- Glutamate-based theories of schizophrenia focus on dysfunction of brain glutamate systems, particularly NMDA receptors. These theories originated over 20 years ago and have led to new conceptualizations of schizophrenia and potential assessment and treatment approaches.
- Dopamine dysfunction in schizophrenia may be caused by genetically determined abnormalities or by NMDA receptor dysfunction impairing dopamine system regulation. Disturbances in both glutamate and dopamine systems likely contribute to positive symptoms.
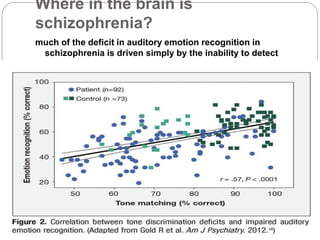
- Glutamate and NMDA receptors are widely distributed in the brain, suggesting schizophrenia involves dysfunction beyond prefrontal and limbic regions, including sensory cortices. Deficits in auditory and visual processing correlate with impaired functioning.
- While past drug trials targeting glut