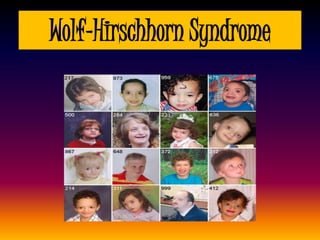
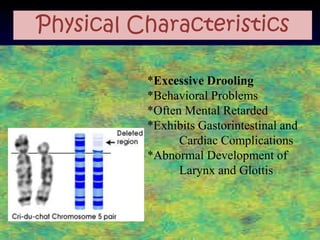
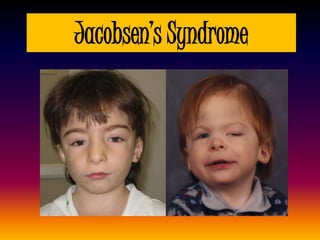
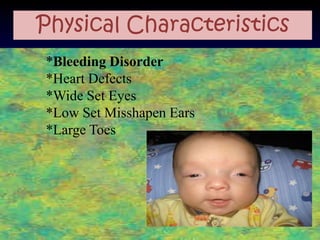
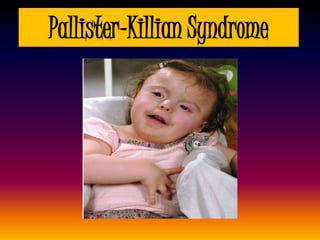
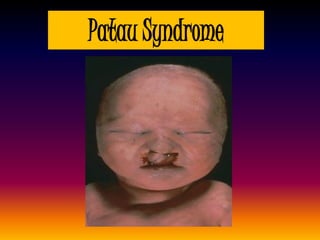
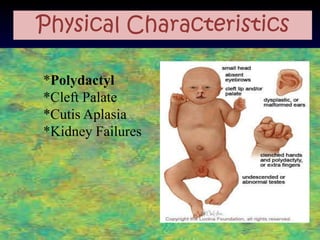
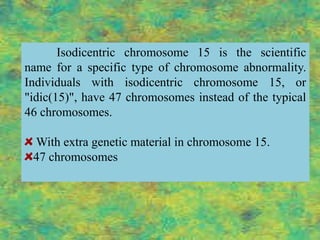
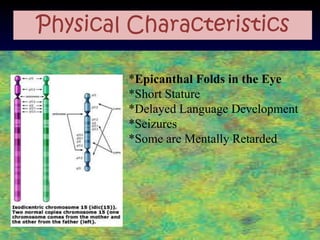
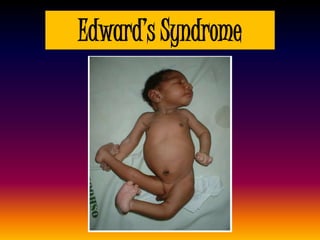
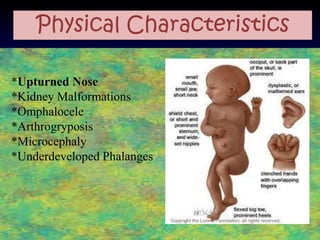
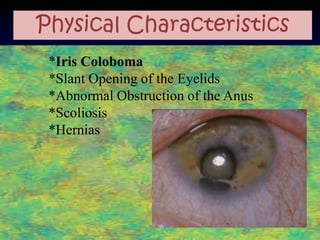
The document discusses several autosomal aberrations including deletions, duplications, and trisomies of different chromosomes that result in genetic disorders. It describes the signs and symptoms of several conditions including Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome caused by a deletion on chromosome 4, Cri du Chat caused by a deletion on chromosome 5, and Down Syndrome caused by trisomy of chromosome 21. It also provides details on the characteristic physical features of each condition.