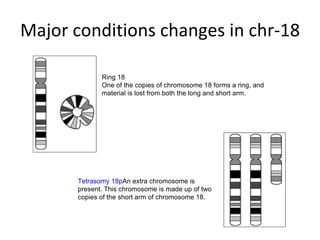
Chromosome 17 and 18 each contain around 1,200-1,500 genes. Chromosome 17 is associated with conditions like acute promyelocytic leukemia and neurofibromatosis type 1. Chromosome 18 is associated with conditions such as Niemann-Pick disease, Pitt-Hopkins syndrome, and osteopetrosis. Pitt-Hopkins syndrome is caused by mutations in the TCF4 gene on chromosome 18 and is characterized by developmental and facial abnormalities.





![Changes in conditions of Chr-17 ACUTE PROMYELOCYTIC LEUKEMIA caused by a rearrangement (translocation) of genetic material between chromosomes 15 and 17 [t(15;17)] fuses part of the PML gene from chromosome 15 with part of the RARA gene from chromosome 17. somatic mutation not inherited. The t(15;17) translocation is called a balanced reciprocal translocation The protein produced from this fused gene is known as PML-RARα.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kromosom1718-111108225655-phpapp02/85/Kromosom-17-18-6-320.jpg)
![Scheme of acute promyelocytic leukemia PML gene (chr-15) >< RARA gene (chr-17) [t(15;17) balanced reciprocal translocation] PML-RARα RARα a protein tumor suppressor blood cells are stuck at the promyelocyte stage, and they proliferate abnormally. Excess promyelocytes accumulate in the bone marrow and normal white blood cells cannot form, leading to acute promyelocytic leukemia.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kromosom1718-111108225655-phpapp02/85/Kromosom-17-18-7-320.jpg)