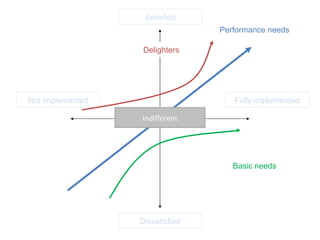
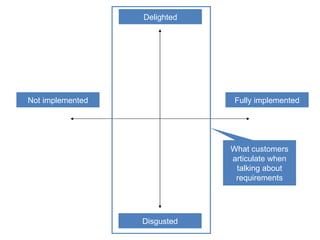
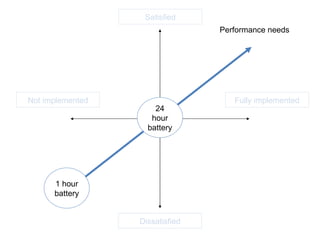
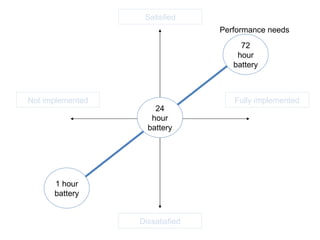
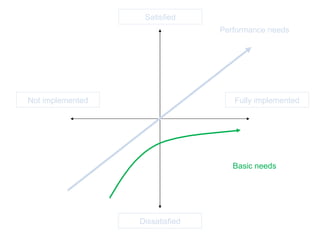
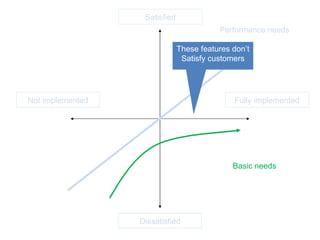
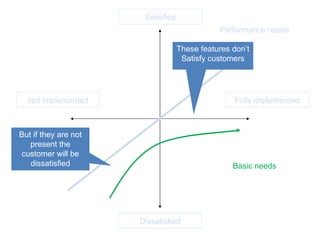
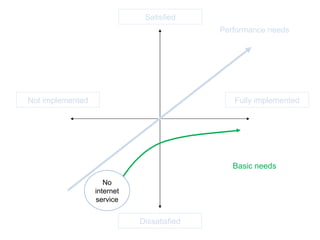
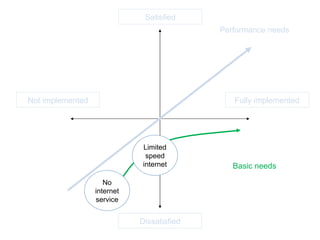
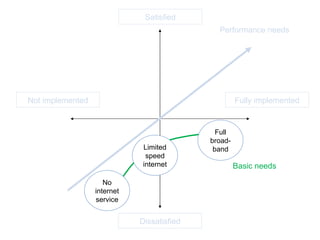
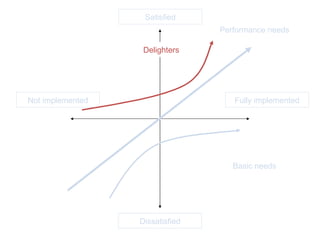
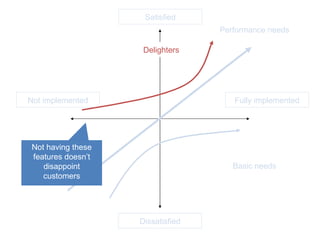
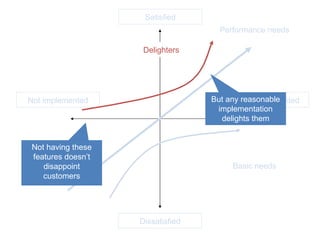
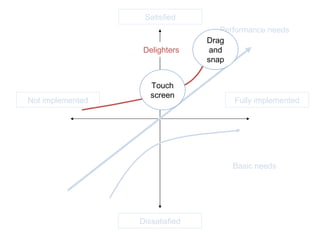
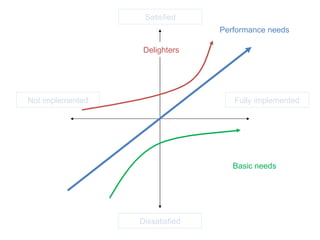
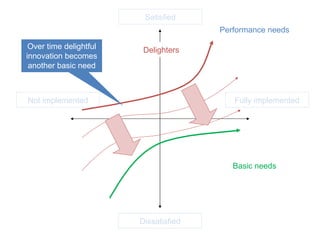
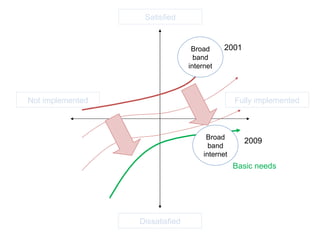
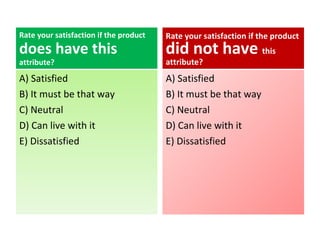
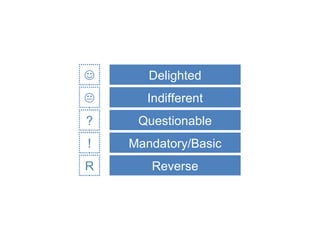
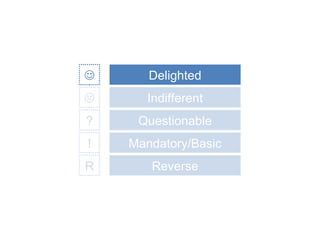
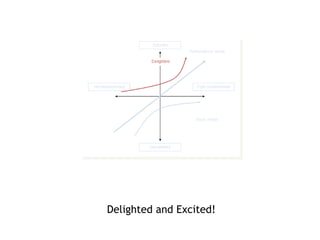
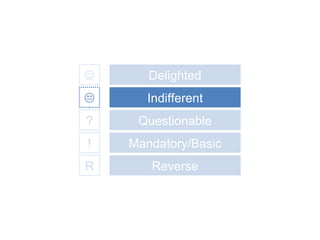
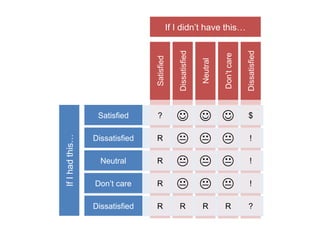
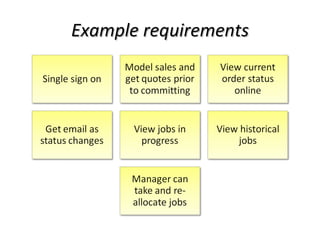
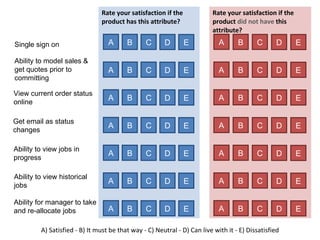
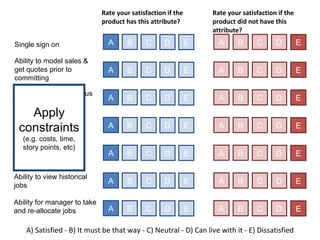
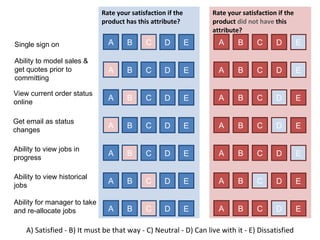
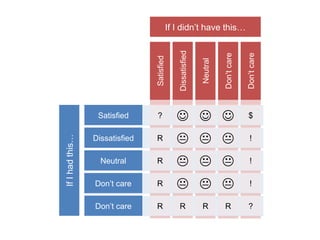
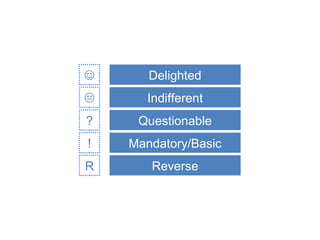
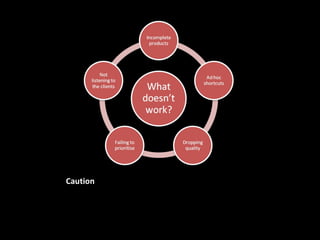
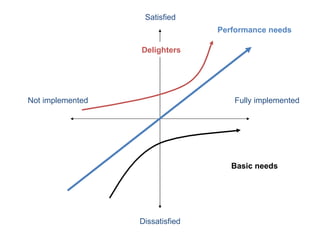
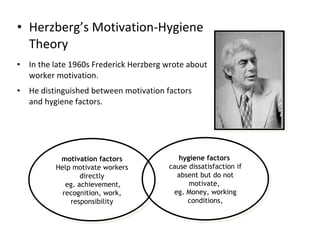
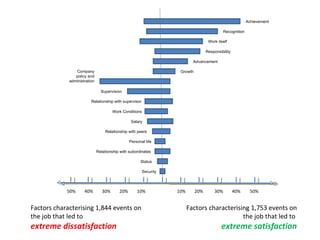
