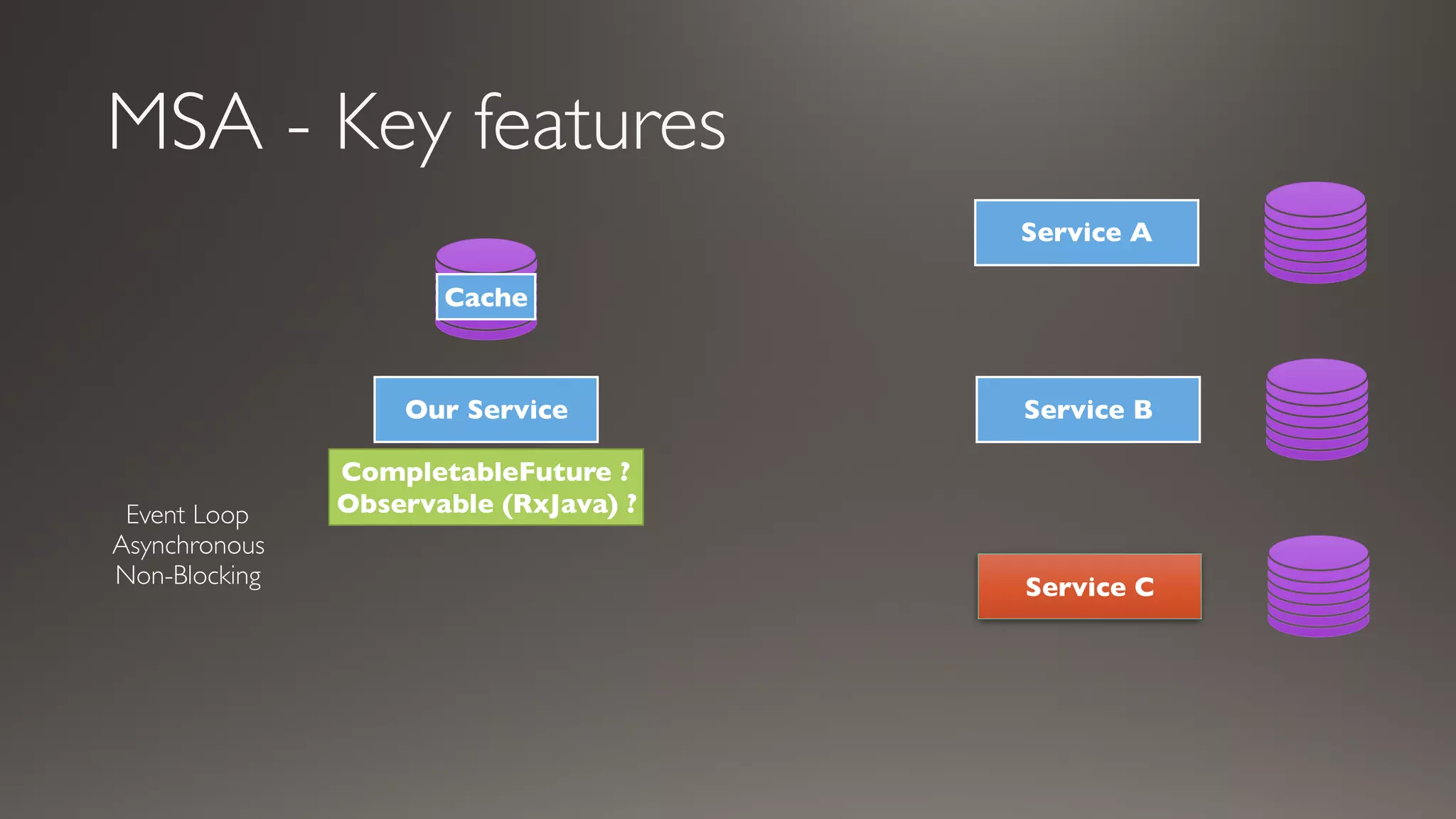
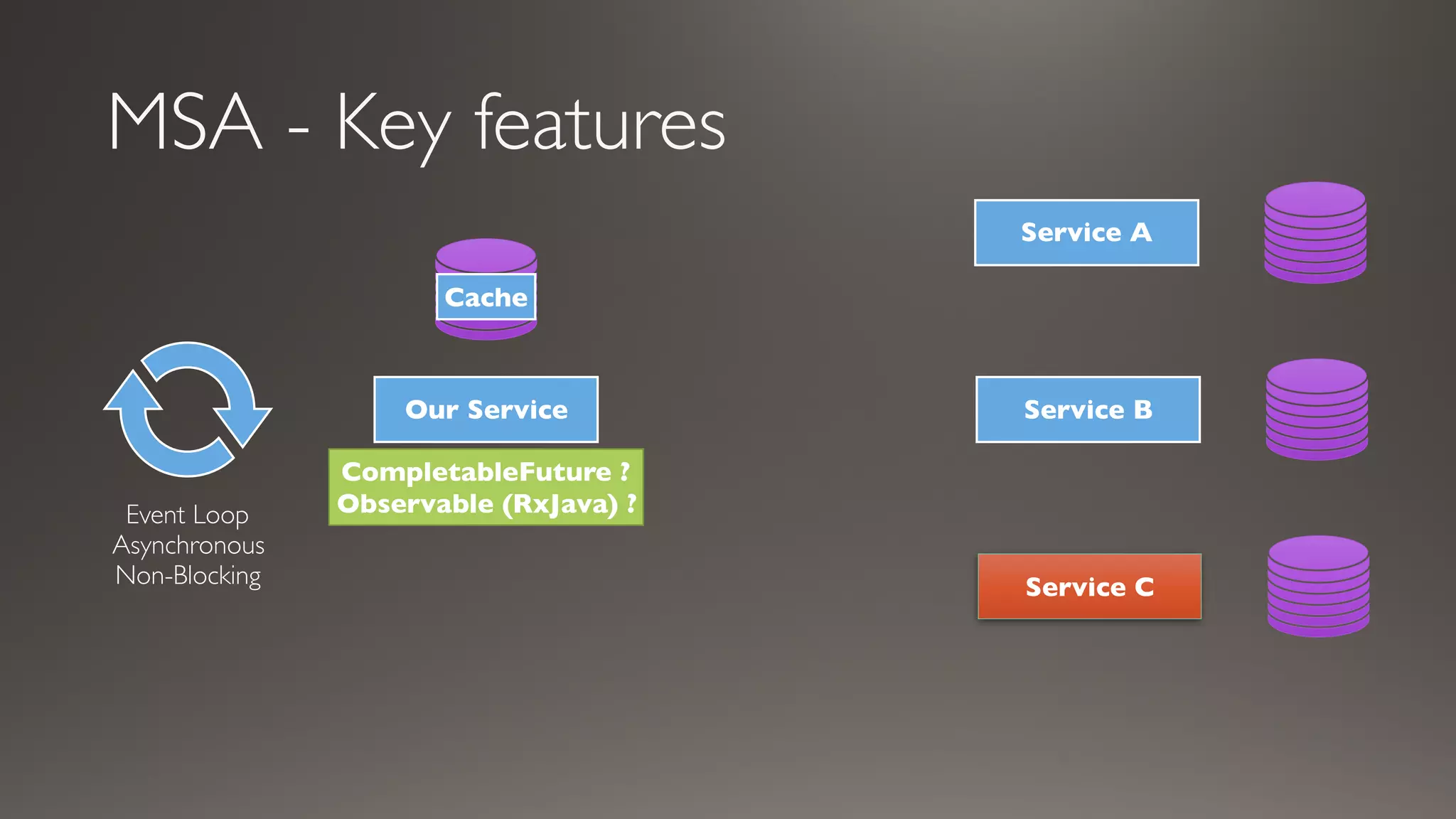
