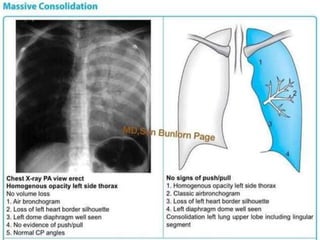
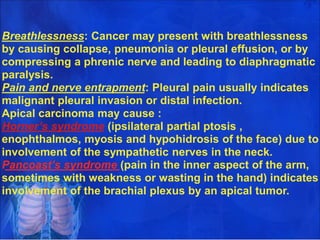
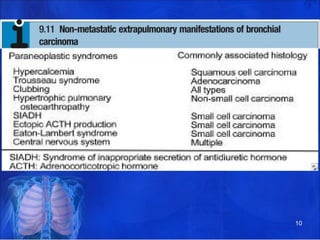
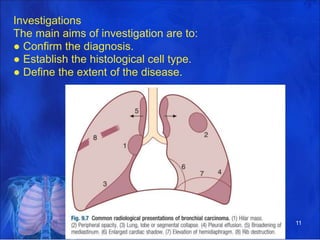
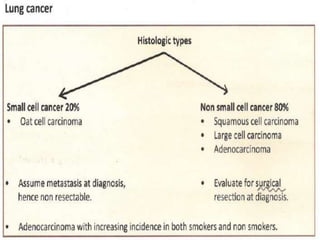
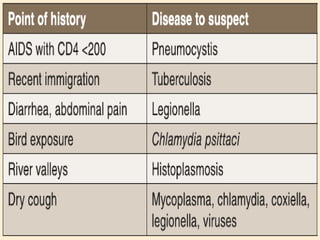
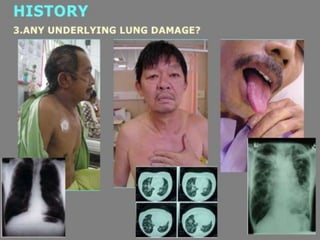
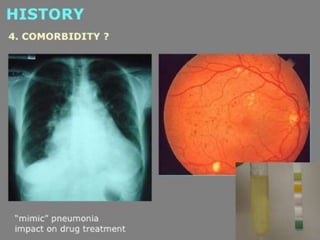
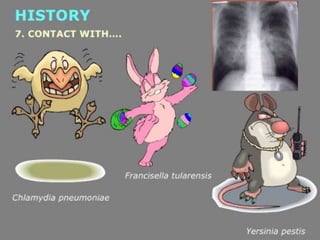
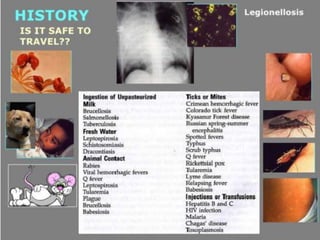
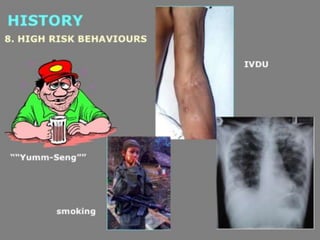
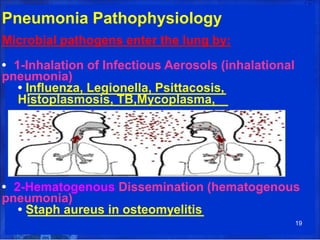
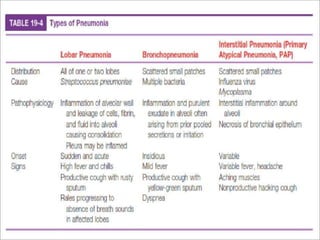
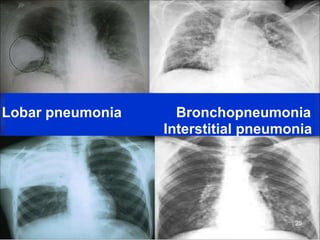
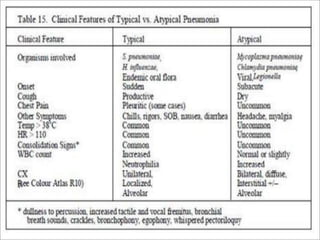
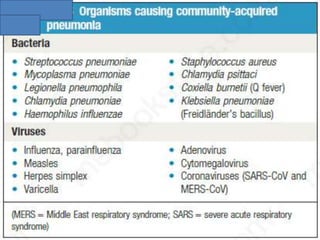
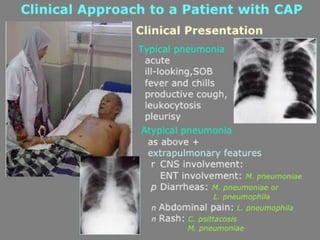
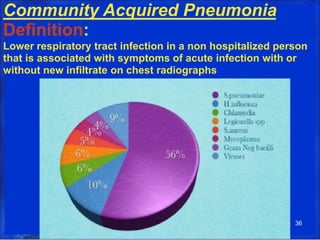
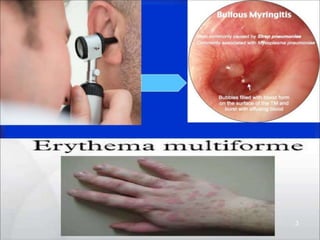
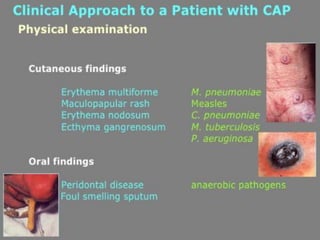
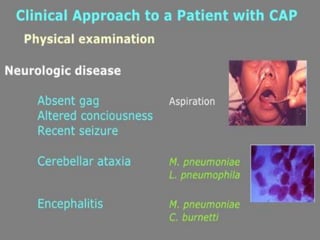
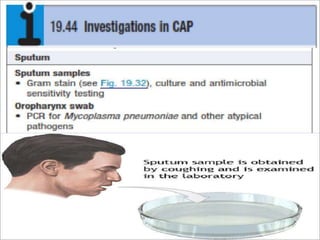
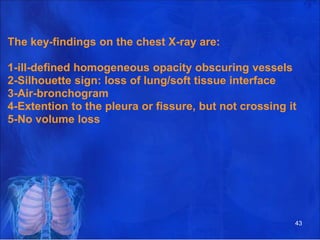
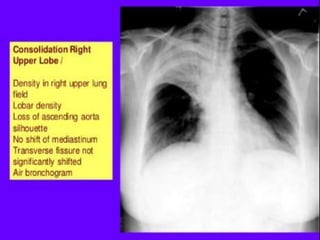
