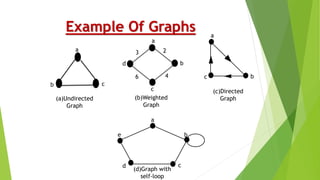
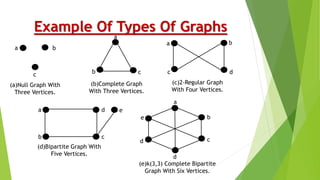
Graph theory is the study of points and lines, and how sets of points called vertices can be connected by lines called edges. It involves types of graphs like regular graphs where each vertex has the same number of neighbors, and bipartite graphs where the vertices can be partitioned into two sets with no edges within each set. Graphs can be represented using adjacency matrices and adjacency lists. Basic graph algorithms include depth-first search, breadth-first search, and finding shortest paths between vertices. Graph coloring assigns colors to vertices so that no adjacent vertices have the same color.





![Representation Of Graph
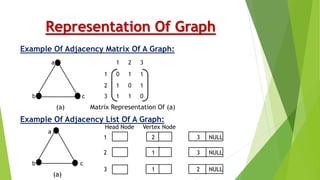
Two most common ways to represent a Graph:
1. Adjacency Matrix
2. Adjacency List
Adjacency Matrix:
Adjacency Matrix is a 2D array of size V x V where V is the number of
vertices in a graph.
Let the 2D array be adj [][], a slot adj [i][j] = 1 indicates that there is
an edge from vertex i to vertex j.
Adjacency matrix for undirected graph is always symmetric.
Adjacency Matrix is also used to represent weighted graphs.
If adj [i][j] = w, then there is an edge from vertex i to vertex j with
weight w.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheory-190319062009/85/Graph-theory-8-320.jpg)
![Representation Of Graph
Adjacency List:
An array of lists is used.
Size of the array is equal to the number of vertices.
Let the array be array []. An entry array [i] represents the
list of vertices adjacent to the ith vertex.
This representation can also be used to represent a
weighted graph.
The weights of edges can be represented as lists of pairs.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheory-190319062009/85/Graph-theory-9-320.jpg)