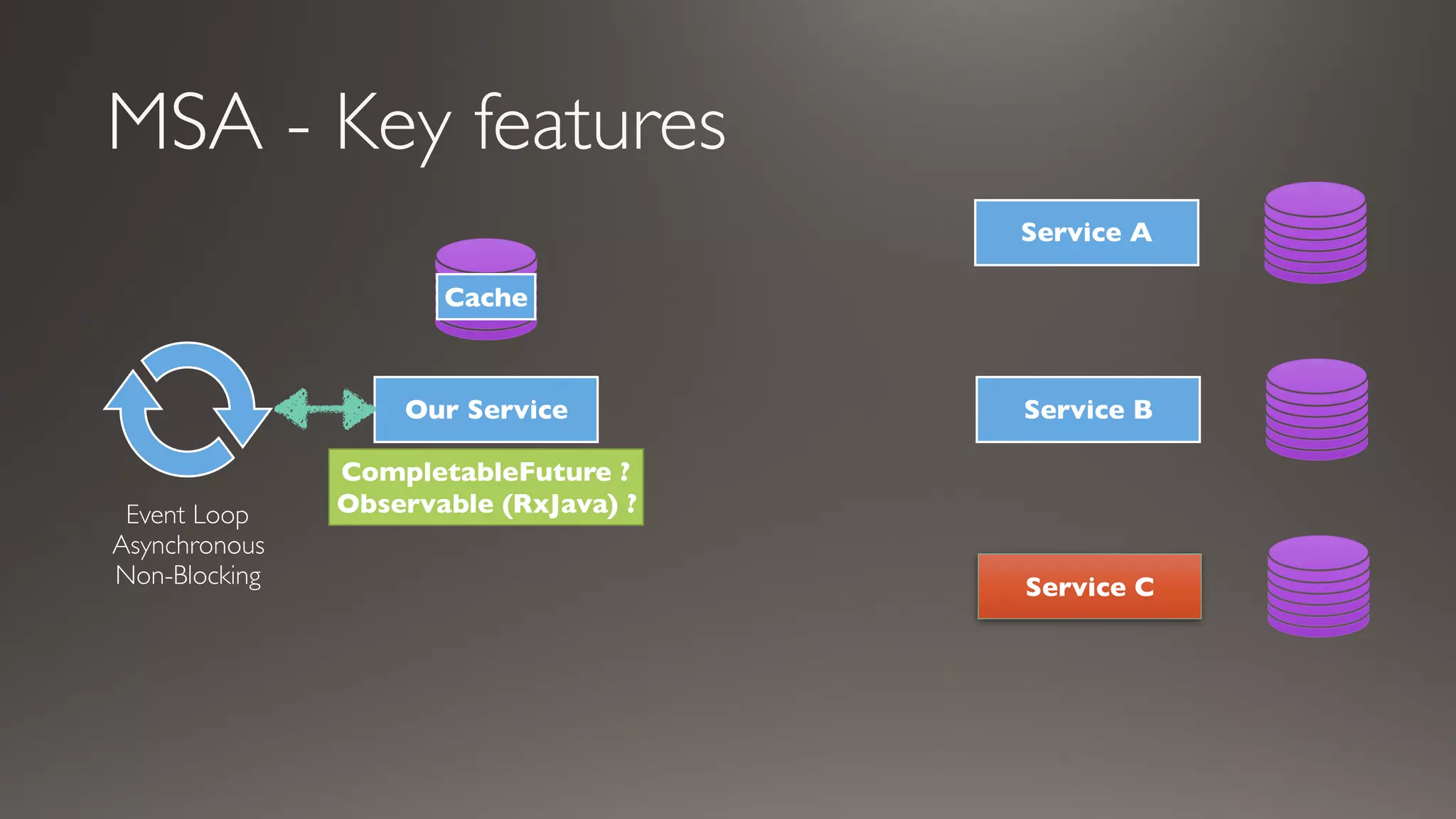