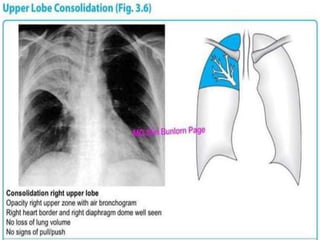
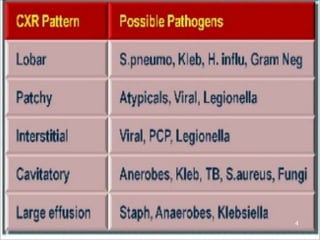
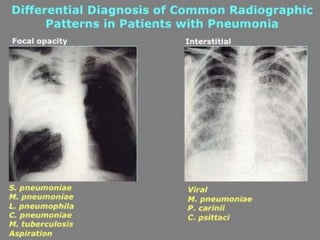
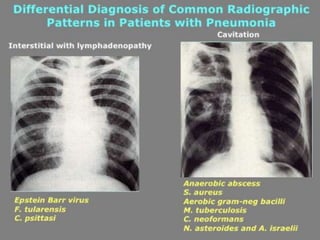
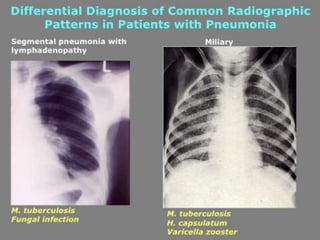
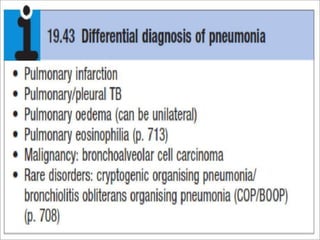
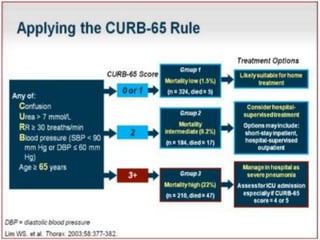
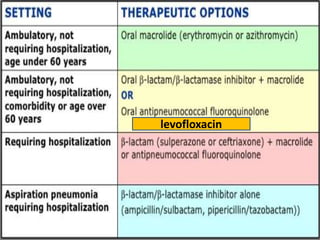
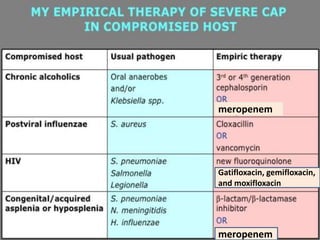
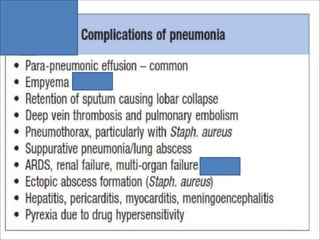
Lung consolidation is caused by pneumonia, malignancy, or infarction and results in the accumulation of solid and liquid material in the air spaces of the lung. Pneumonia is the most common cause and presents with symptoms like fever and productive cough. Malignancy like lung cancer often presents with cachexia, clubbing, and productive cough. The document discusses the diagnosis, causes, and types of pneumonia and lung cancer. Smoking is responsible for 90% of lung cancers. Pneumonia can be classified by pathogen, anatomy, or presentation as lobar, bronchial, or atypical.