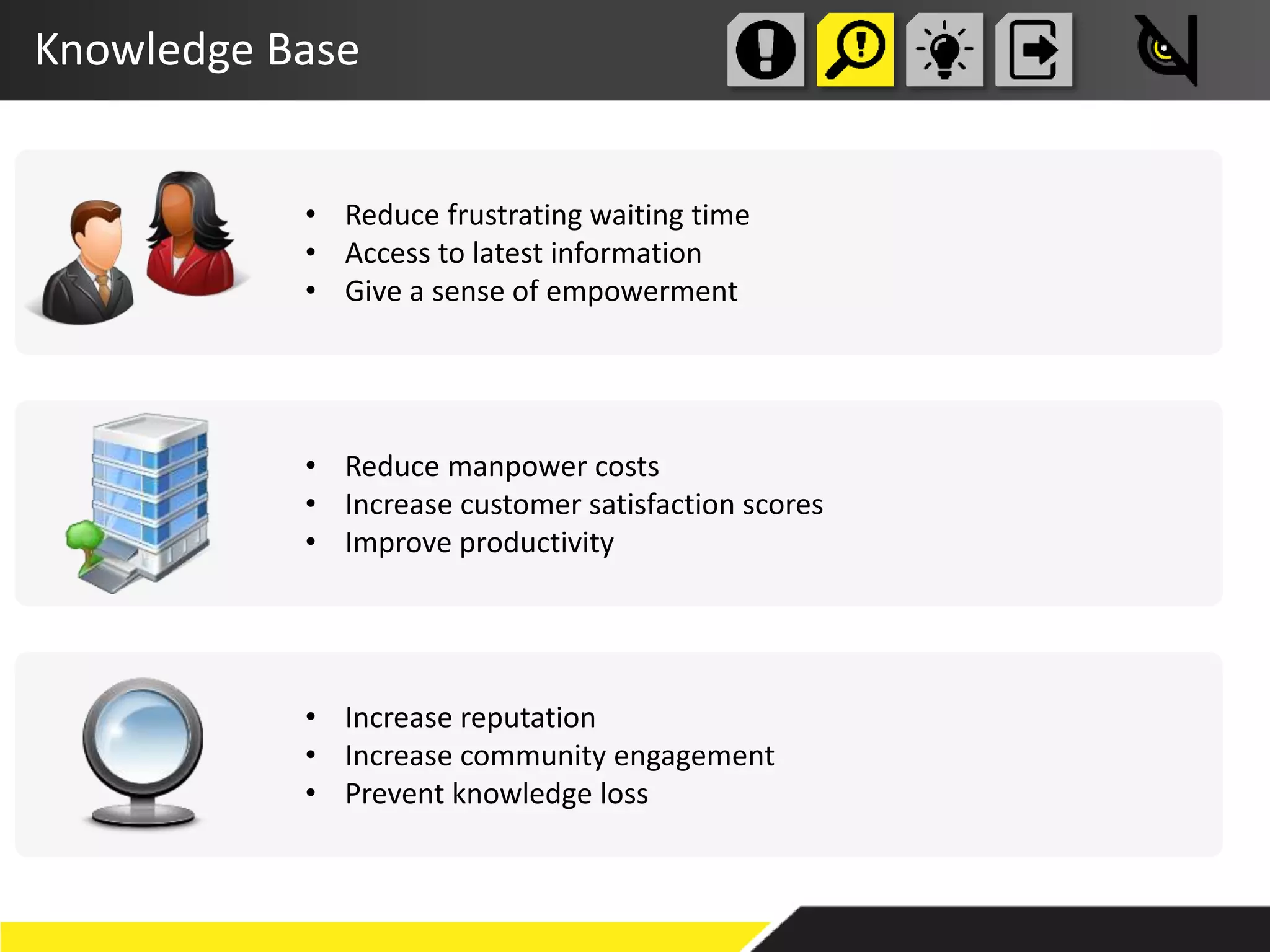
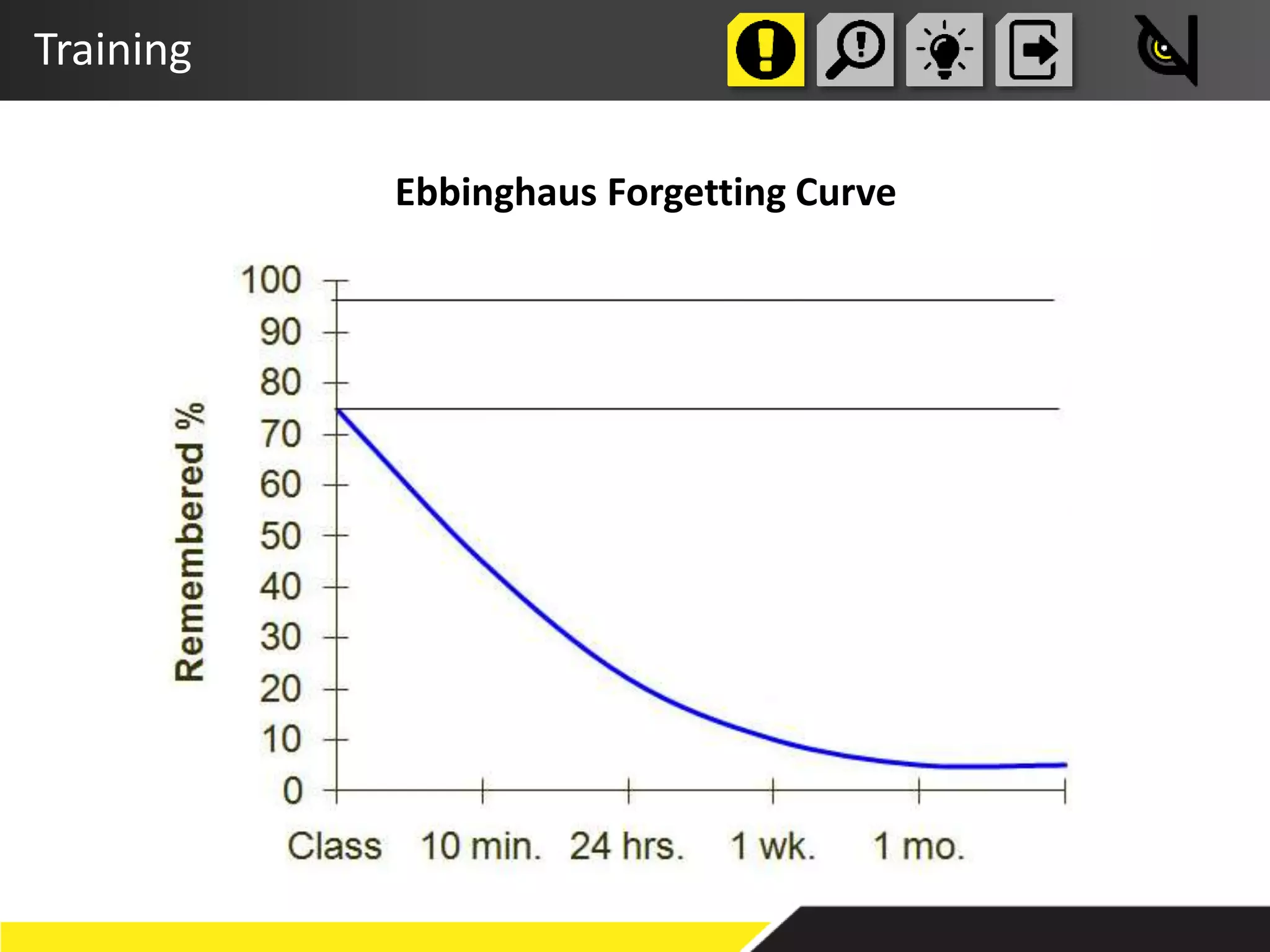
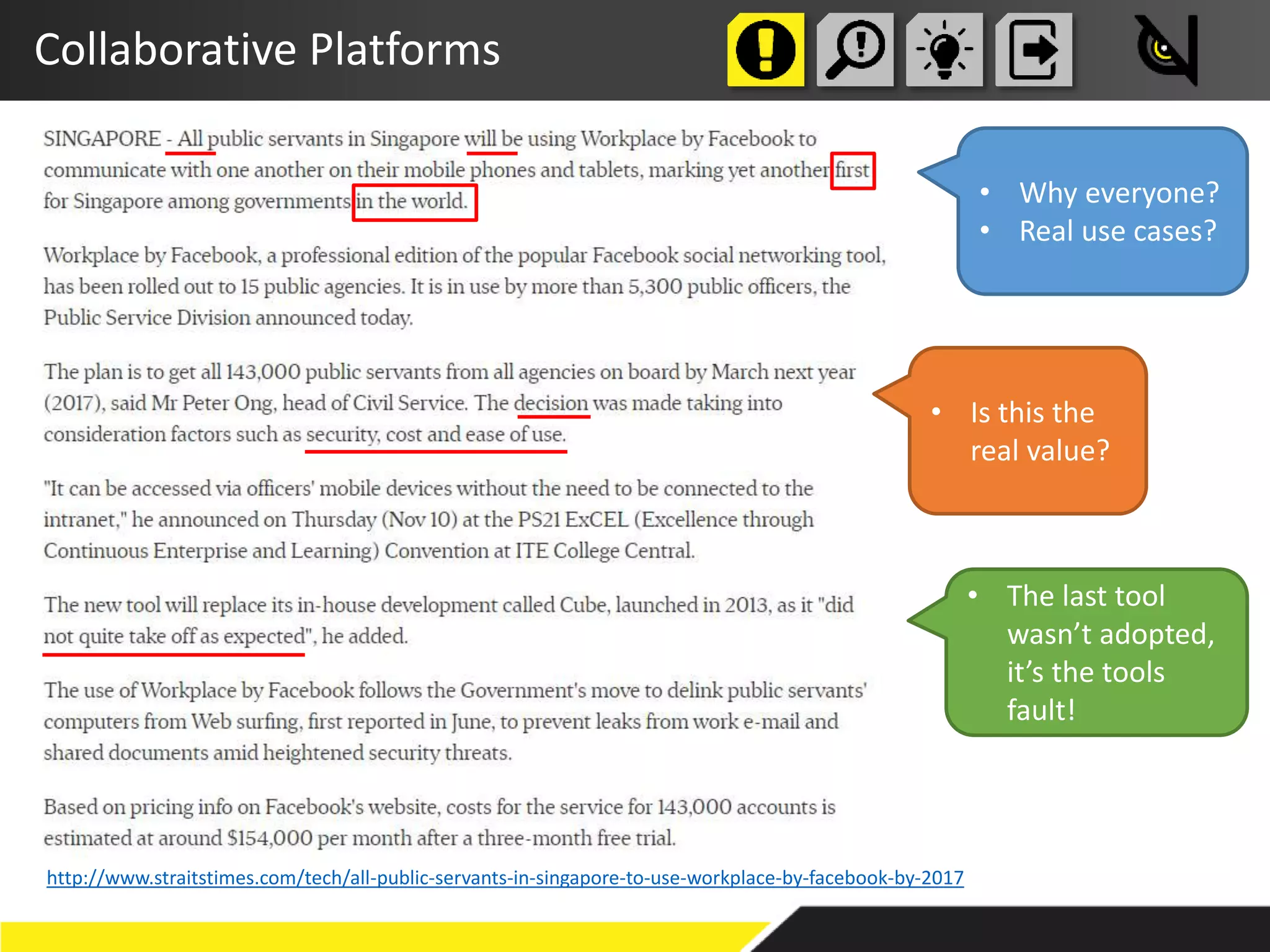
The document discusses the importance of prioritizing people in knowledge management over tools and processes, emphasizing that successful implementation relies on a genuine desire to help each other within organizations. It outlines various approaches, including knowledge bases and communities of practice, to enhance knowledge sharing and improve organizational outcomes. Furthermore, it highlights the need for critical success factors and key performance indicators to measure the effectiveness of knowledge management initiatives.