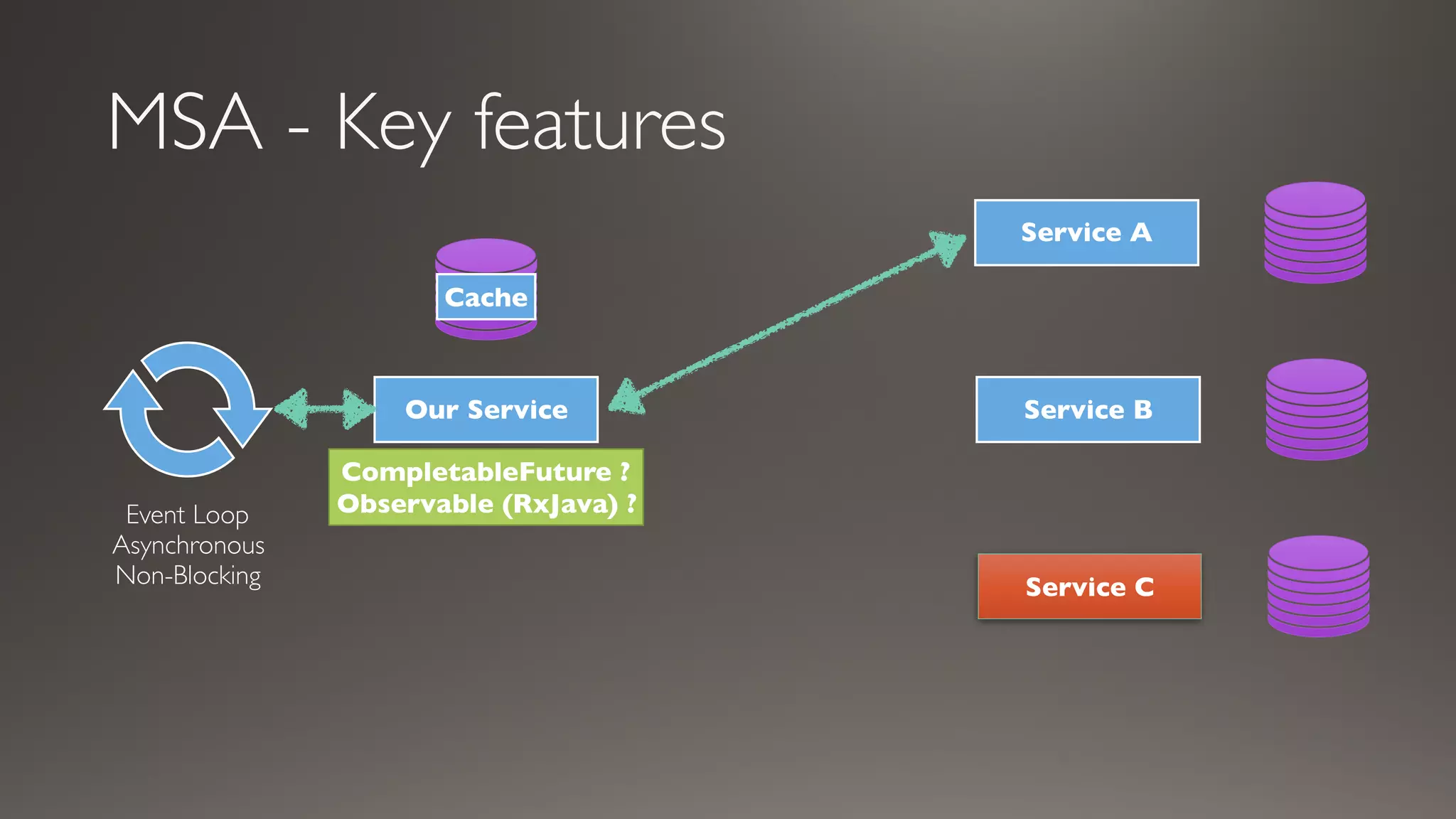
