Embed presentation
Downloaded 288 times





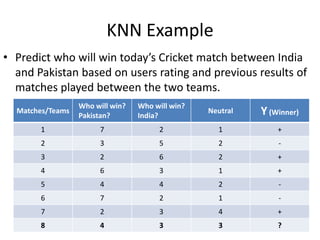

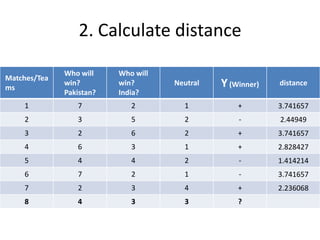
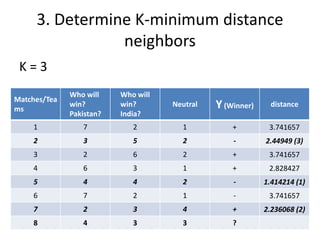
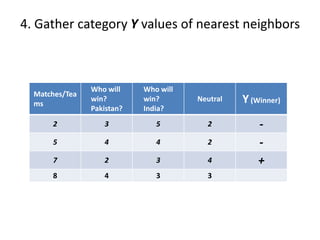
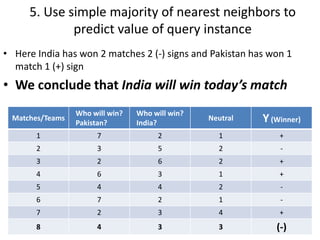



The document summarizes the K-nearest neighbor (KNN) algorithm. KNN is a memory-based algorithm that finds the K training samples nearest to a query point and predicts the query's classification based on the majority classification of its neighbors. The summary explains: 1) KNN measures the distance between query points and training samples to classify new objects based on the majority category of its K nearest neighbors. 2) To make a prediction, KNN determines K, calculates distances between the query and all training points, identifies the K nearest neighbors, collects their classifications, and predicts the query's classification based on the majority of its neighbors. 3) An example is given where KNN predicts the winner of an












