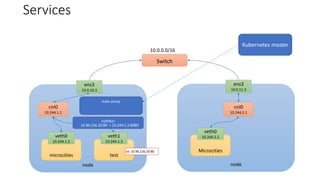
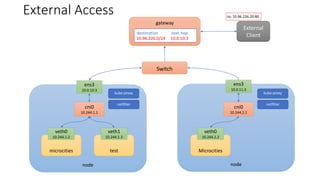
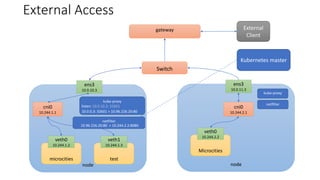
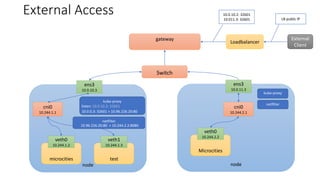
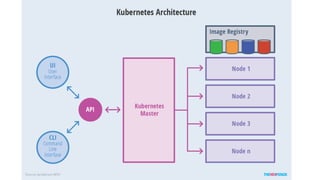
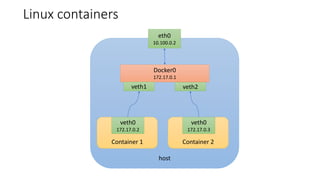
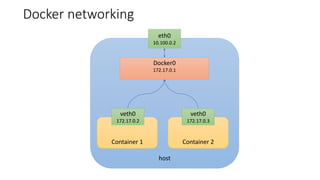
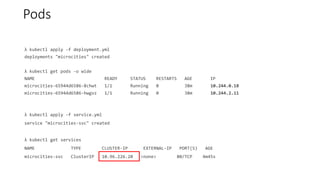
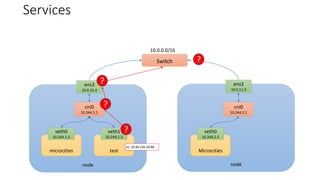
The document discusses Kubernetes networking concepts including pods, services, and ingress. It provides examples of how containers within pods communicate via Docker networking. It also explains how Kubernetes networking solves the problems of pod-to-pod, service-to-pod, and external-to-service communications using services, iptables, and kube-proxy. The document demonstrates creating a deployment, service, and ingress to expose an application externally via a load balancer.















![apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: test
spec:
restartPolicy: Never
containers:
- name: test
image: alpine
command: ["/bin/sh"]
args: ["-c", "echo 'GET / HTTP/1.1rnrn' | nc 10.244.0.18 8080"]
test.yml](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kubernetesnetworking-191017074359/85/Kubernetes-networking-basics-20-320.jpg)





![What is a netfilter and iptables[tl;dr]
• netfilter is a rules-based packet processing engine. It runs in kernel
space and gets a look at every packet at various points in its life cycle.
• It matches packets against rules and when it finds a rule that matches
it takes the specified action.
• Among the many actions it can take is redirecting the packet to
another destination.
• iptables is a user space interface to netfilter](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kubernetesnetworking-191017074359/85/Kubernetes-networking-basics-28-320.jpg)