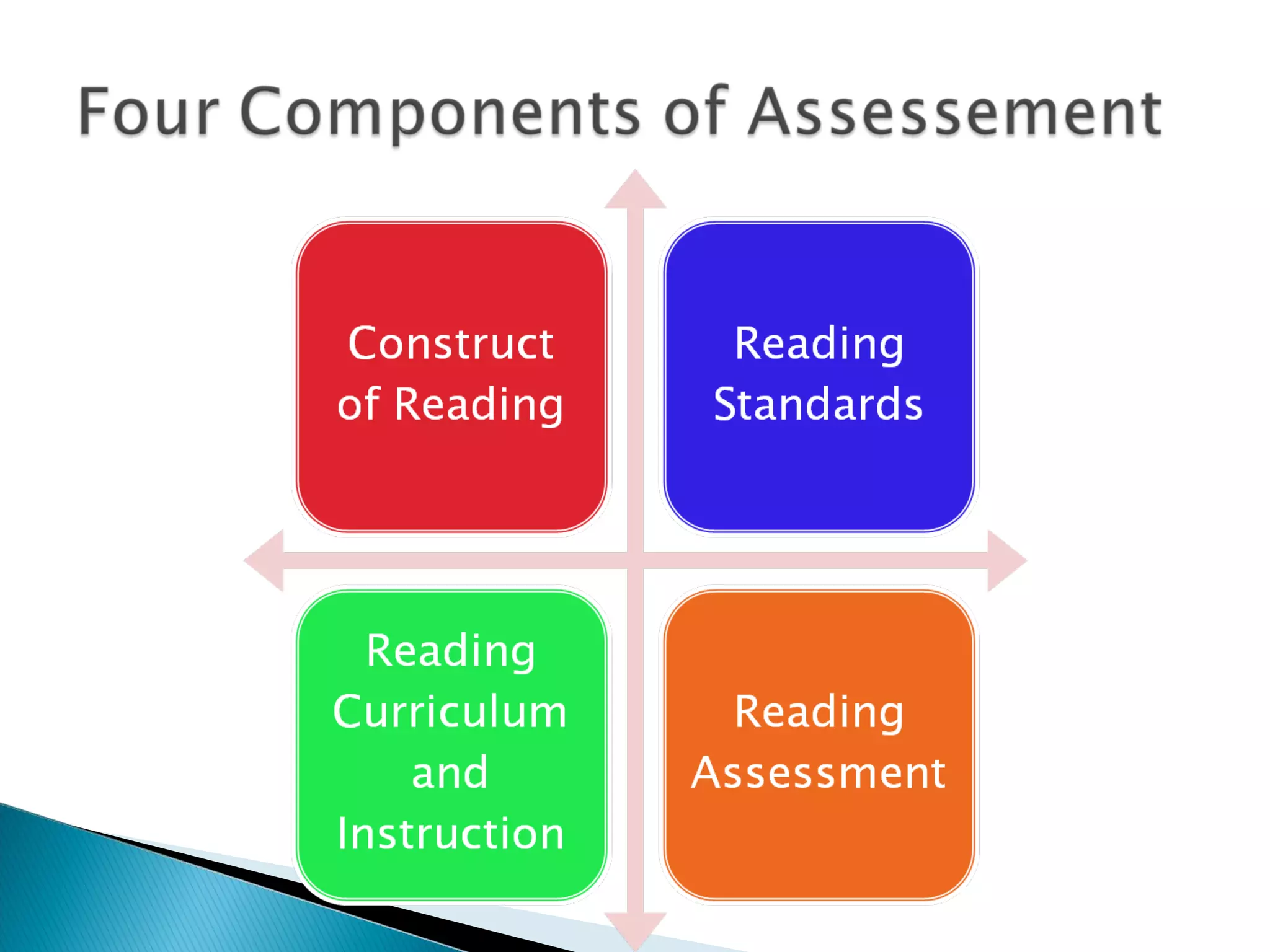
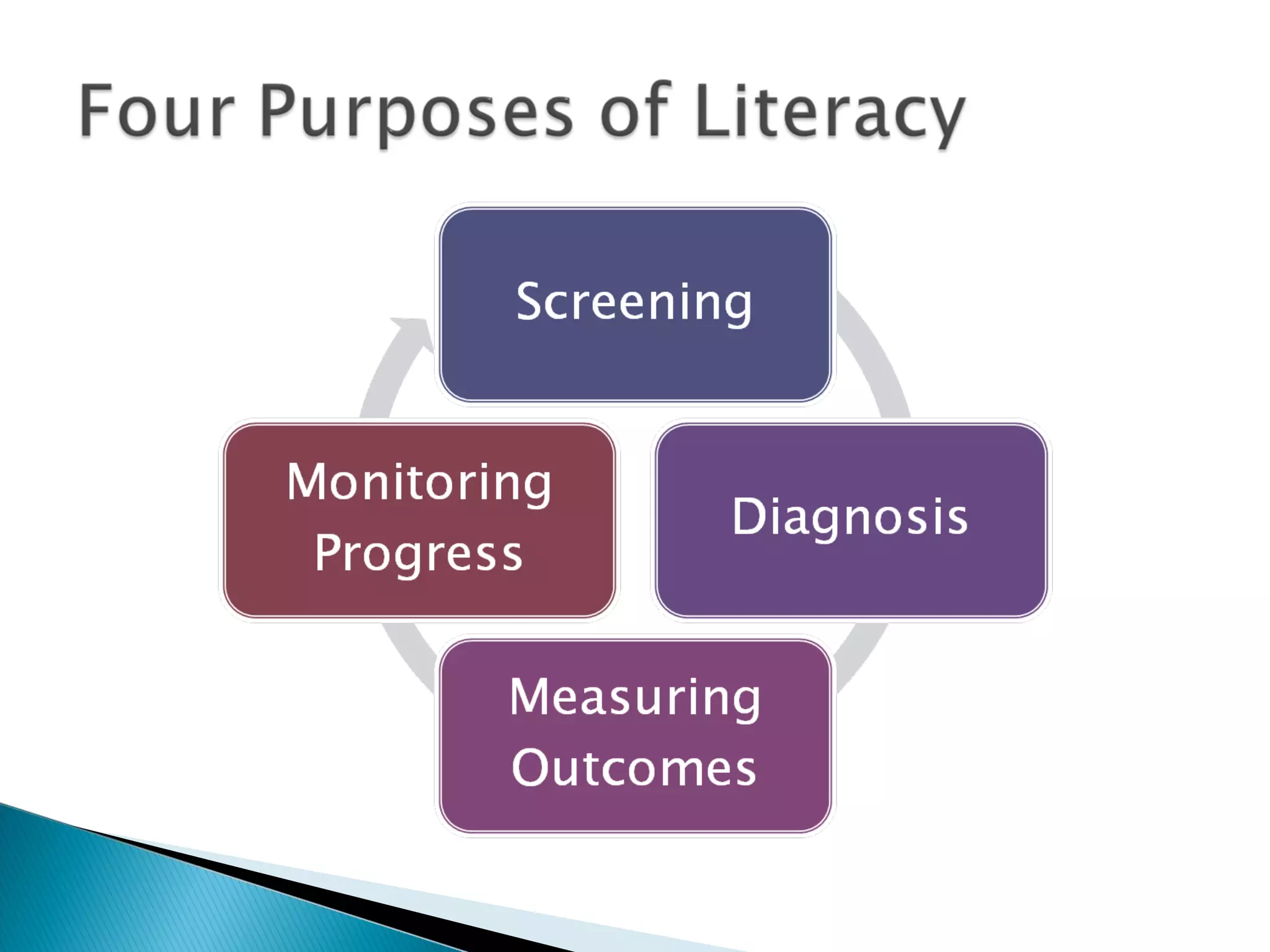
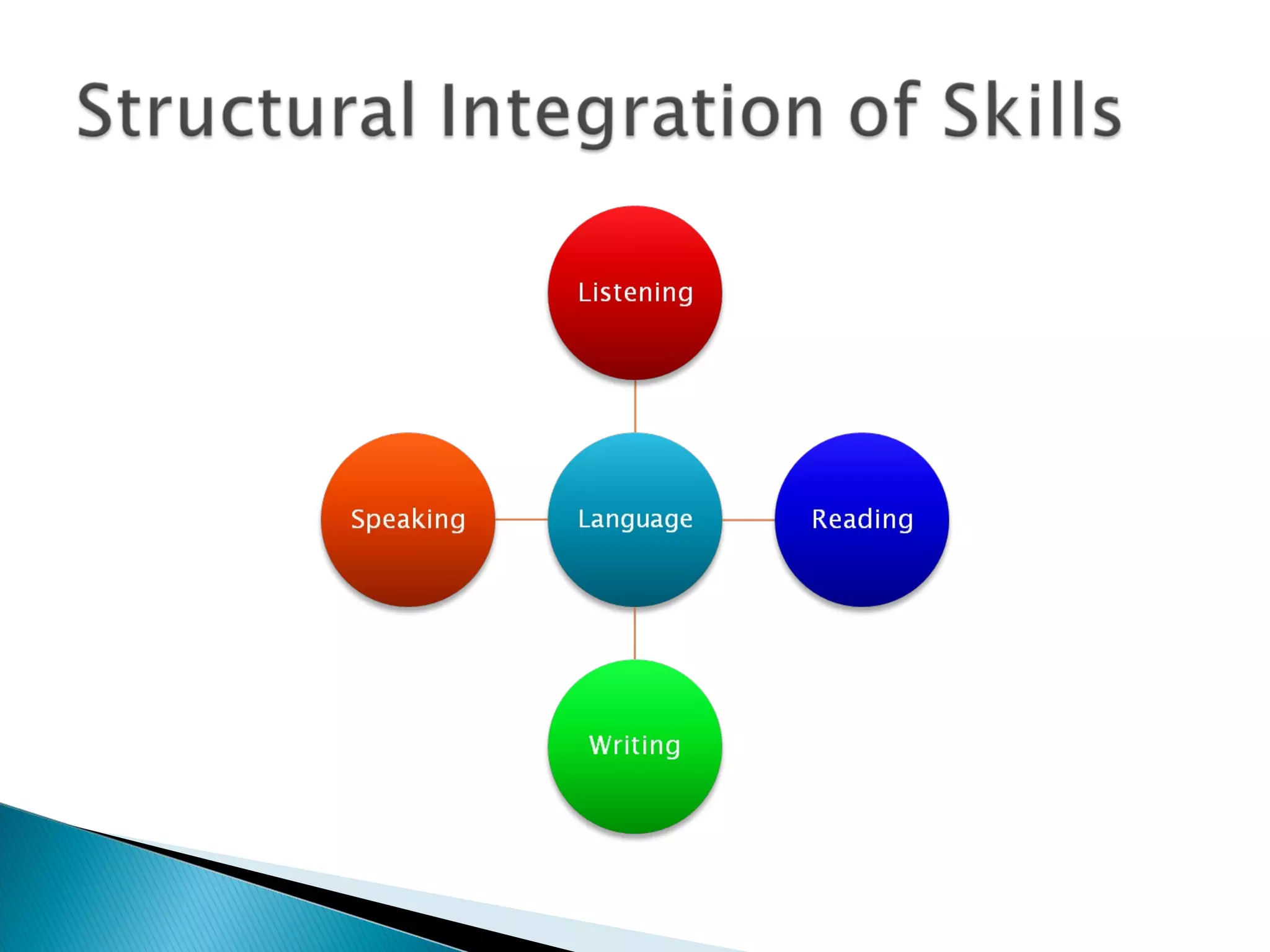
