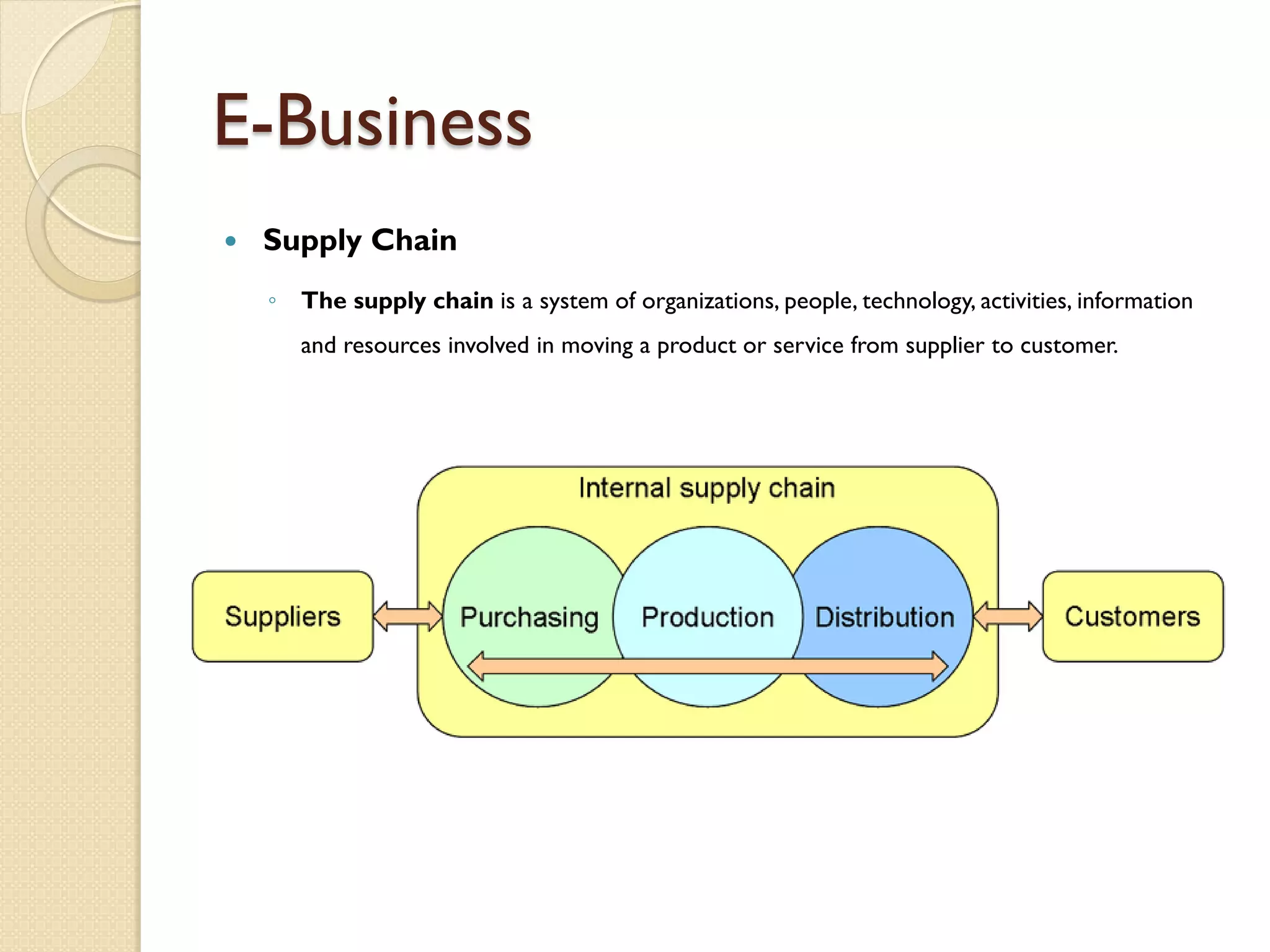
The document discusses how electronic facilities like intranets, extranets, and groupware enable knowledge transfer and exchange regardless of location. Intranets are used internally, while extranets allow knowledge sharing between business partners. Groupware applications include email, calendars, document sharing and workflow tools. E-business models involve business-to-business and business-to-consumer transactions over the internet. Effective supply chain management integrates customer relationship management and order fulfillment across a network of organizations.