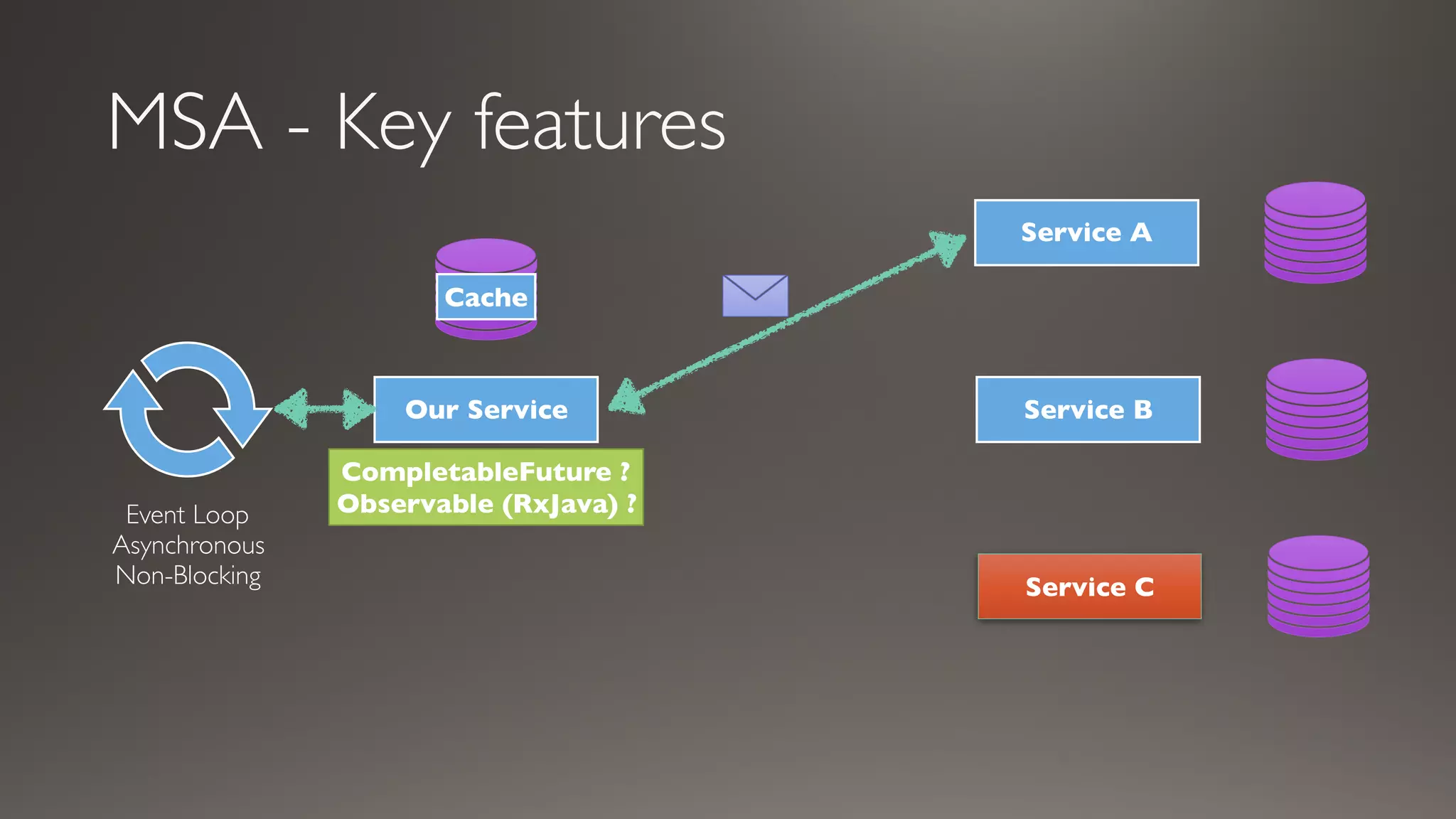
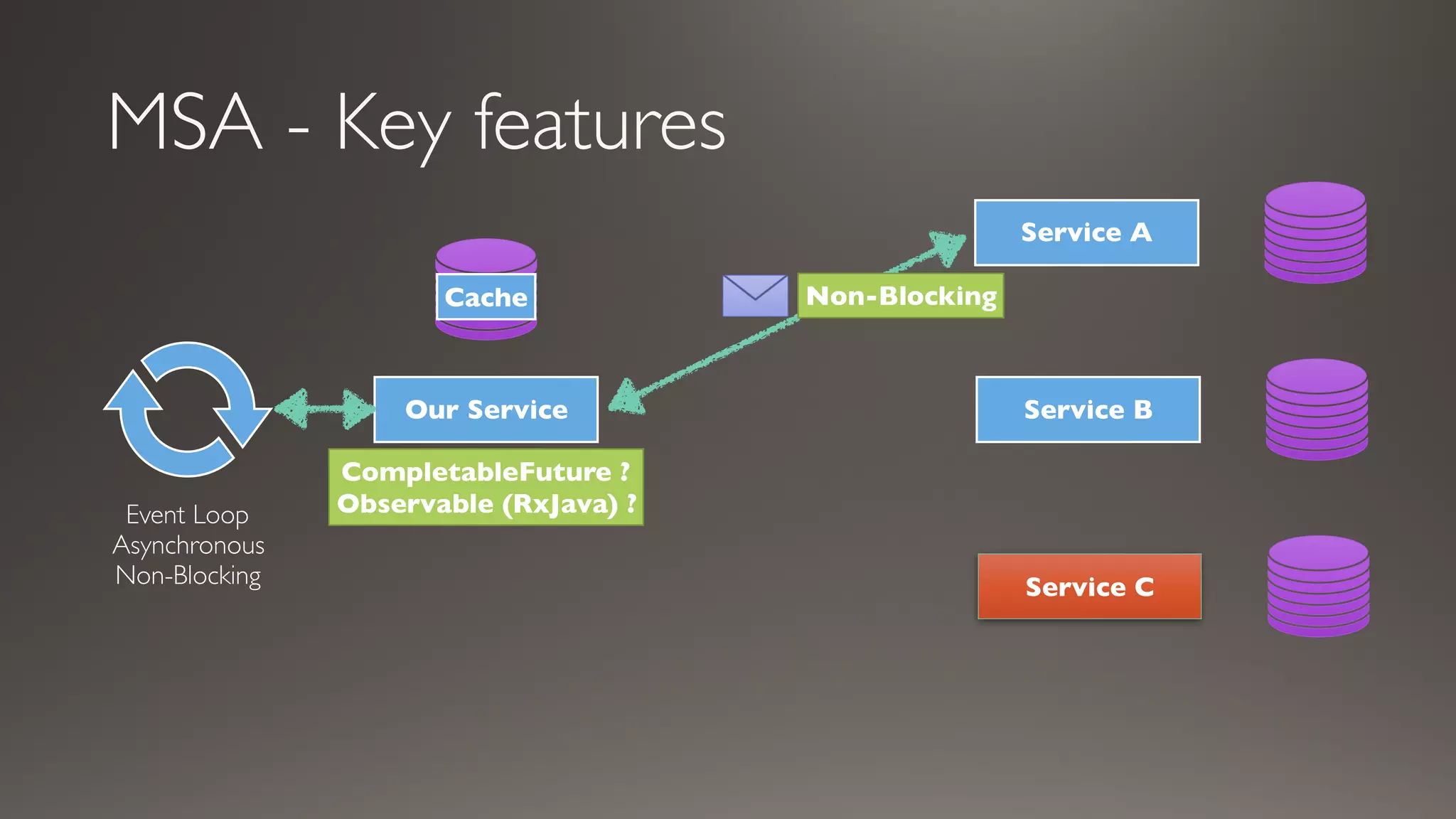
