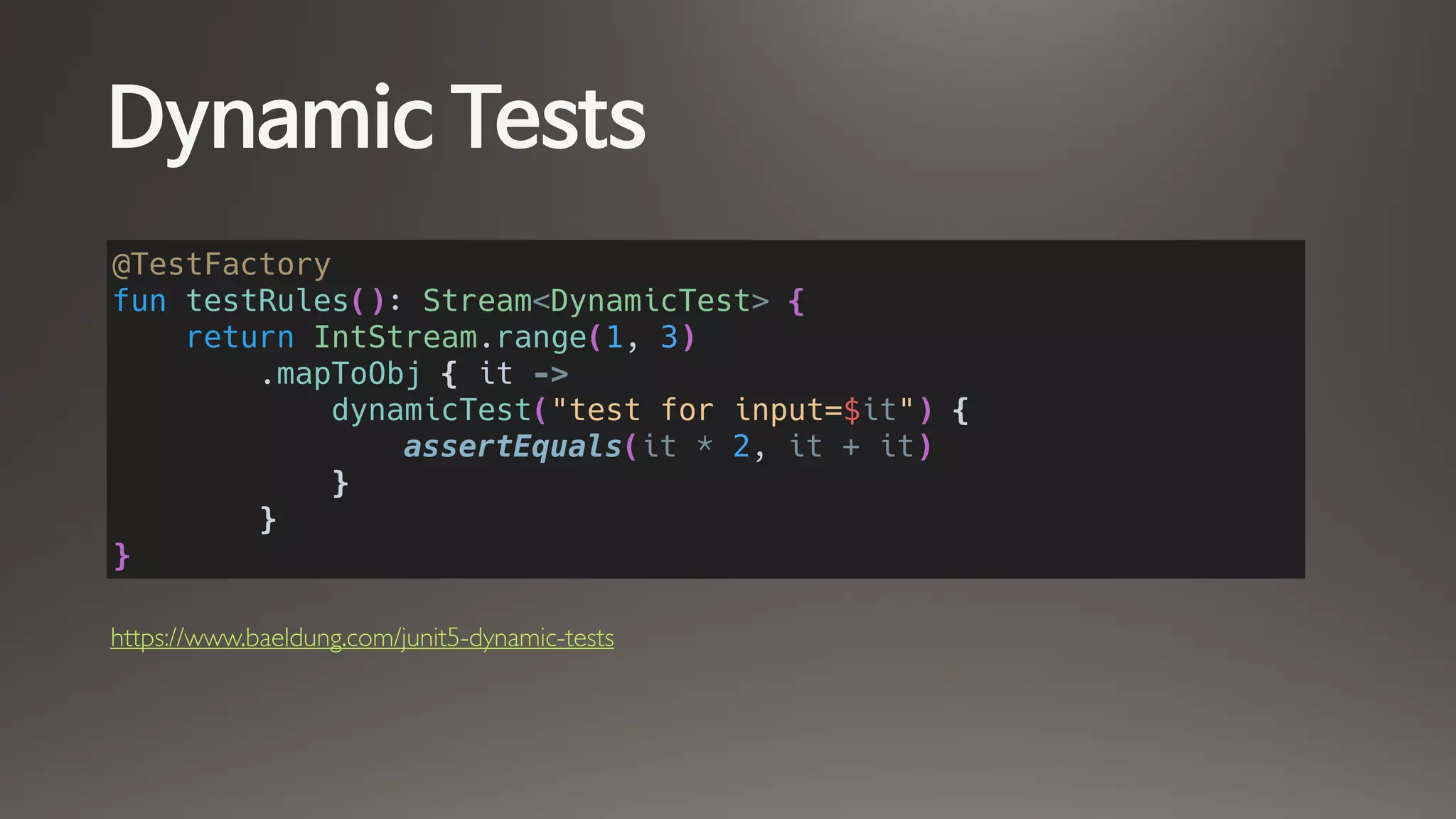
This document provides an overview of JUnit 5 and TestContainers. It discusses how JUnit 5 is composed of the JUnit Platform, JUnit Jupiter, and JUnit Vintage modules. It covers JUnit 5 annotations, assertions, assumptions, parameterized and conditional tests. It also discusses how TestContainers allows tests to use live Docker containers as their test environment by launching containers during tests. This includes using generic containers, specialized database containers, and configuring container properties. Resources for further learning about both tools are also provided.




