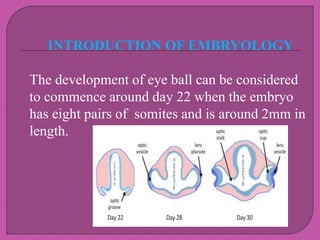
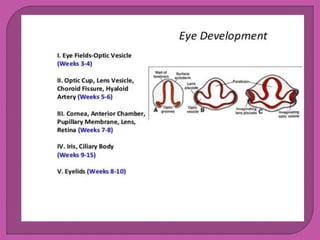
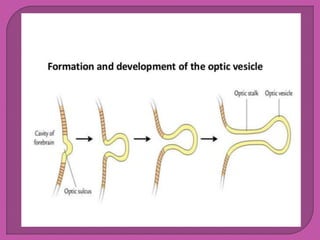
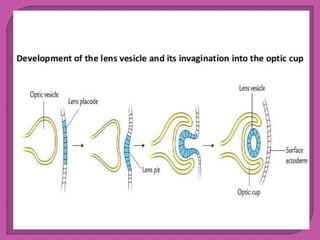
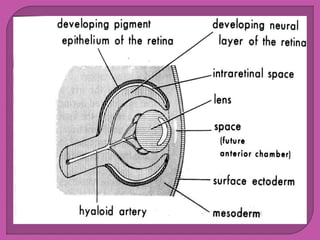
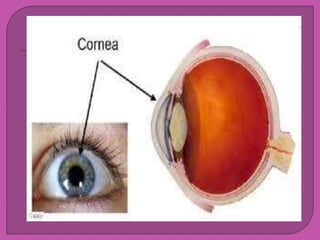
Eye development begins at 3 weeks in the embryo and continues through 10 weeks. Cells from both mesodermal and ectodermal tissues contribute to eye formation, with the eye derived from neuroepithelium surface ectoderm and extracellular mesenchyme. The major eye structures including the retina, lens, cornea, iris, ciliary body, choroid, and optic nerve are developed from the optic vesicle, lens placode, and surrounding mesenchyme between 3-10 weeks of gestation.