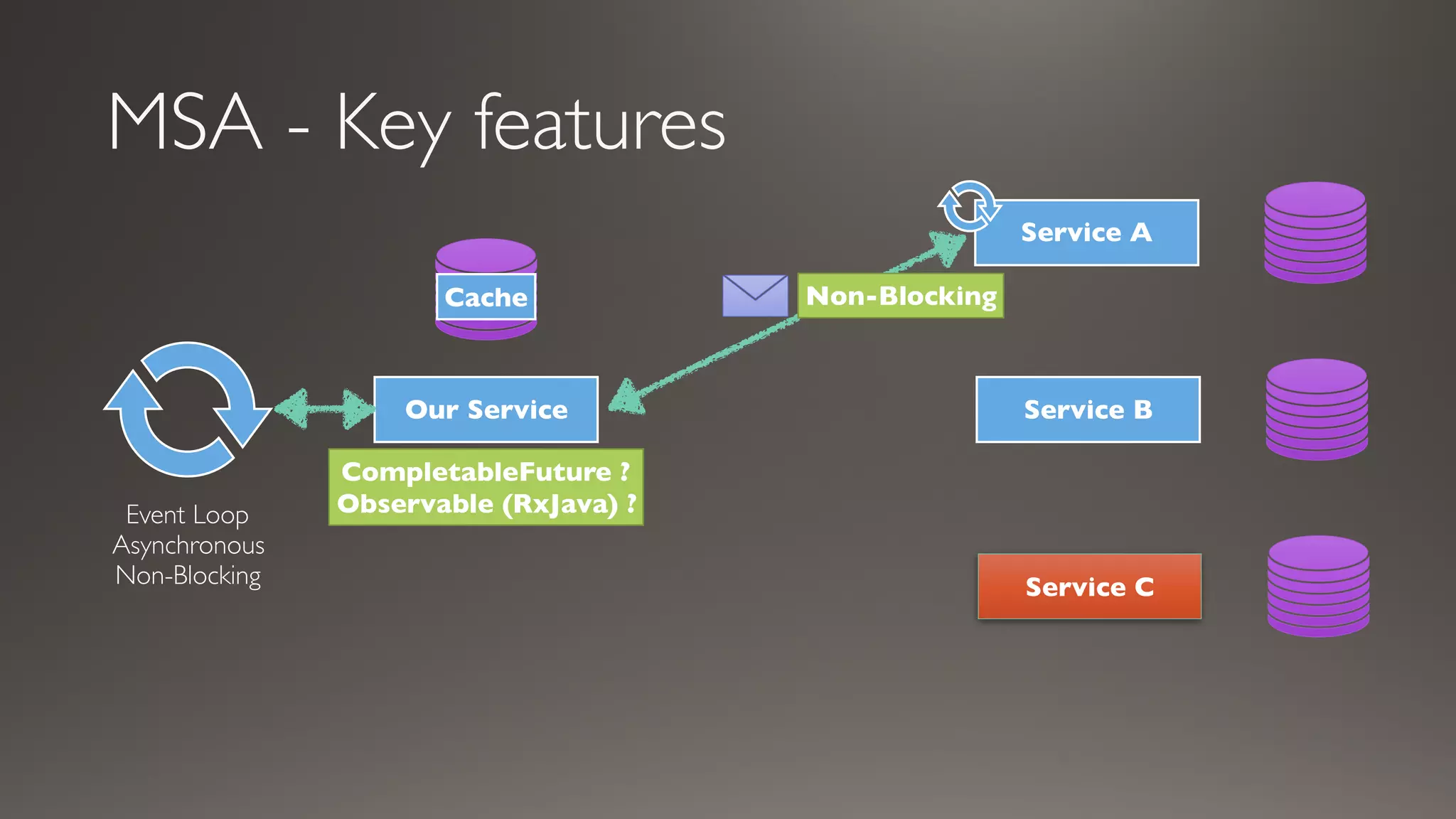
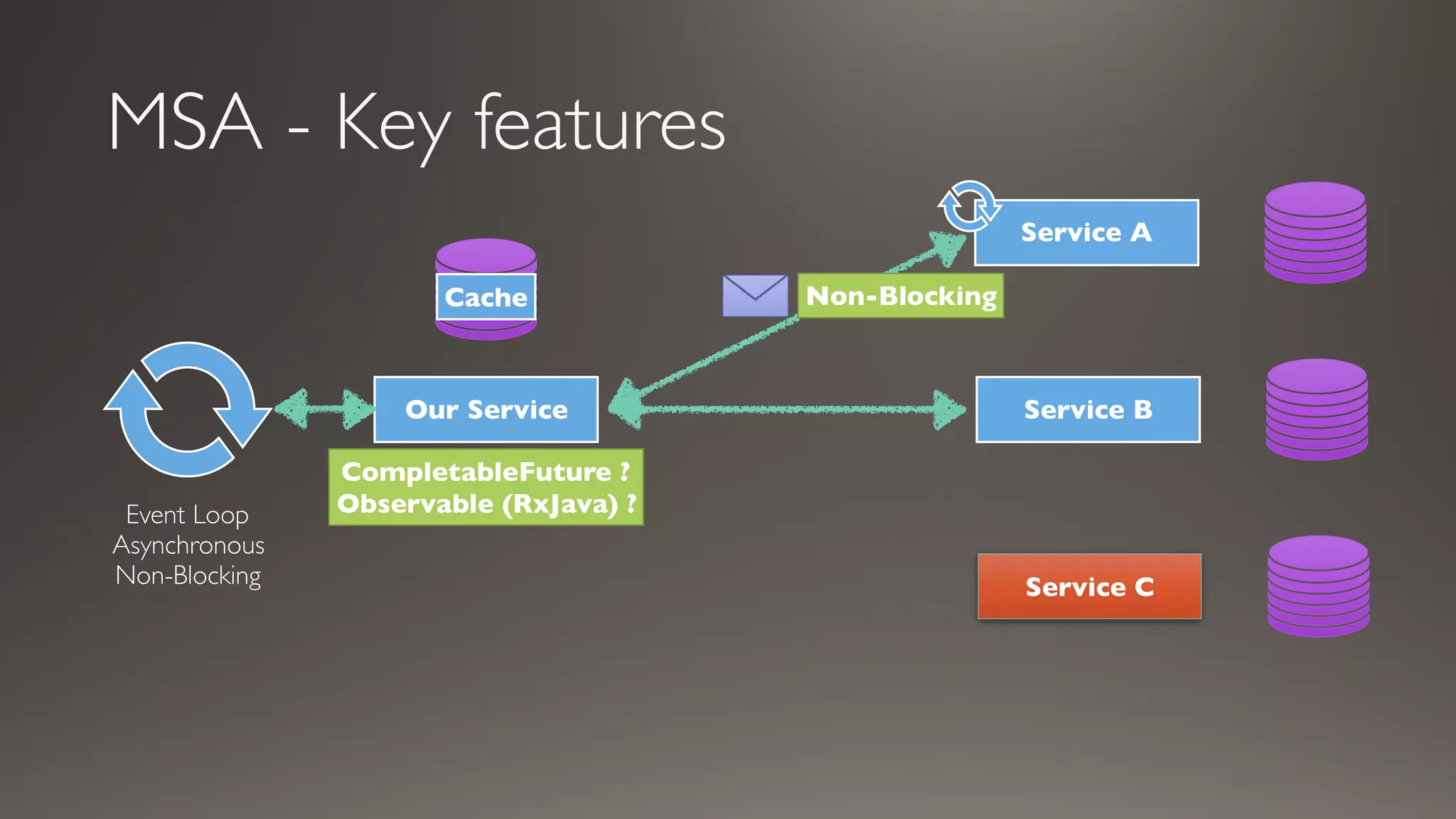