![Example import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
@BeforeEach
fun setup() {
facts.clear()
}
@Test
fun `facts must have unique name`() {
facts.put("foo", 1)
facts.put("foo", 2)
facts.size shouldEqual 1
assertEquals(2, facts["foo"] !!)
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/junit5testcontainers-190321150815/75/JUnit5-and-TestContainers-6-2048.jpg)
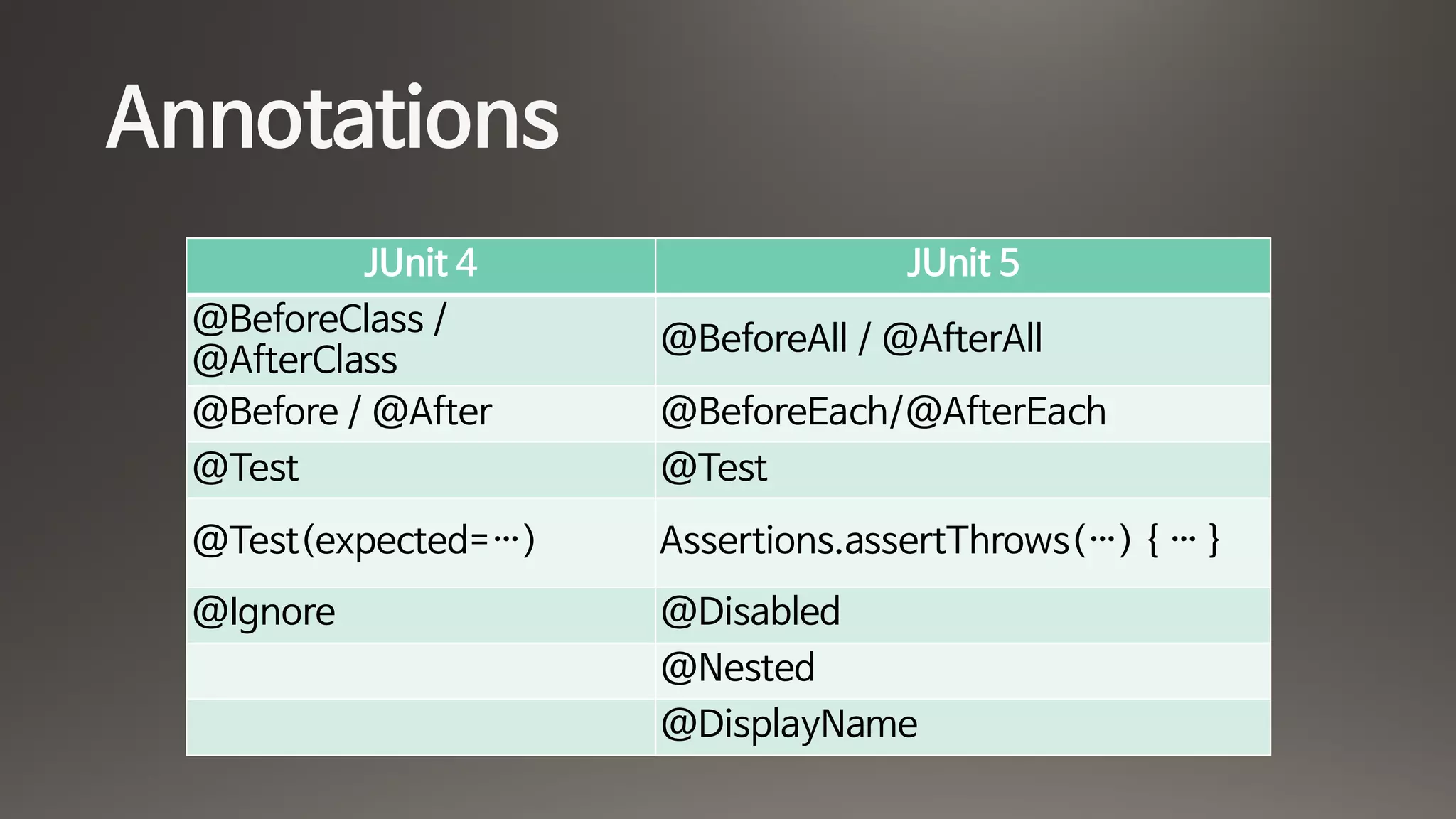
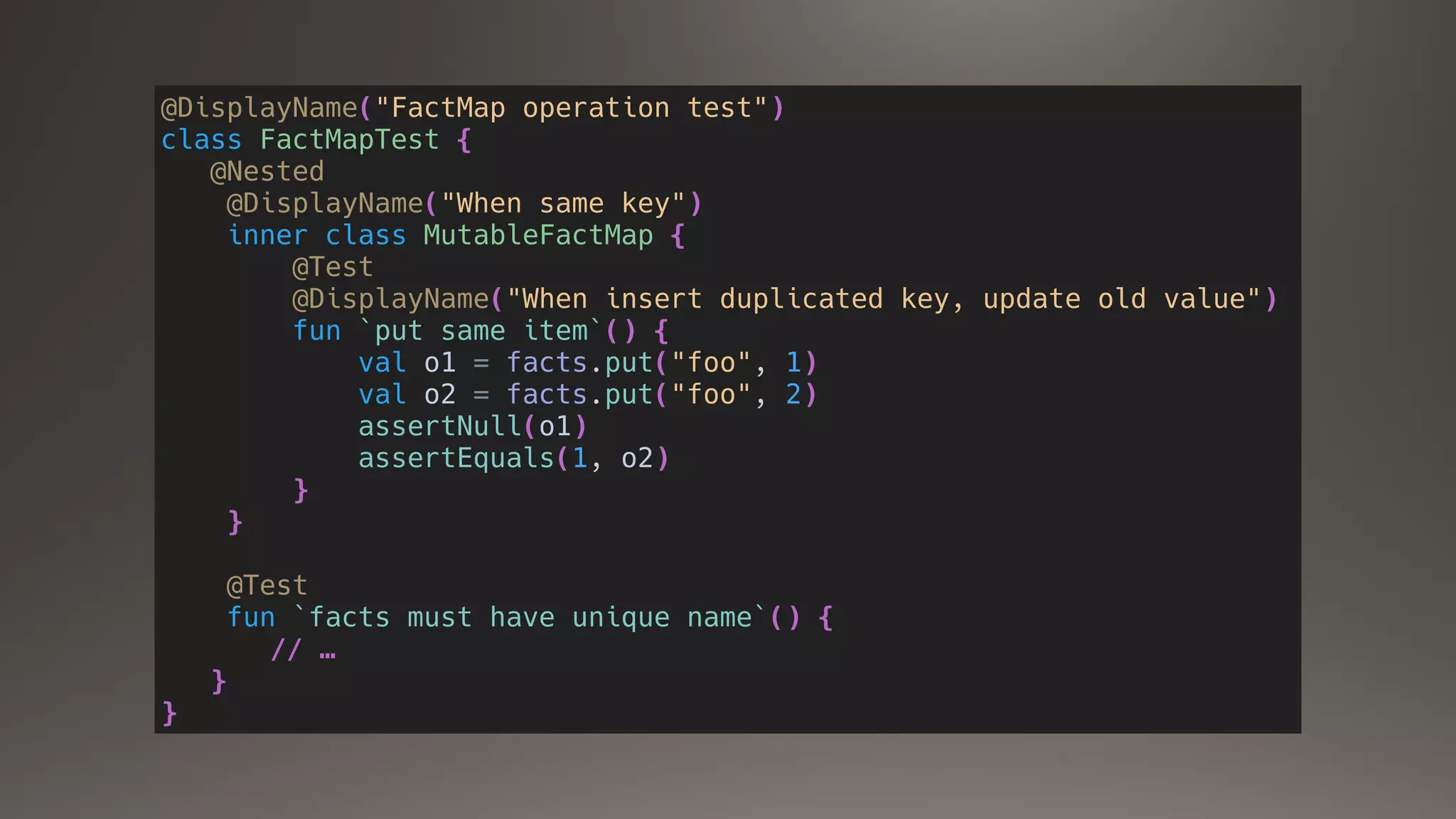
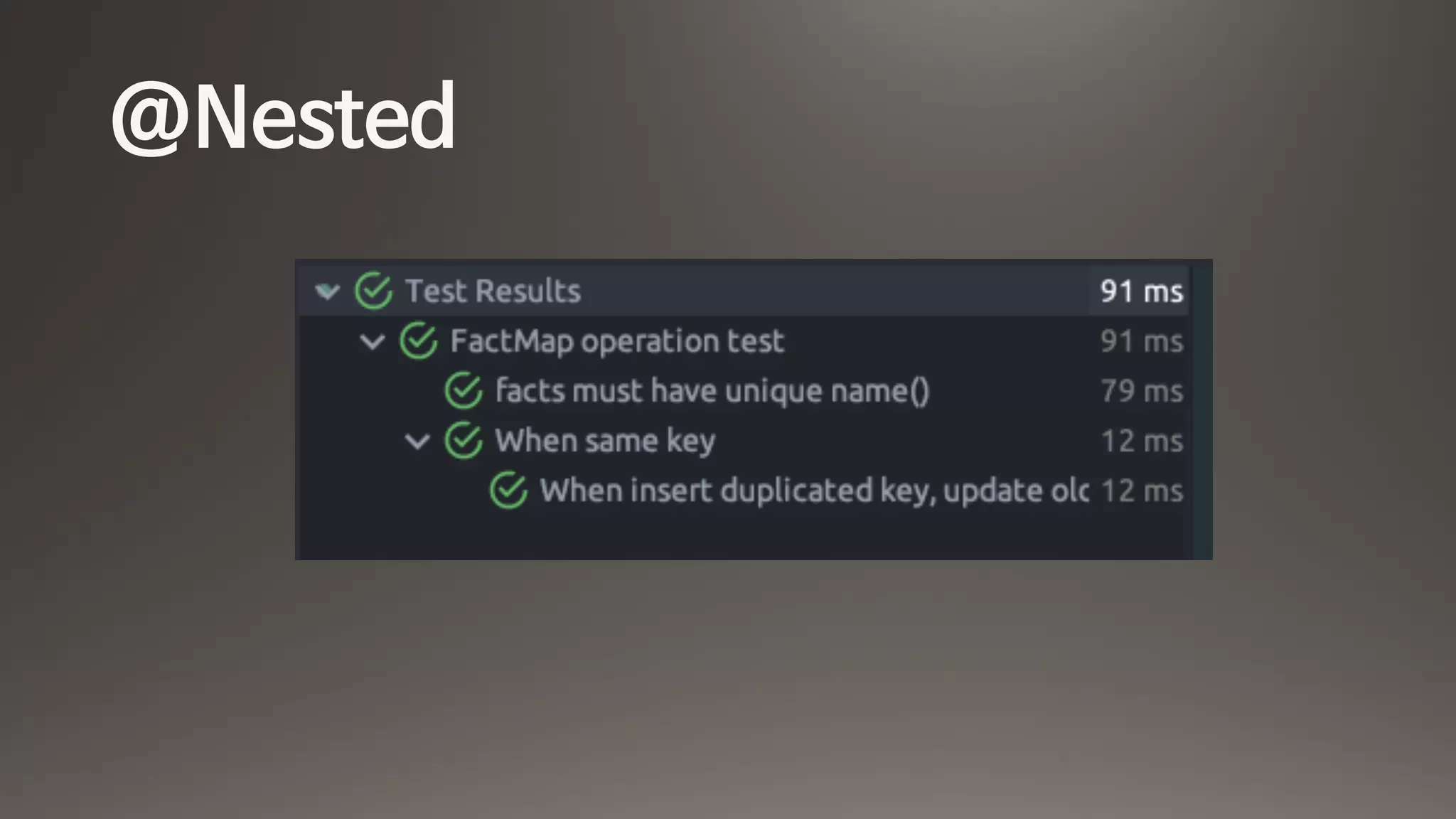


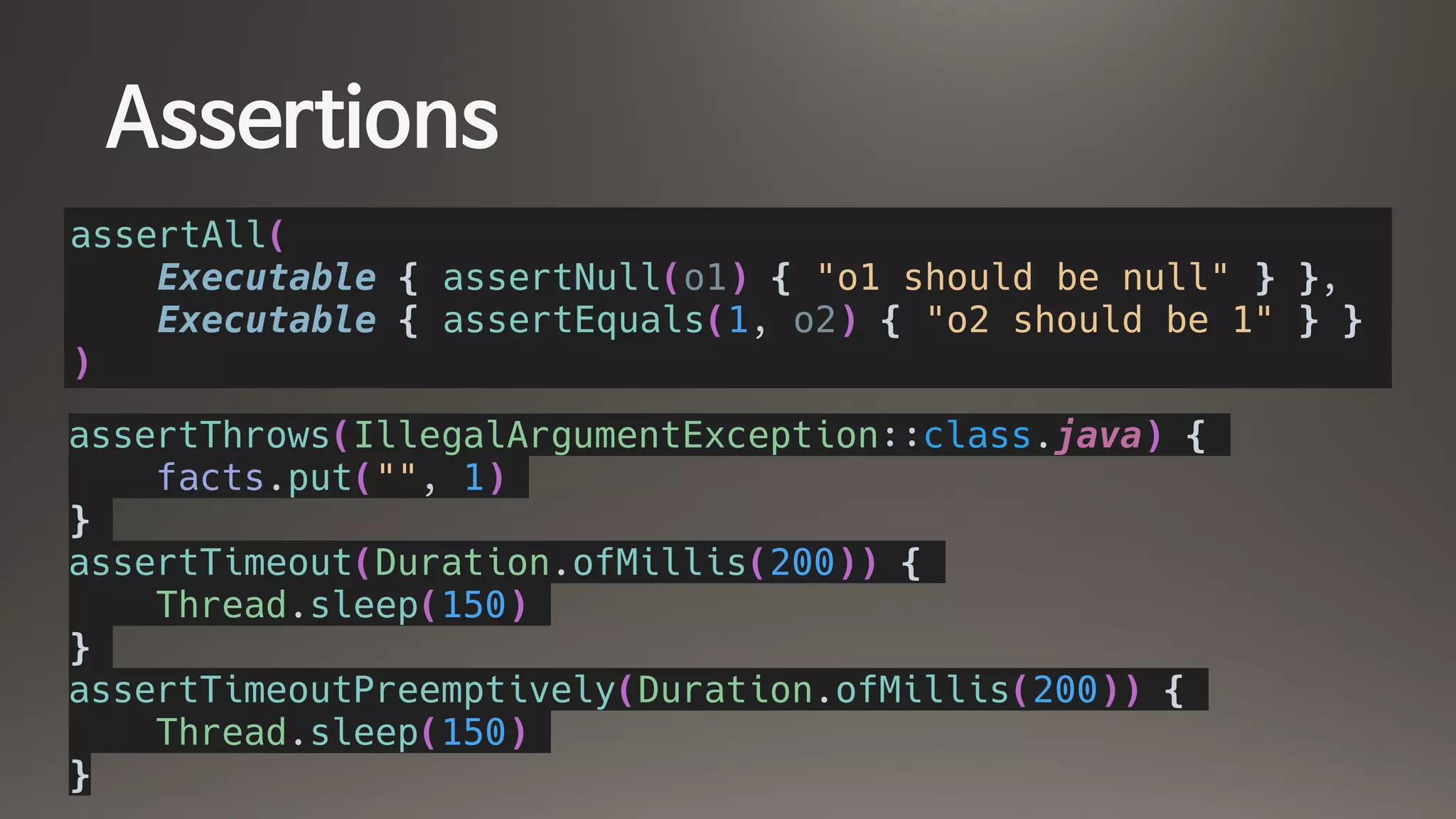




![Parameterized Tests
@ParameterizedTest
@ValueSource(strings = ["java8", "java9", "java10"])
fun `parameterized test`(param:String) {
param shouldContain "java"
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/junit5testcontainers-190321150815/75/JUnit5-and-TestContainers-18-2048.jpg)
![Parameterized Tests
@ParameterizedTest(name = "[{index}]=> {arguments}")
@ValueSource(strings = ["java8", "java9", "java10"])
fun `parameterized test`(param: String) {
param shouldContain "java"
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/junit5testcontainers-190321150815/75/JUnit5-and-TestContainers-19-2048.jpg)