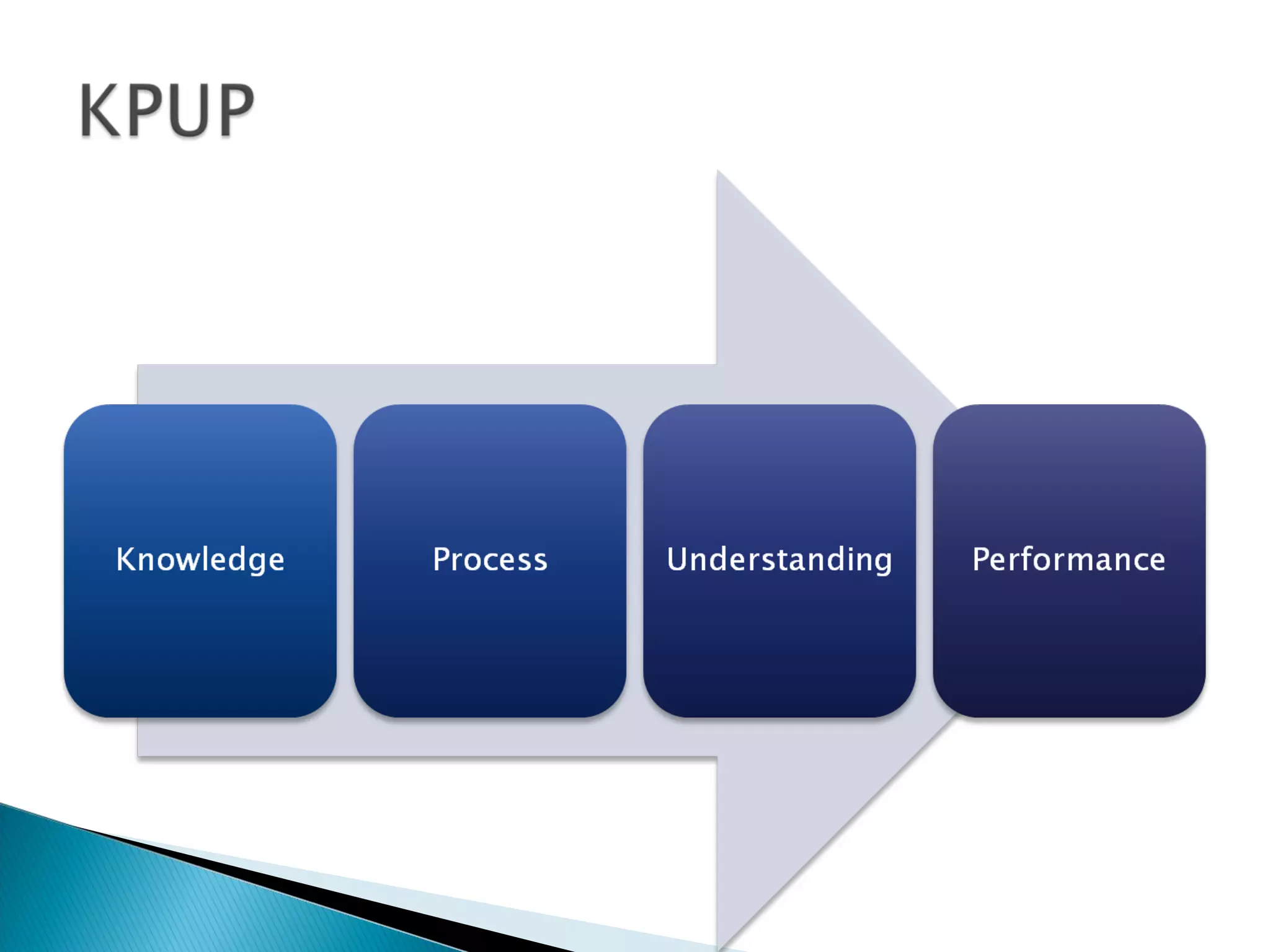
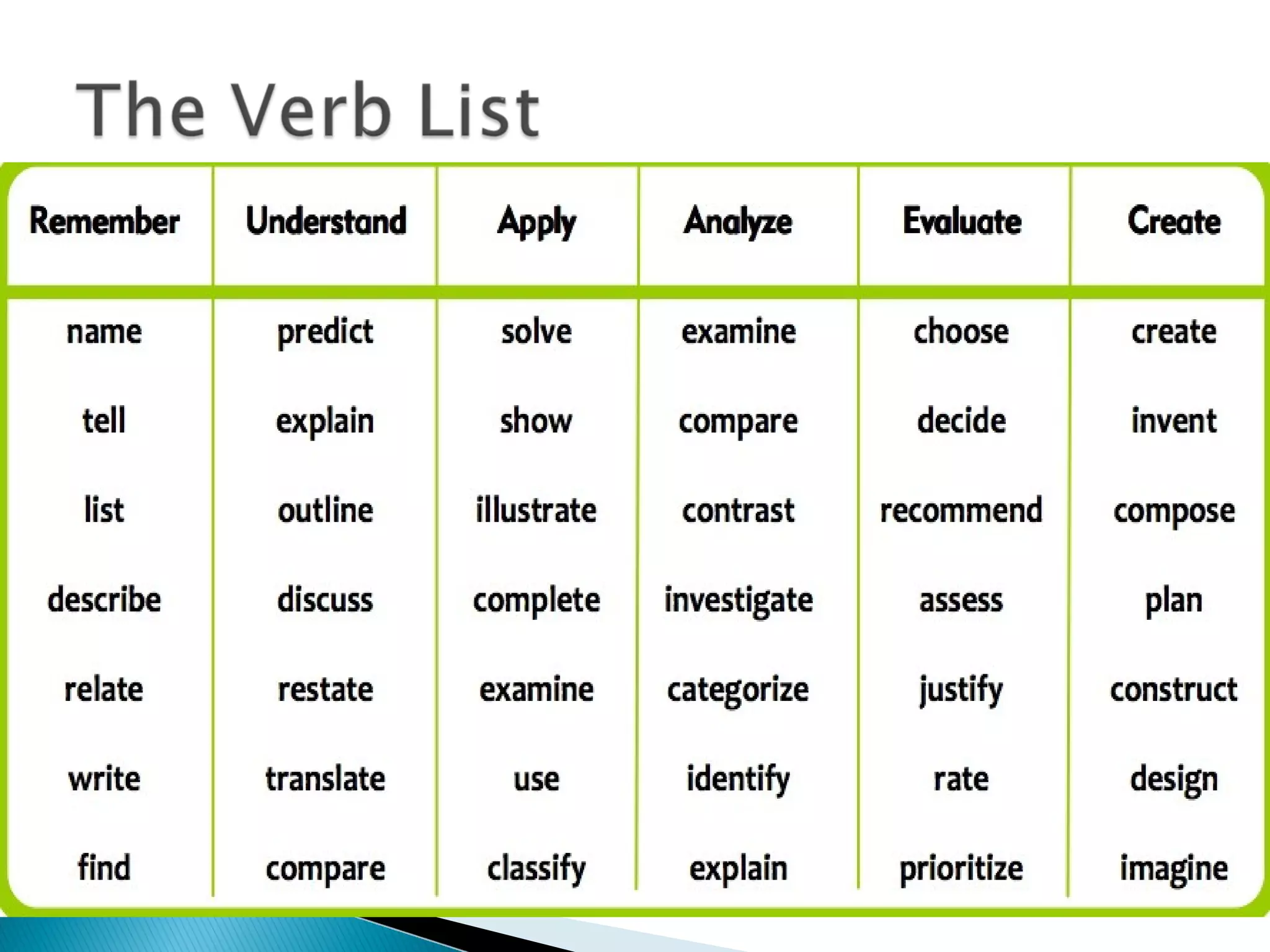