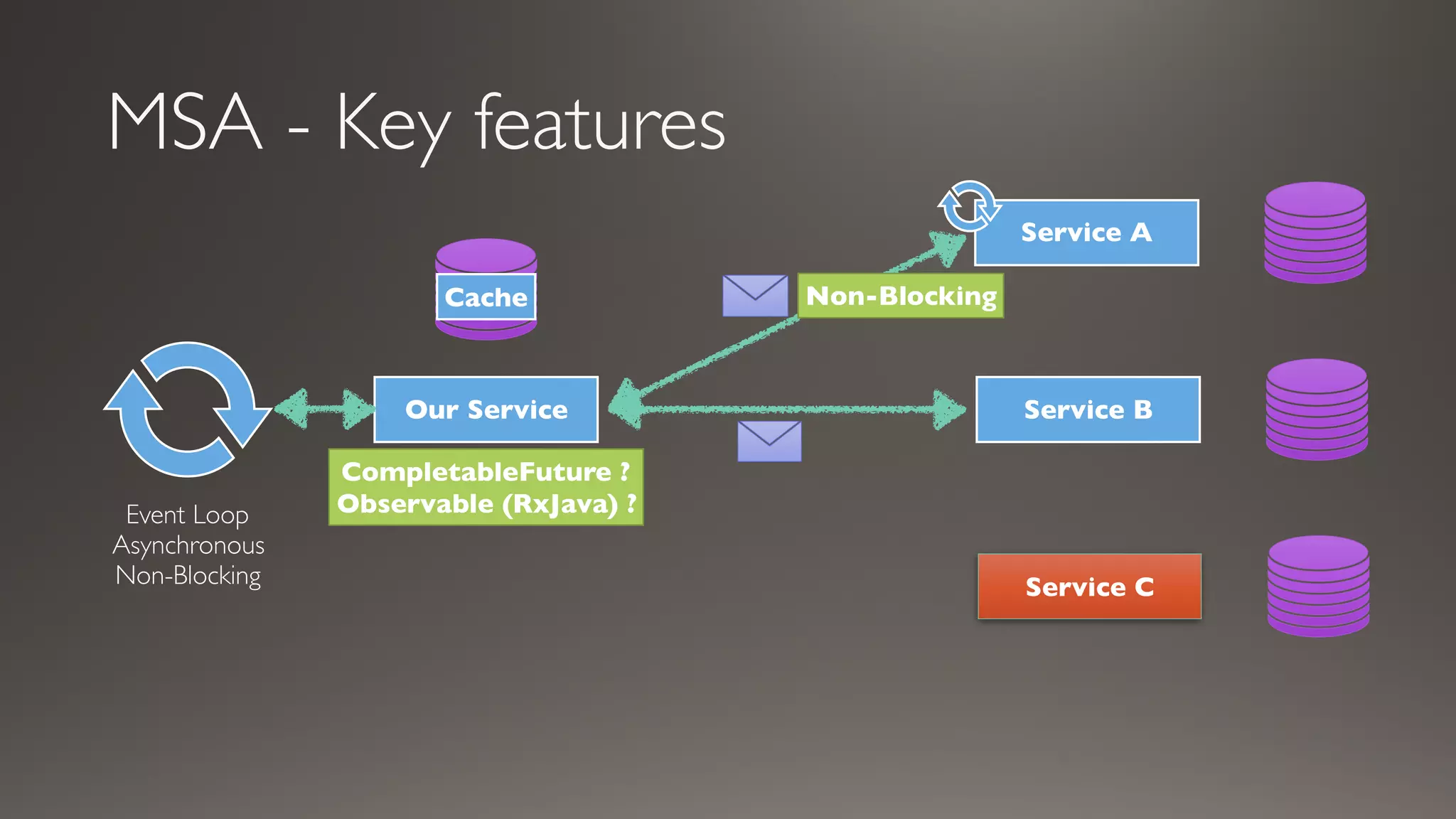
