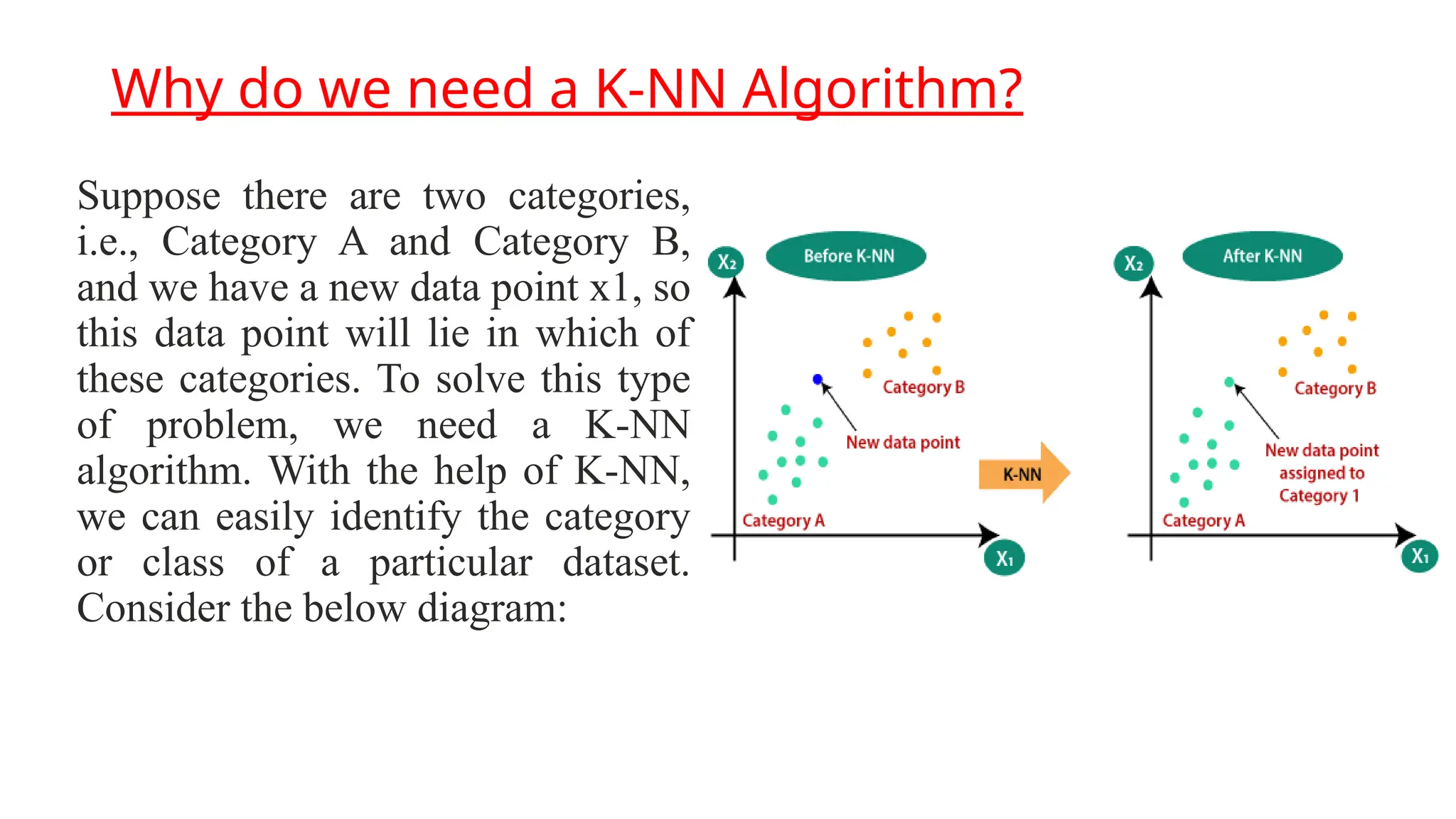
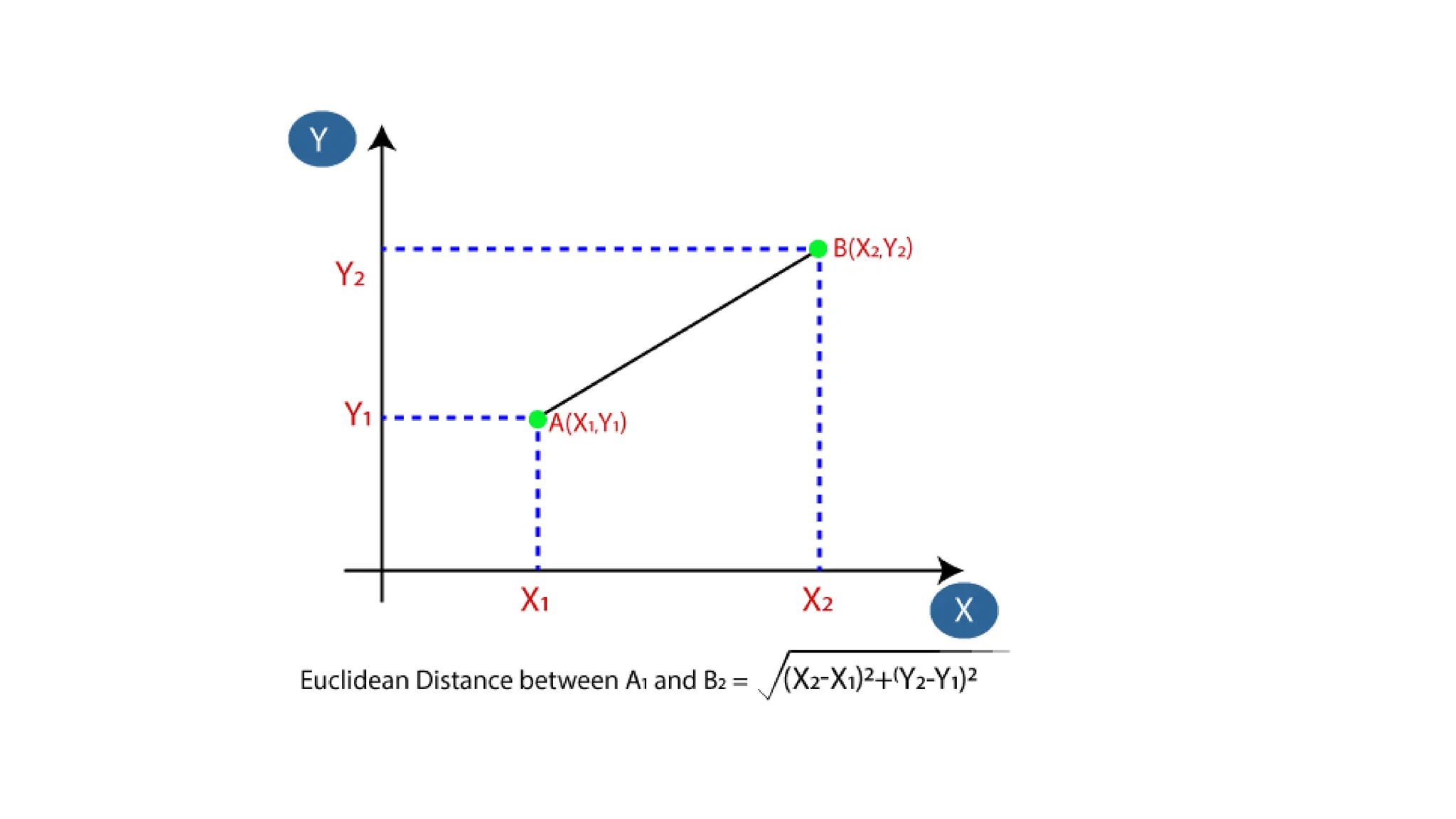
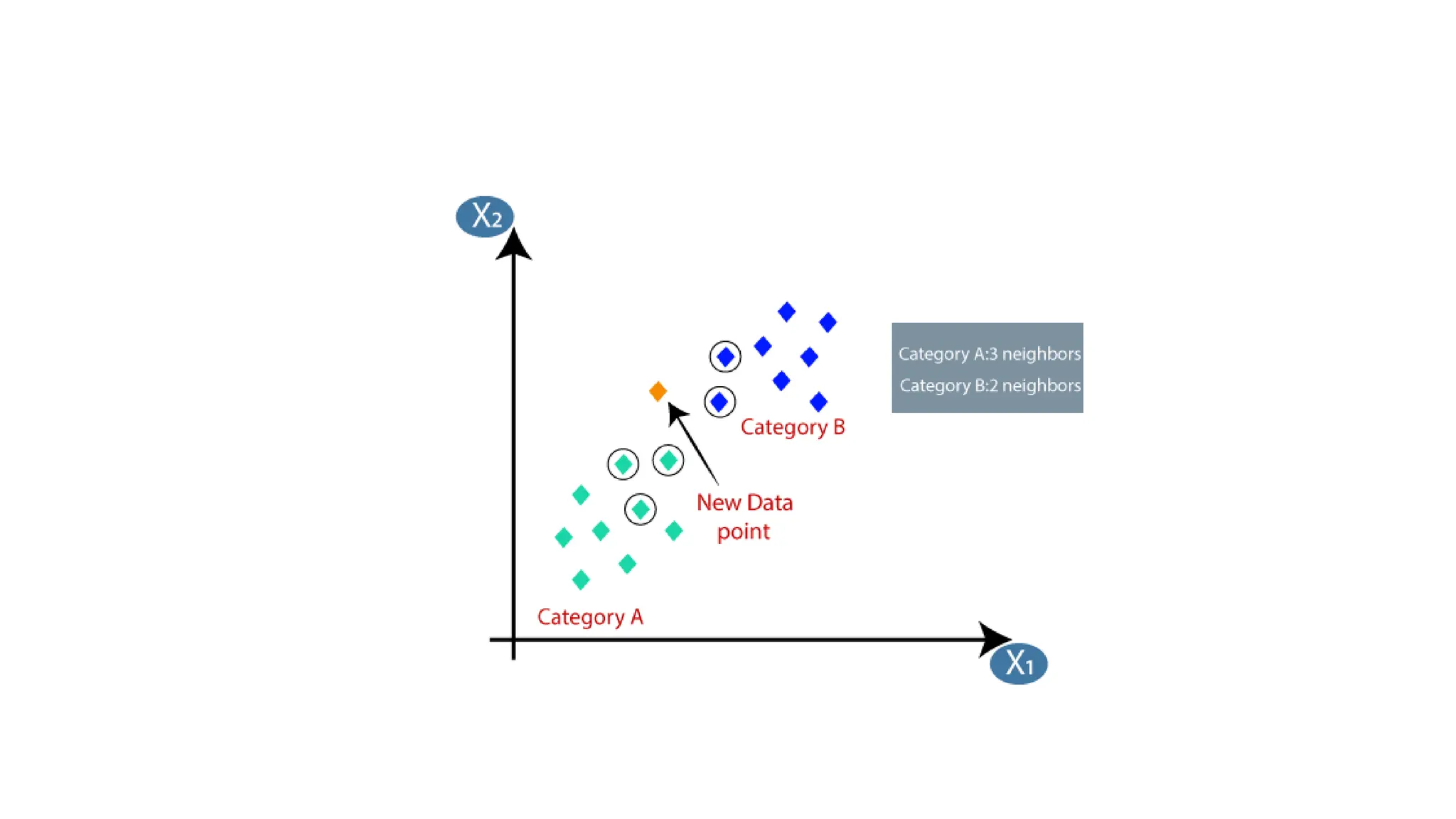
The k-nearest neighbor (k-nn) algorithm is a supervised learning method used primarily for classification but can also handle regression tasks. It classifies new data points based on the similarity to existing data, storing all available cases without immediate learning, which is why it's termed a 'lazy learner.' Although the algorithm is simple and robust to noisy data, it requires careful determination of the parameter k and can be computationally intensive due to distance calculations.