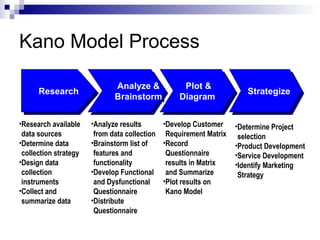
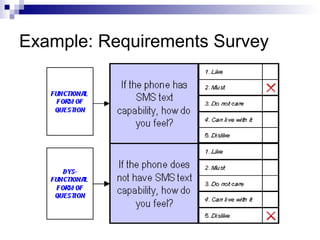
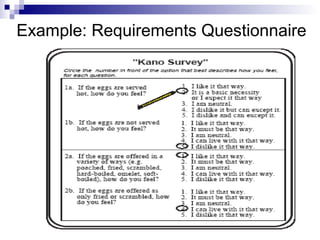
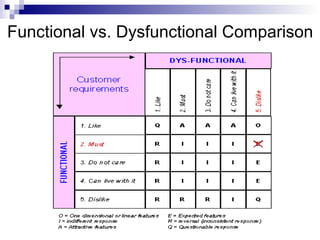
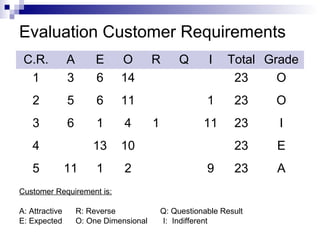
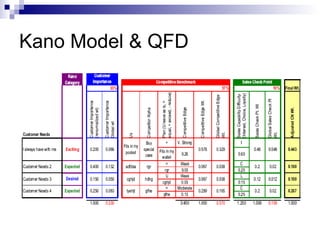
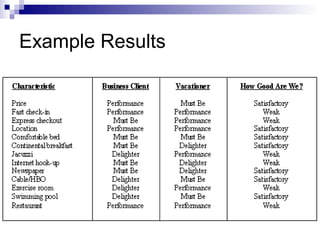
The Kano Model is a theory of product development and customer satisfaction developed by Noriaki Kano. It classifies product attributes into three categories: must-be attributes which customers expect, performance attributes where more is better, and attractive/delighter attributes which provide surprise and delight. The Kano Model provides a methodology to analyze customer needs, prioritize attributes, and guide new product development strategies to meet and exceed customer expectations.