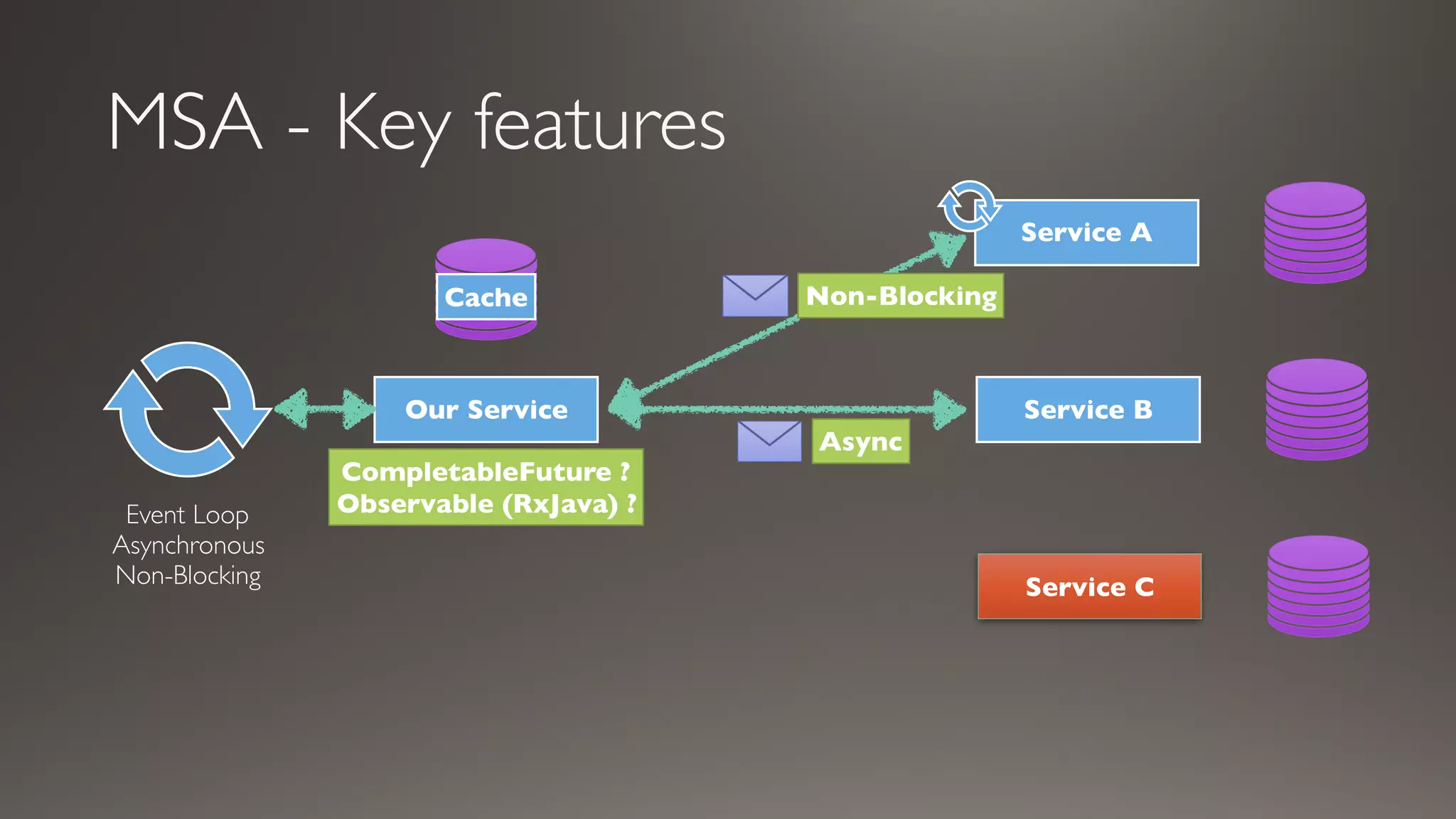
