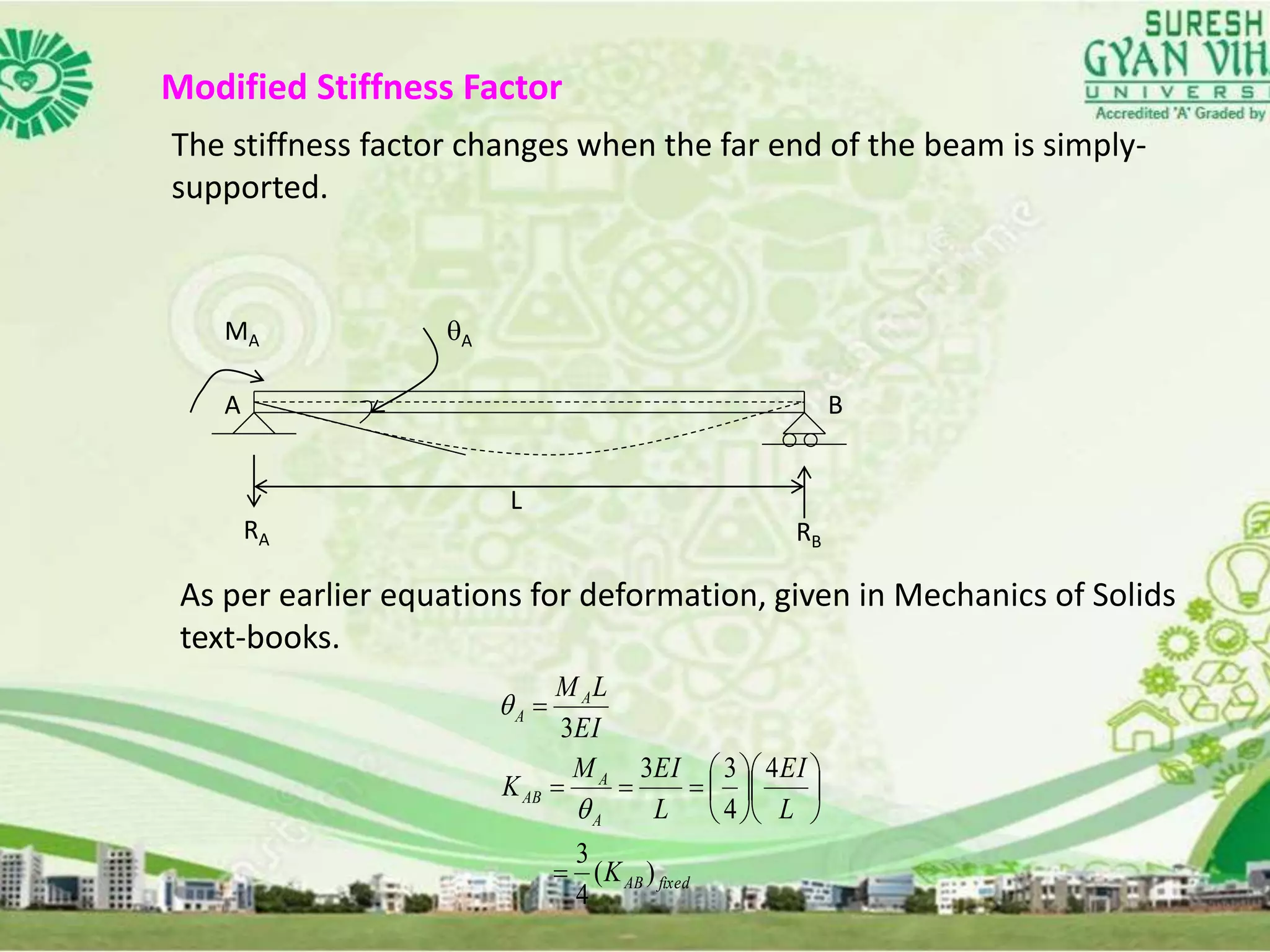
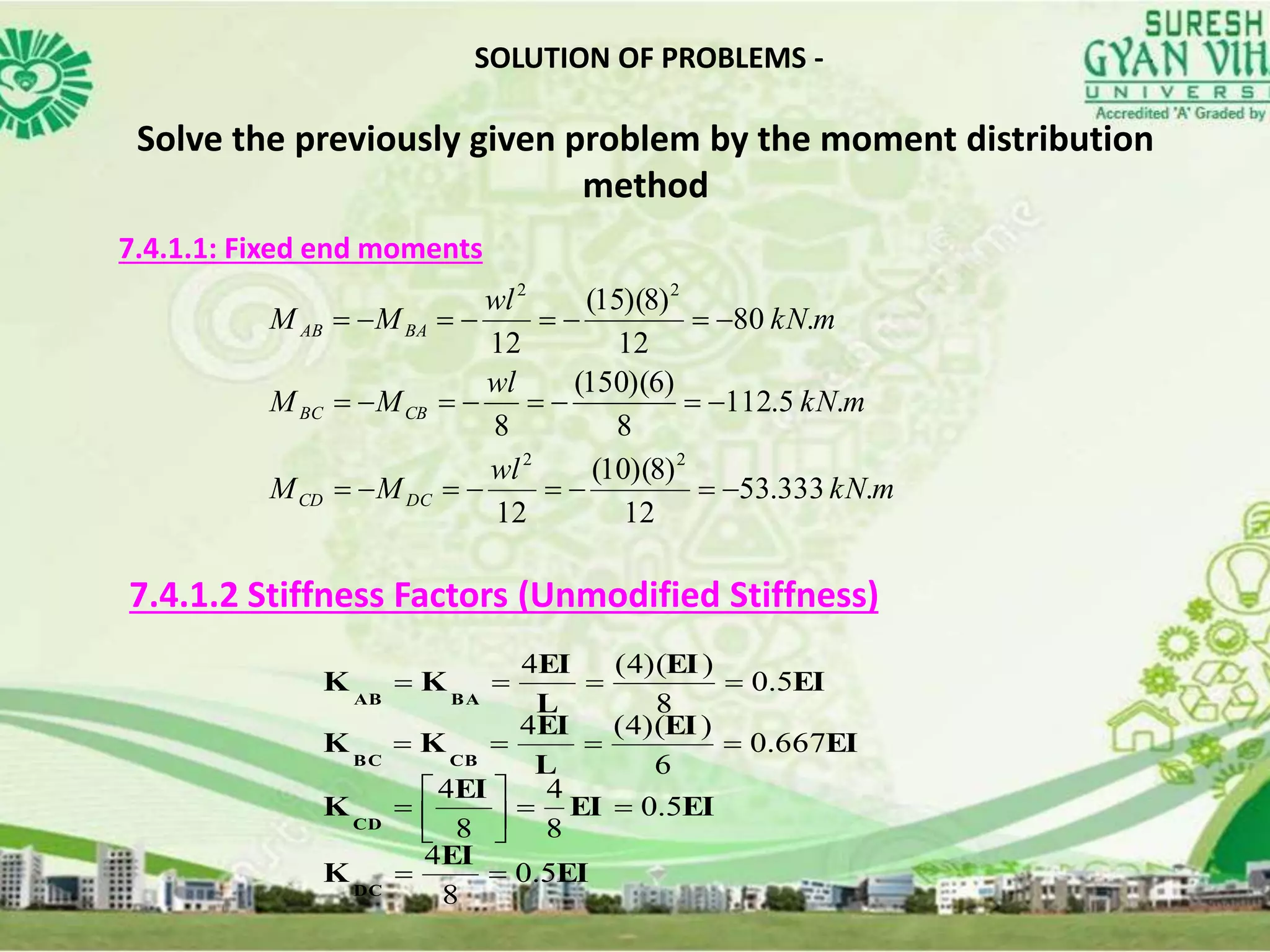
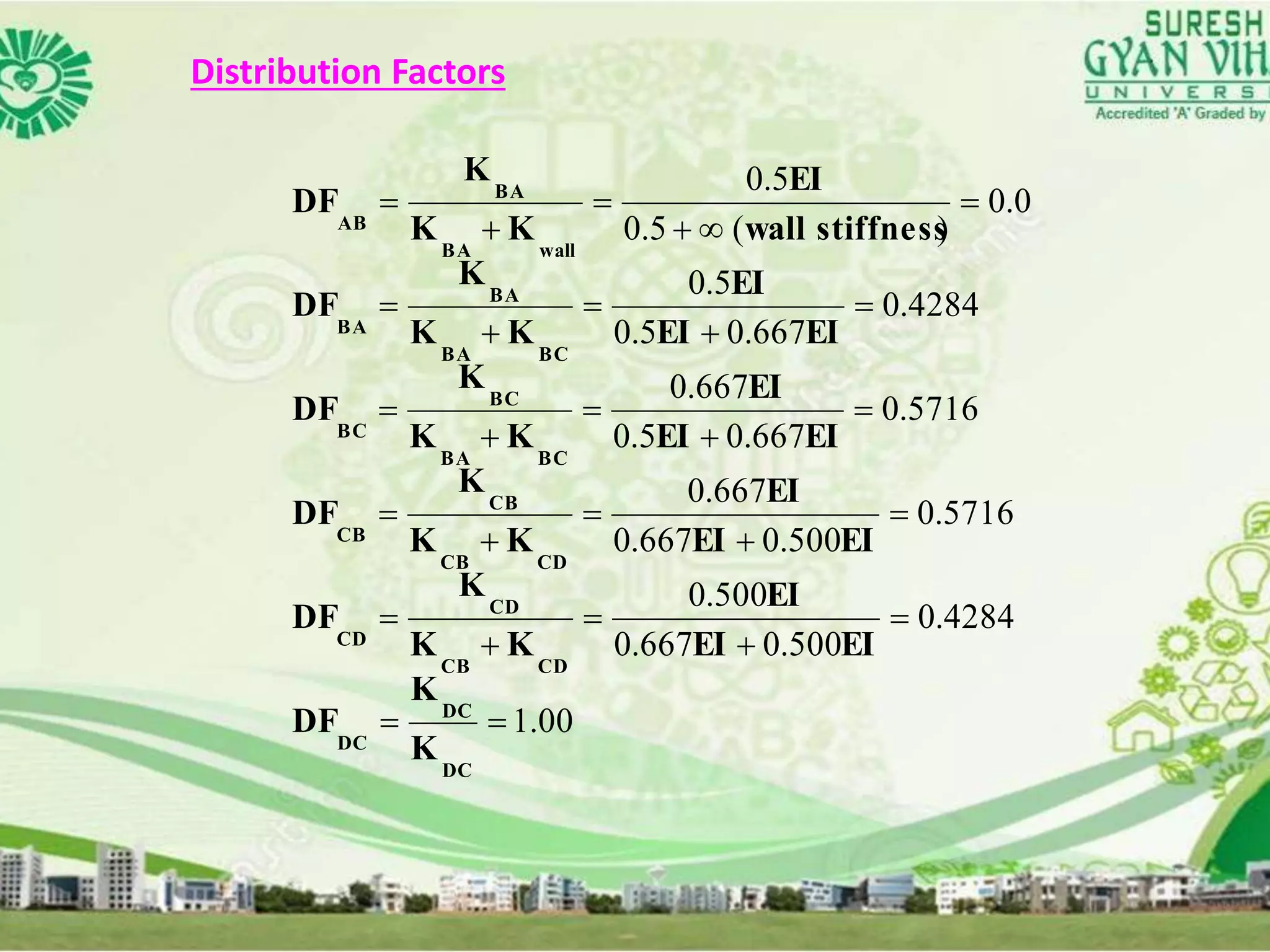