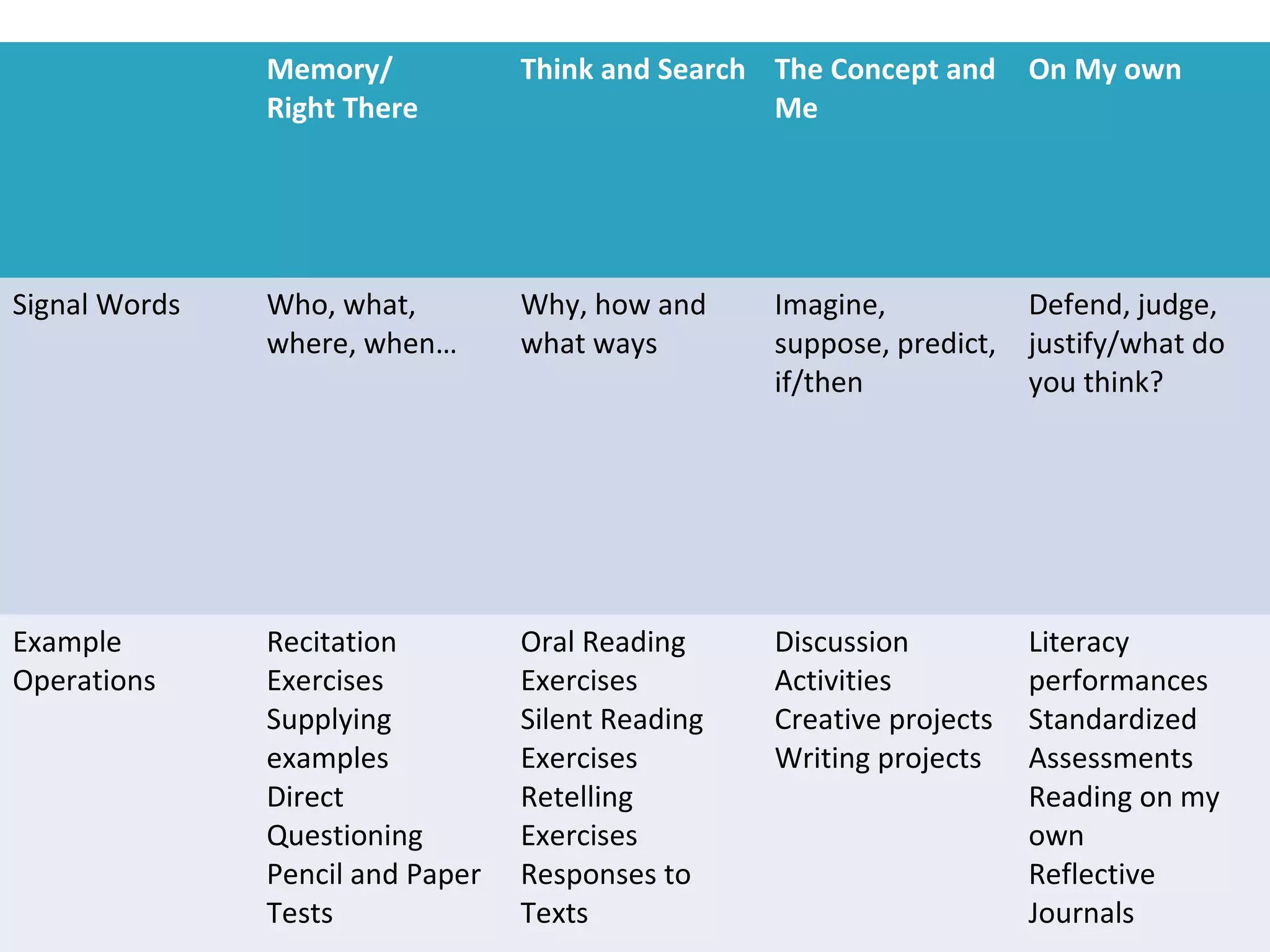
This document discusses the importance of assessment in education. It provides examples of assessment questions teachers can ask to evaluate reading programs and student progress. Effective assessment should be holistic, standards-based, formative, and developmental. The goal of assessment is to understand if instruction is working, identify students who need extra help, and improve teaching and learning over time.