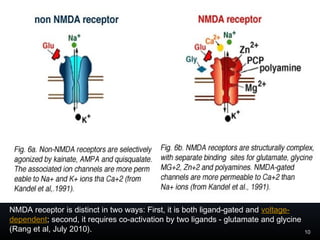
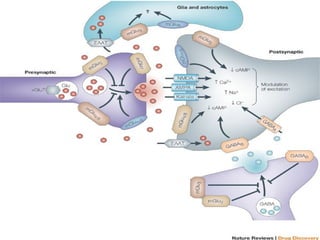
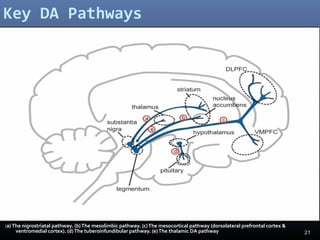
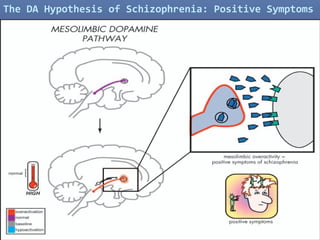
The document discusses the glutamate hypothesis of schizophrenia and glutamate-linked treatments. It proposes that hypofunction of the NMDA glutamate receptor contributes to the symptoms of schizophrenia. Specifically:
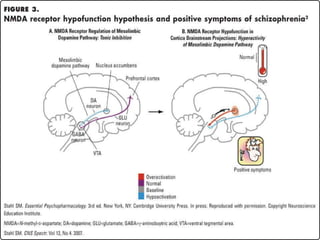
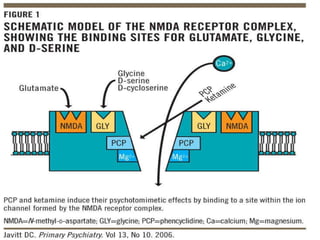
1. Antipsychotic drugs and conditions that block NMDA receptors can induce schizophrenia-like symptoms, supporting NMDA hypofunction.
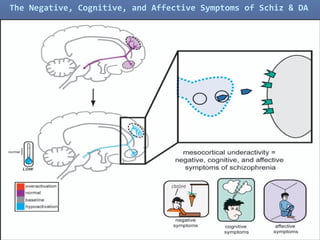
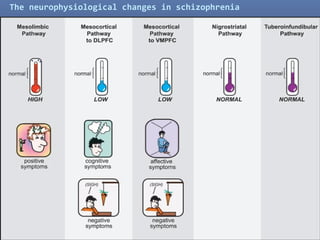
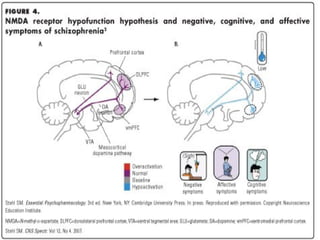
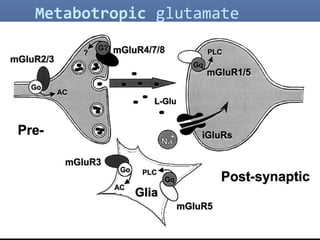
2. Glutamate-linked drugs may improve both positive and negative symptoms by targeting NMDA receptors in the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, and other brain regions.
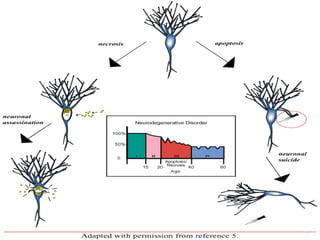
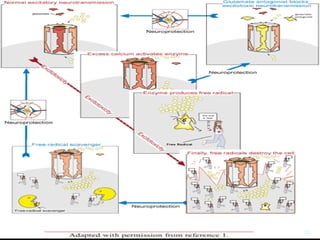
3. NMDA hypofunction during neurodevelopment or through excitotoxicity could underlie schizophrenia by disrupting processes like neural migration, pruning, and plasticity.
Glutamate-linked treatments may