The document discusses Kirchhoff's matrix tree theorem which provides a formula for calculating the number of spanning trees in a finite graph based on the graph's Laplacian matrix. It provides an example of applying the theorem to calculate that a particular graph has 29 spanning trees by taking the determinant of the Laplacian matrix with a row and column removed. Finally, it discusses several applications that rely on building and analyzing spanning trees, such as routing algorithms, power networks, and telecommunications networks.



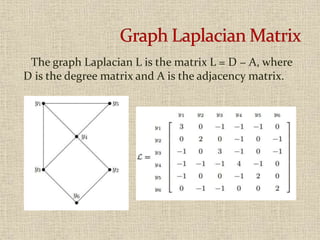
![Suppose that L{k} denotes the submatrix of L obtained by
deleting row k and column k corresponding to vertex yk
Statement:
If Ω = {spanning trees of T}, then
det[L{1}] = det[L{2}] = · · · = det[L{n}= det[L{n+1}]
and that these are equal to |Ω|, the number of
spanning trees of T.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kirchoffsmatrixtreetheorem-200410125106/85/Kirchoff-s-matrix-tree-theorem-6-320.jpg)
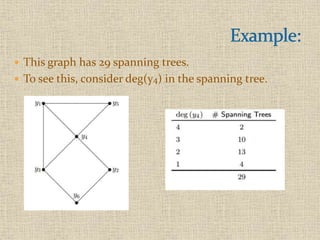
![ This graph has 29 spanning trees. For example, using
MTT, det[L{5}] = 29.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kirchoffsmatrixtreetheorem-200410125106/85/Kirchoff-s-matrix-tree-theorem-8-320.jpg)