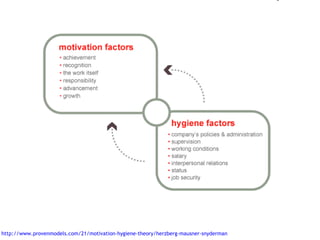
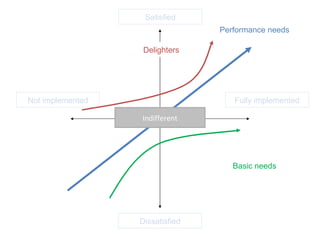
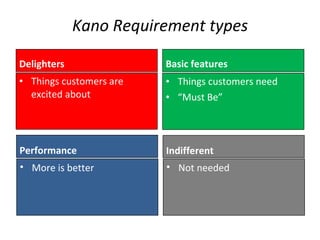
The document discusses Kano analysis, a framework for prioritizing stakeholder requirements developed by Noriaki Kano, which helps distinguish between mandatory, performance, and delightful requirements in business and software contexts. It emphasizes the role of business analysts in delivering valuable products while addressing common challenges in requirements elicitation, management, and validation. The presentation also includes references to Herzberg's motivation-hygiene theory and offers insights on planning releases and ensuring stakeholder satisfaction.

















![Secondary Key Plus Basic Llosa (1997 [8] , 1999 [9] ) Low impact One-dimensional Attractive Basic Brandt and Scharioth (1998) [7] Low Key Value-added Flat Venkitaraman and Jaworski (1993) [6] Unimportant as determinant Hybrid Value enhancing Minimum requirement Brandt (1988) [5] Neutral Critical Satisfier Dissatisfier Cadotte and Turgeon (1988) [4] Indifferent One-dimensional Attractive Must-be Kano (1984) [3] Motivator Hygiene Herzberg et al. (1959) [2] Driver type 4 Driver type 3 Driver type 2 Driver type 1 Author(s)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kanoacstalkfor25june09-090613071323-phpapp02/85/Kano-Analysis-and-Software-Requrements-23-320.jpg)