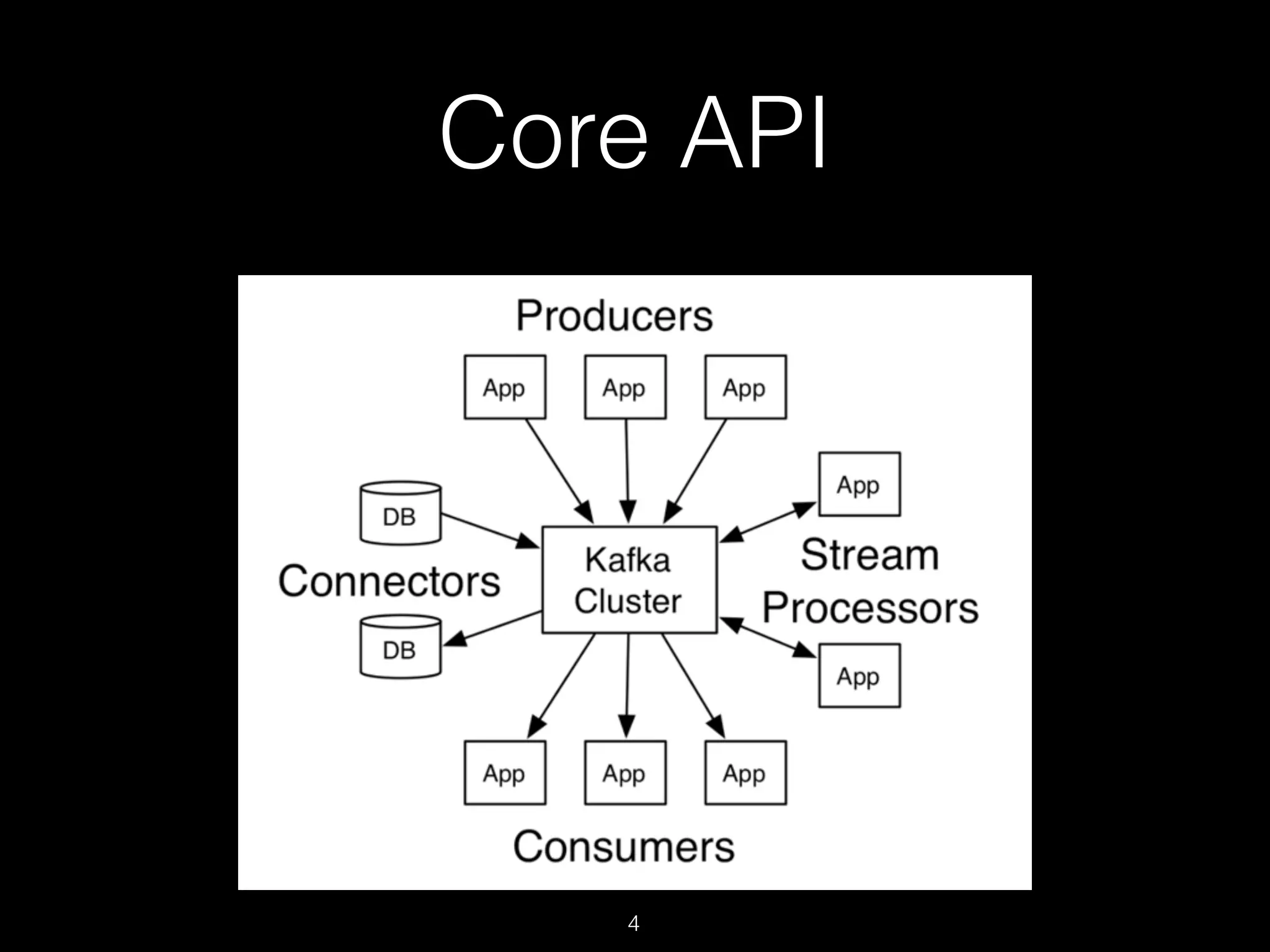
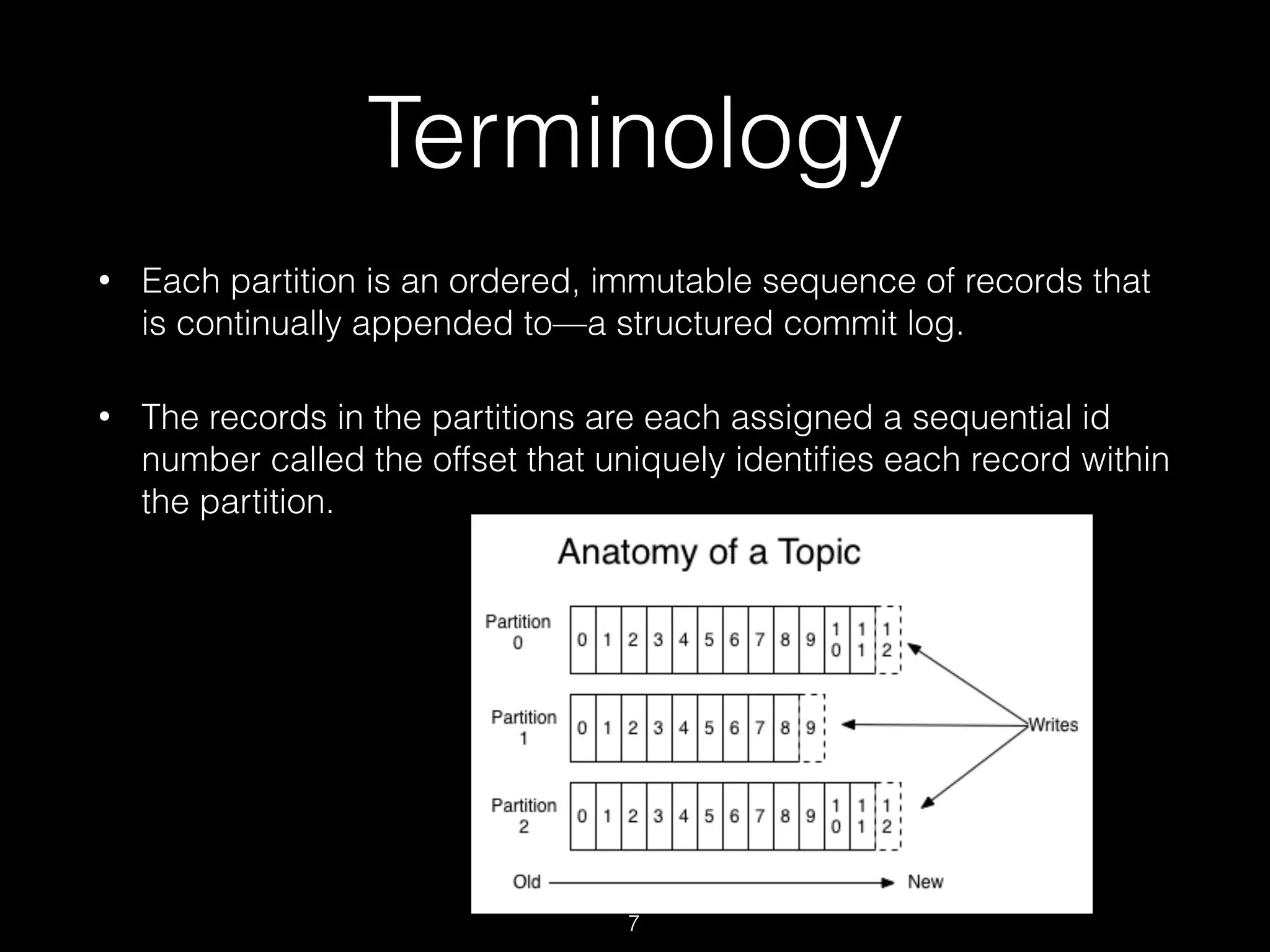
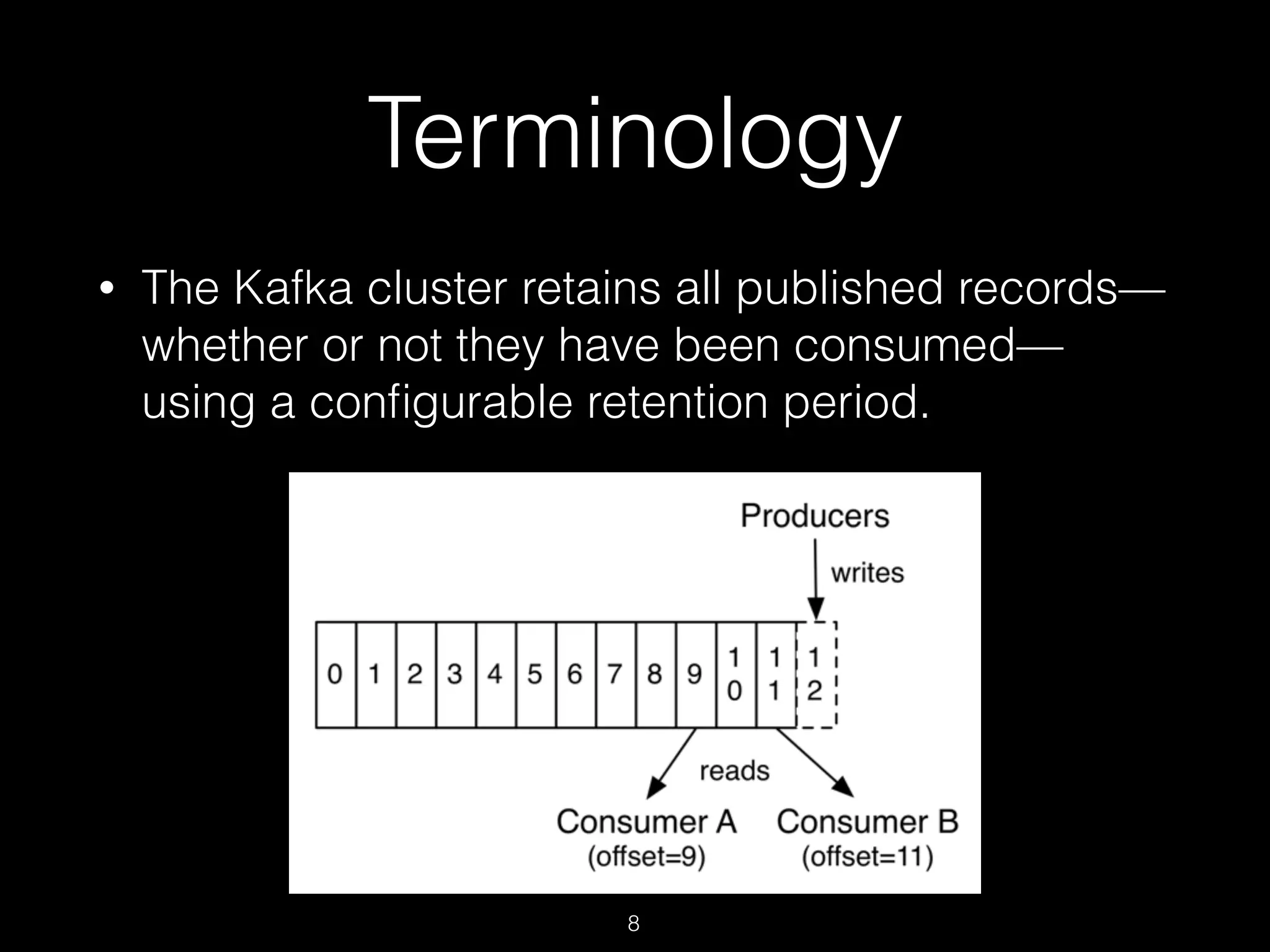
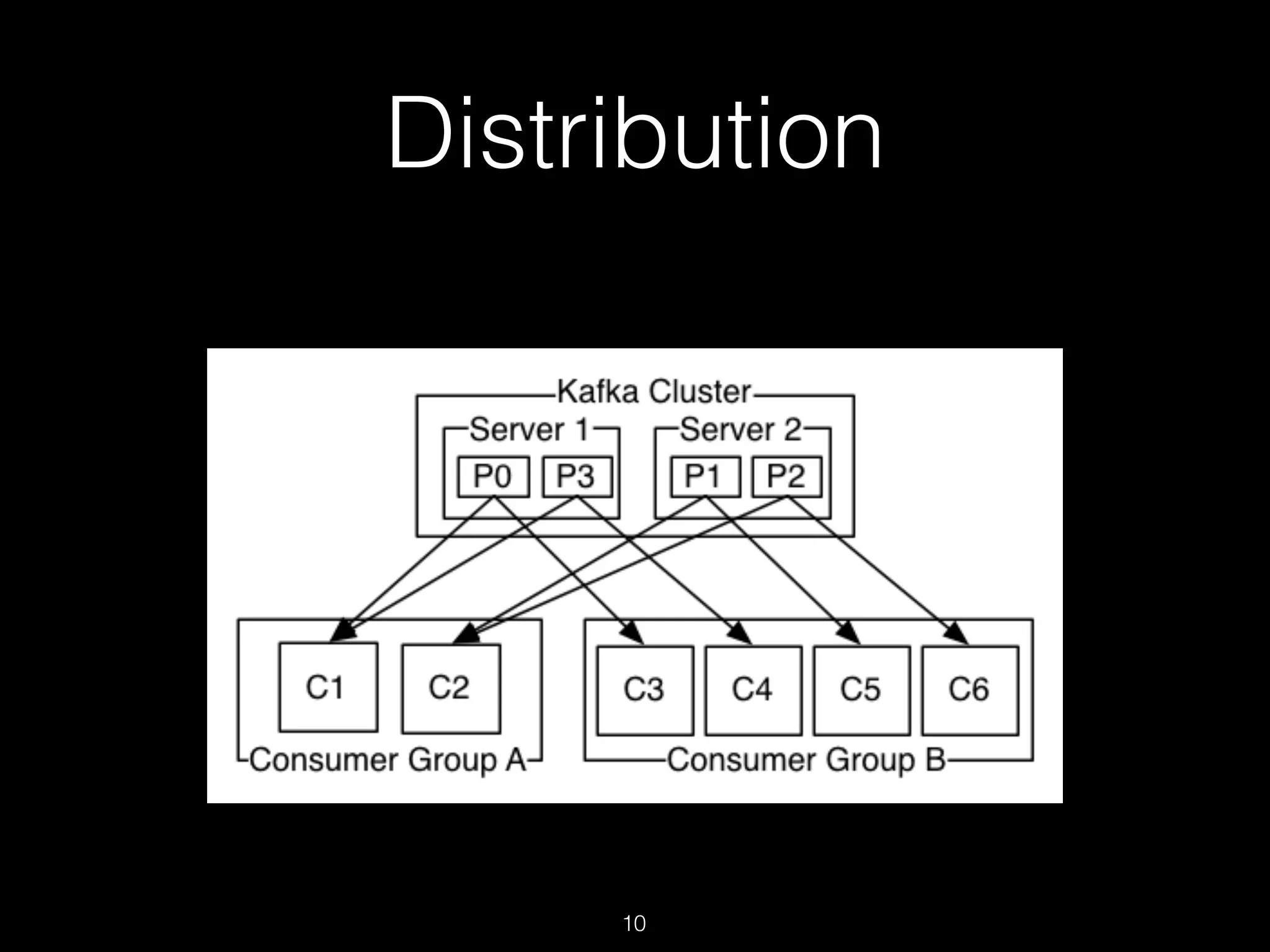
Kafka is a distributed streaming platform used for building real-time data pipelines and streaming applications. It allows for publishing and subscribing to streams of records known as topics in a fault-tolerant, scalable, and fast manner. Producers publish data to topics while consumers subscribe to topics and process the data streams. The Kafka cluster stores these topic partitions across servers and replicates the data for fault tolerance. It provides ordering and processing guarantees through offsets as it retains data for a configurable period of time.