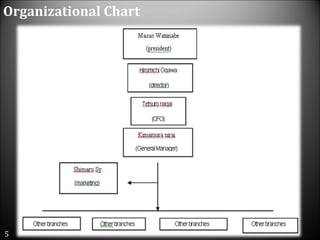
This document provides an organizational review of KFC, including its vision, mission, history, organizational structure, and SWOT analysis. The vision is to be the leading food services group in ASEAN delivering quality products and service. The mission is to maximize profitability and shareholder value through sustainable growth. KFC has changed ownership several times since 1964 and is now owned by PepsiCo, which reorganized KFC under its restaurant divisions.