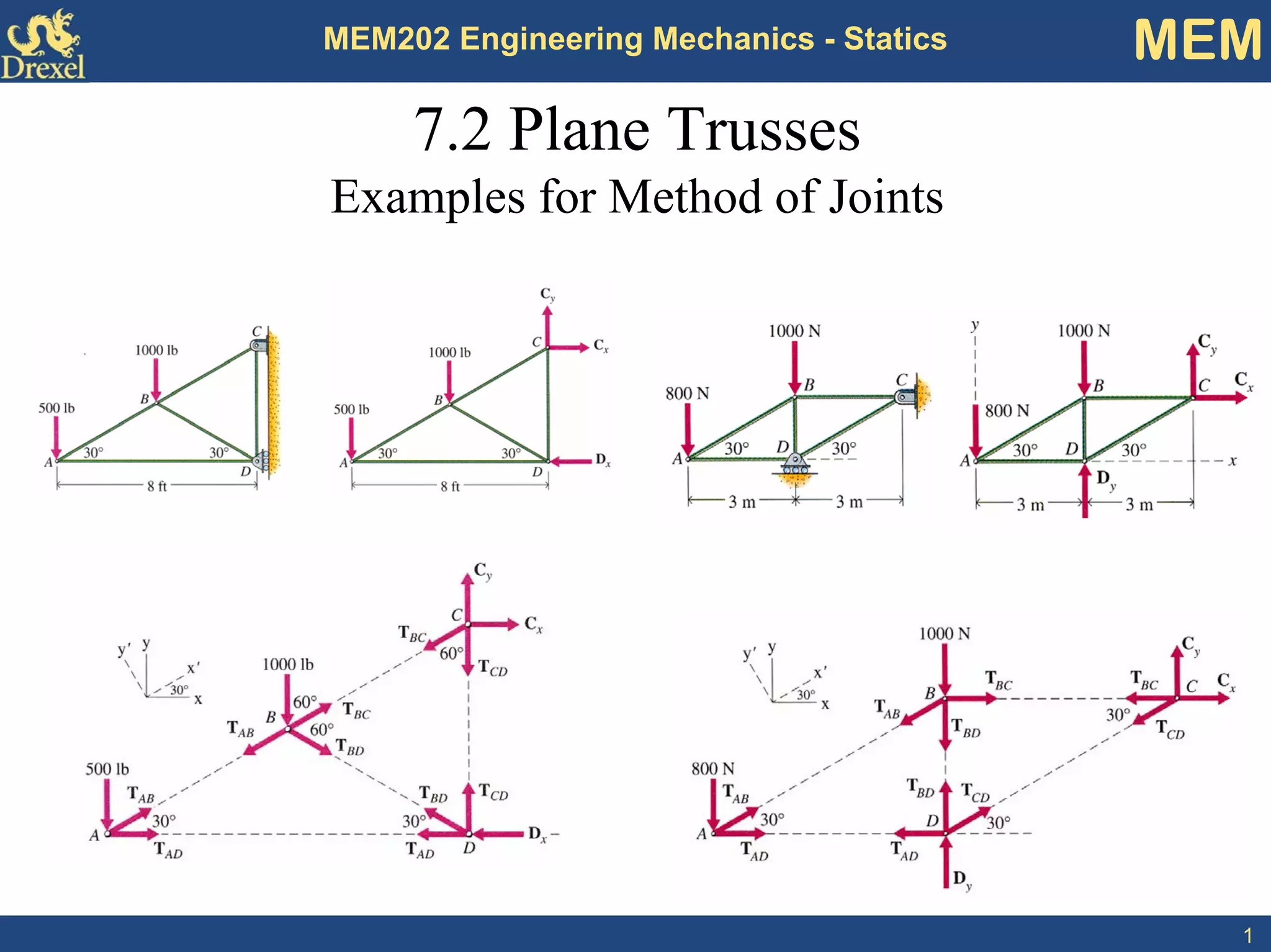
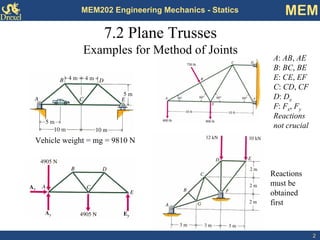
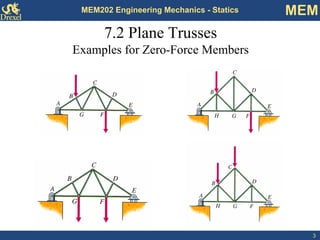
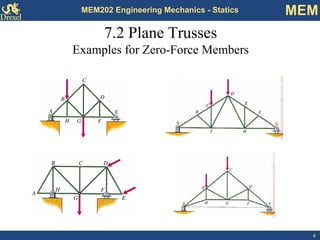
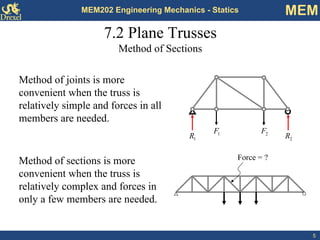
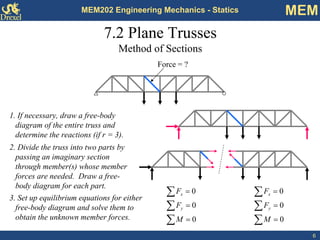
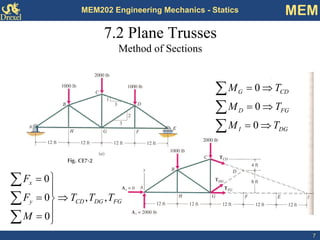
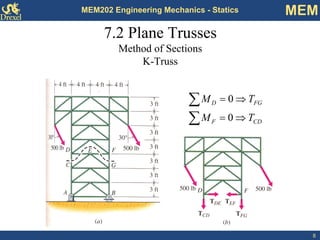
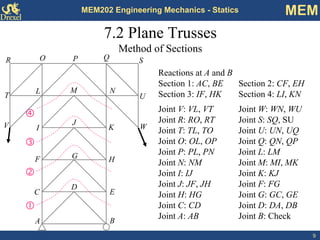
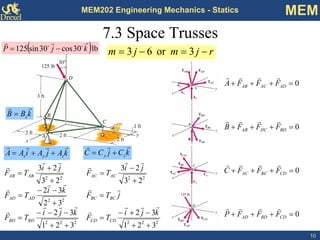
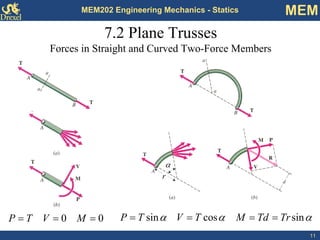
This document discusses methods for analyzing plane trusses, including the method of joints and method of sections. The method of joints is more convenient for simple trusses where all member forces are needed, while the method of sections is better for complex trusses where only a few member forces are required. The method of sections involves dividing the truss into parts with an imaginary cut and using equilibrium equations to solve for unknown member forces. An example of applying the method of sections to a space truss is also provided.