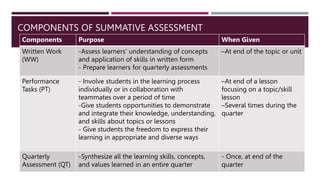
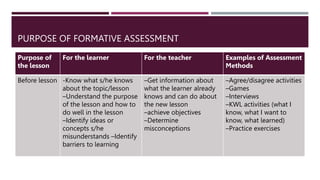
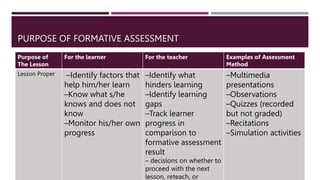
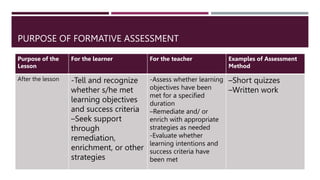
The document discusses the concepts of constructive alignment and standards-based assessment in education. It is summarized as follows:
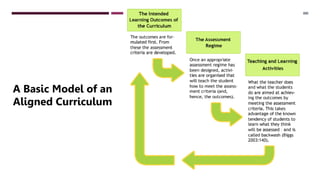
1. Constructive alignment is an approach where learning outcomes are defined before teaching, and teaching/assessment methods are designed to achieve those outcomes and assess student achievement of standards. Assessment criteria are referenced to the defined outcomes.
2. The focus is on what and how students learn rather than just the topics taught. Learning outcomes describe what students should be able to do, like apply procedures or compare theories.
3. The goal is to support student meaning and learning through a well-designed, coherent course where intentions and assessments are aligned based on standards of what students should learn and be able to demonstrate.