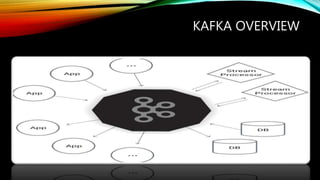
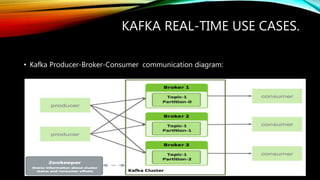
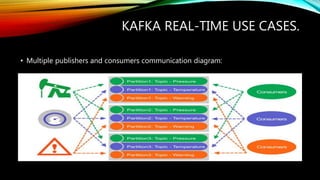
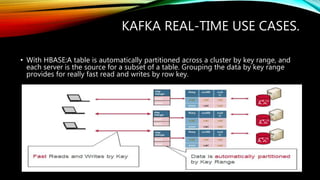
Kafka is an open source messaging system that can handle massive streams of data in real-time. It is fast, scalable, durable, and fault-tolerant. Kafka is commonly used for stream processing, website activity tracking, metrics collection, and log aggregation. It supports high throughput, reliable delivery, and horizontal scalability. Some examples of real-time use cases for Kafka include website monitoring, network monitoring, fraud detection, and IoT applications.