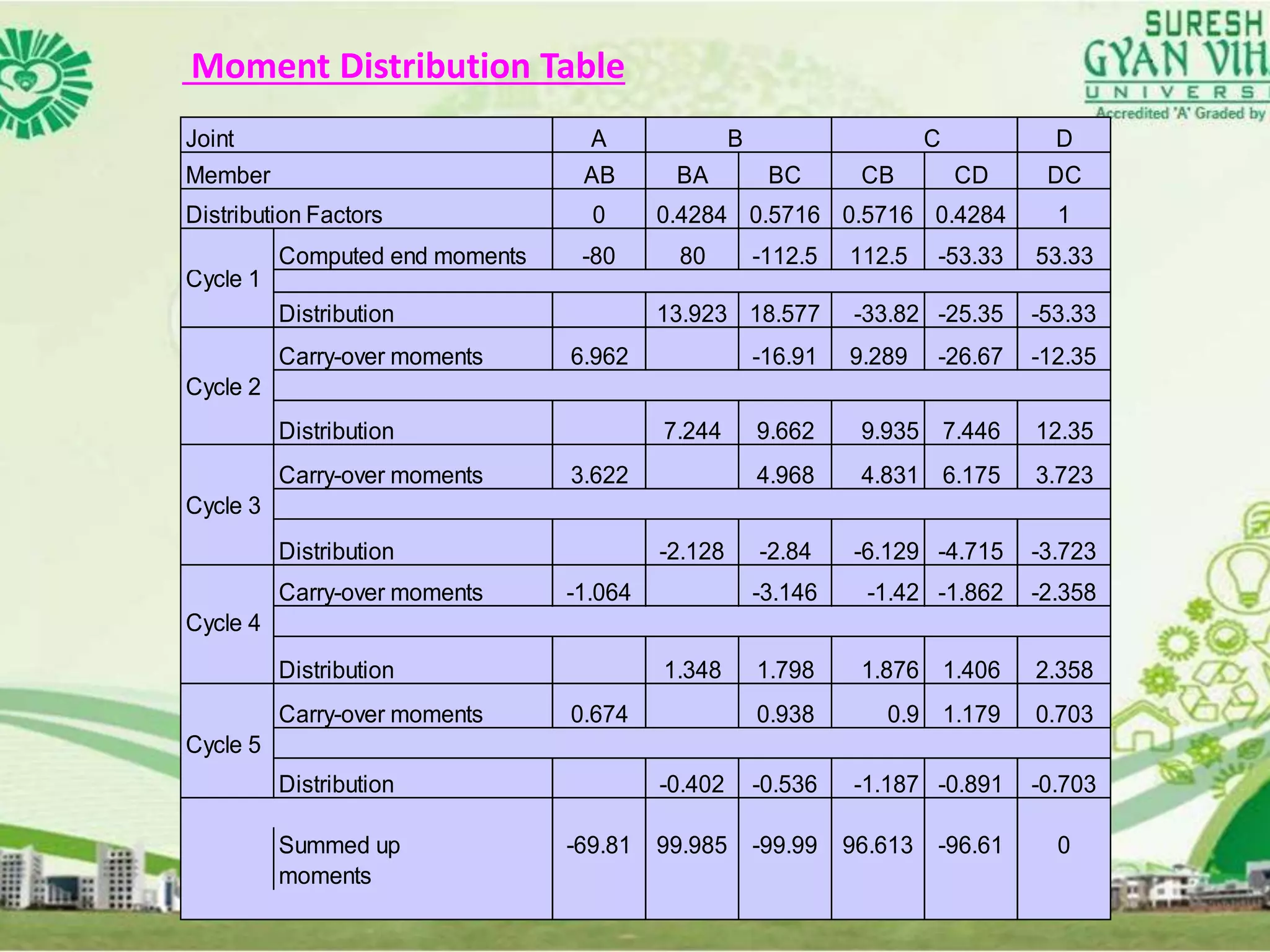
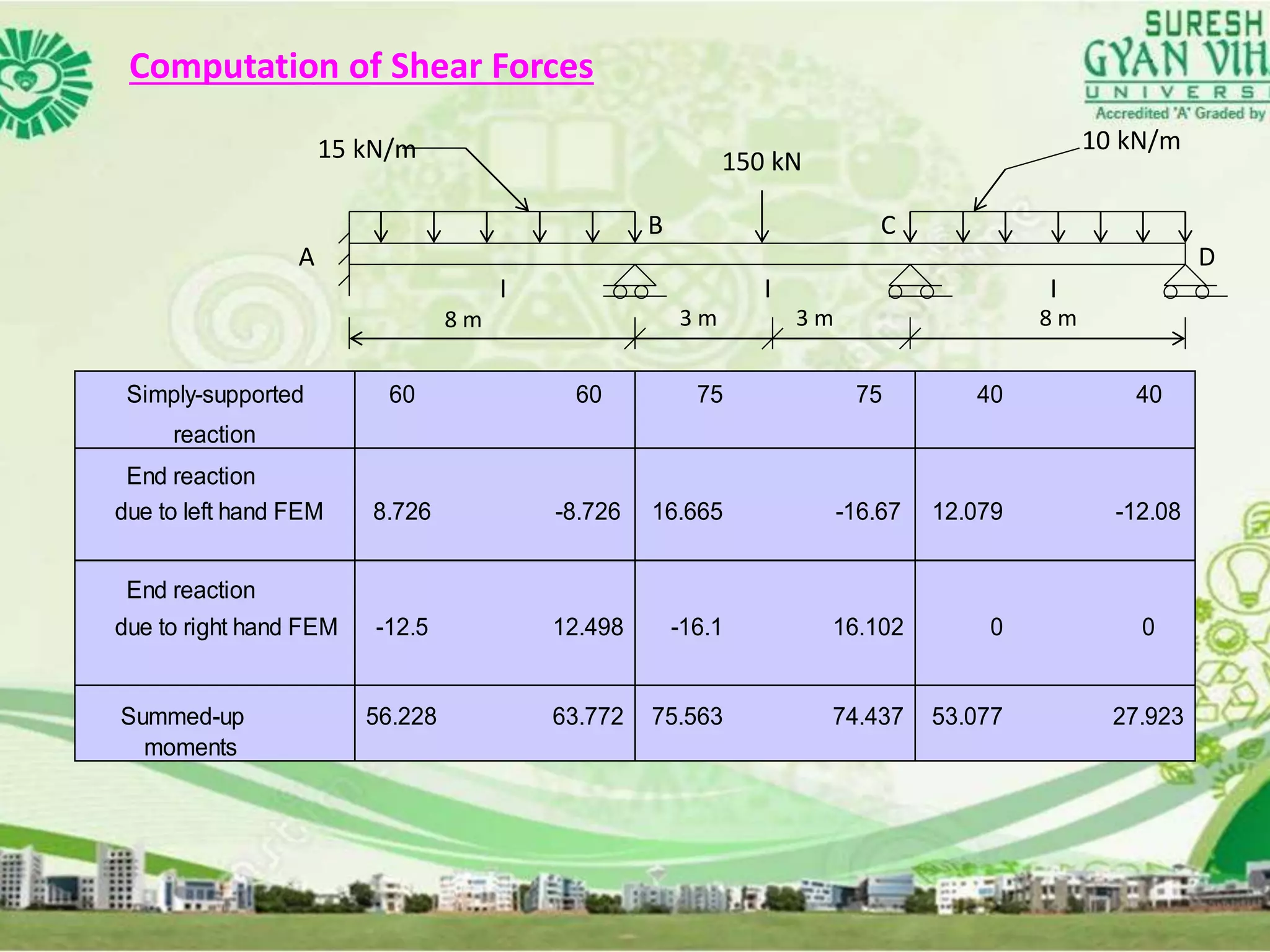
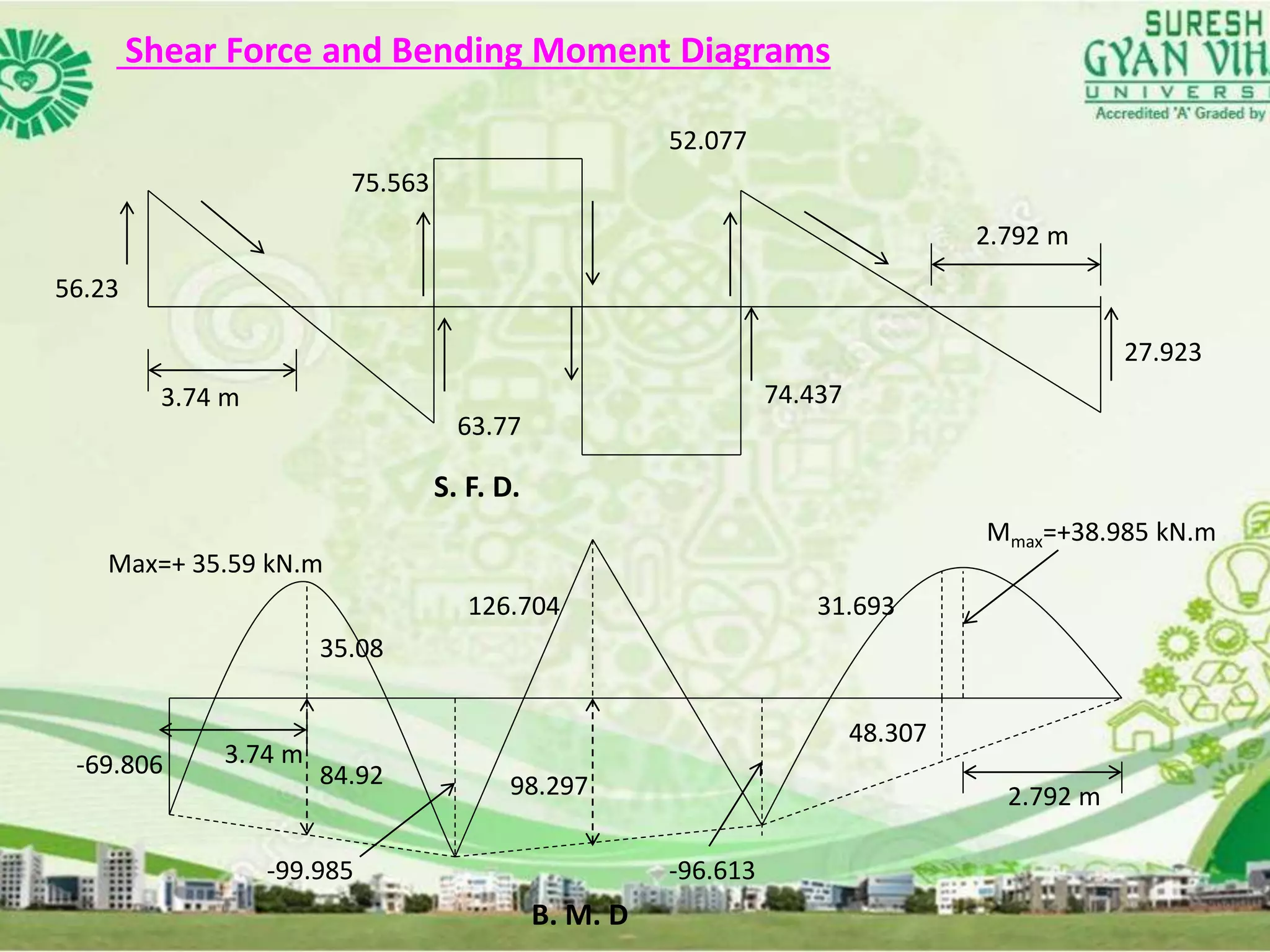
This document discusses the analysis of indeterminate beams using the moment distribution method. It provides the modified stiffness factor equation when the end of the beam is simply supported. It then gives an example problem and shows the step-by-step solution using the moment distribution method, including calculating the distribution factors, compiling the moment distribution table through multiple cycles, and determining the shear forces and bending moments. Finally, it briefly mentions analyzing nonprismatic members and using design tables with the moment distribution method.