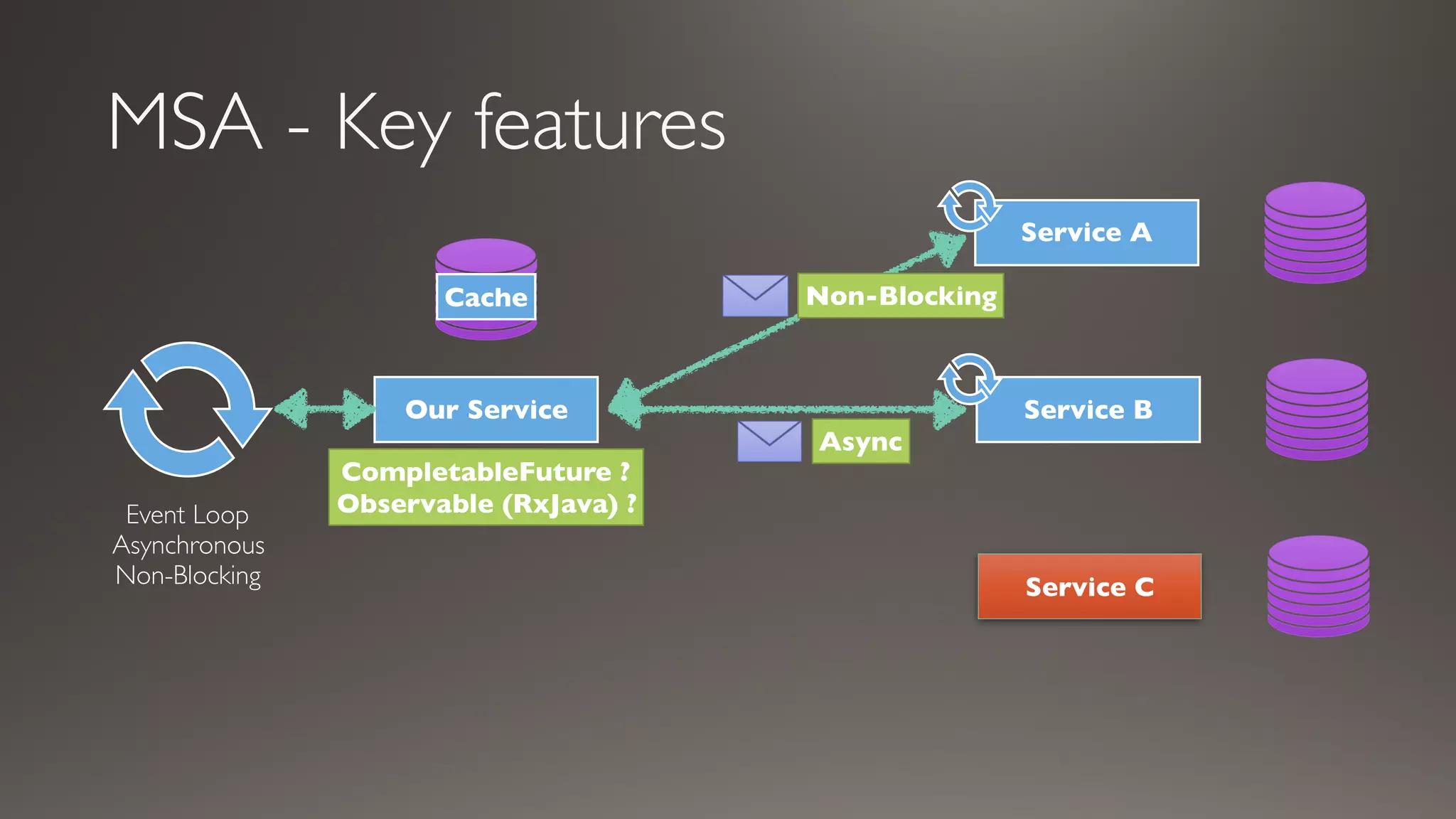
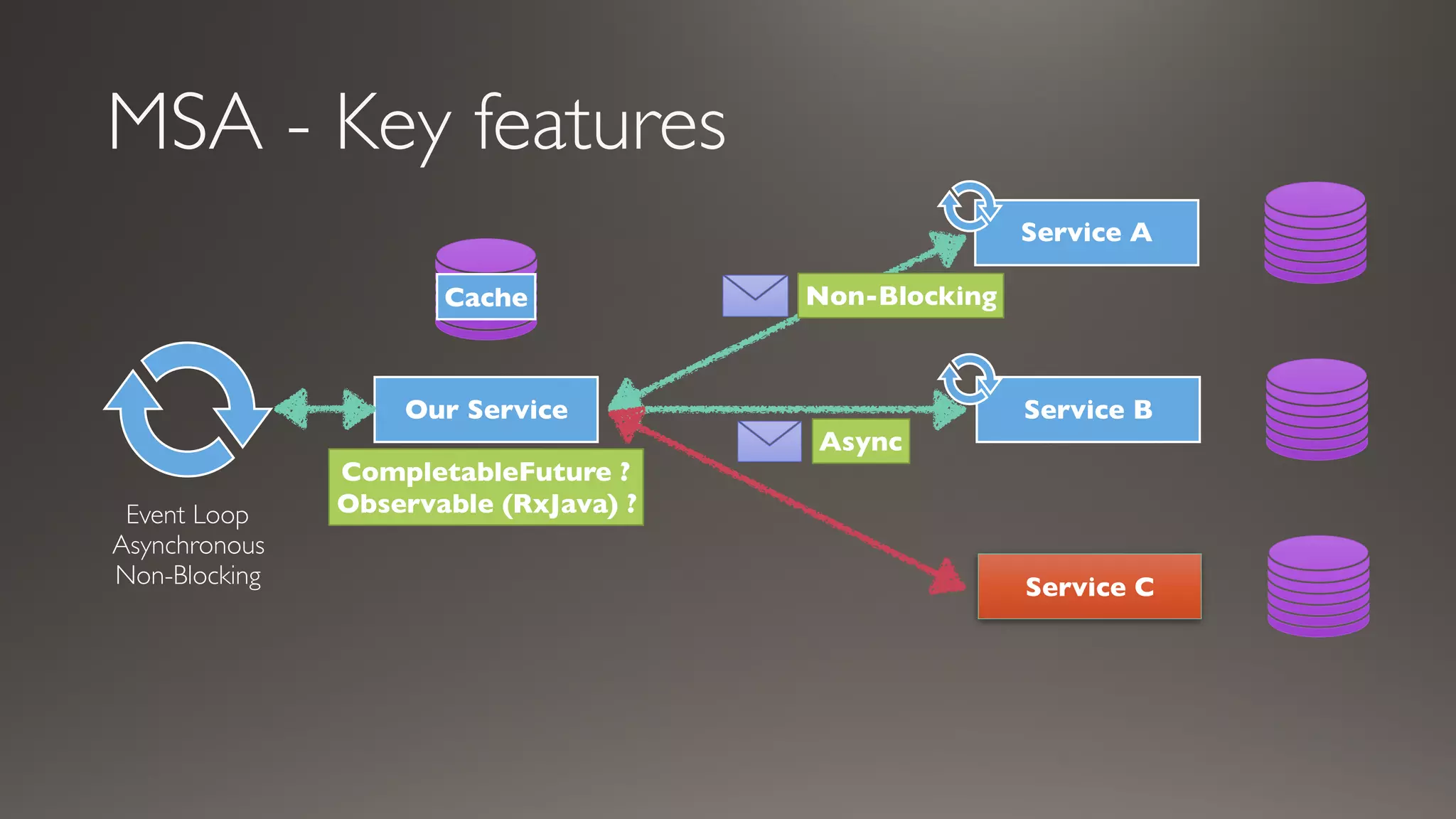
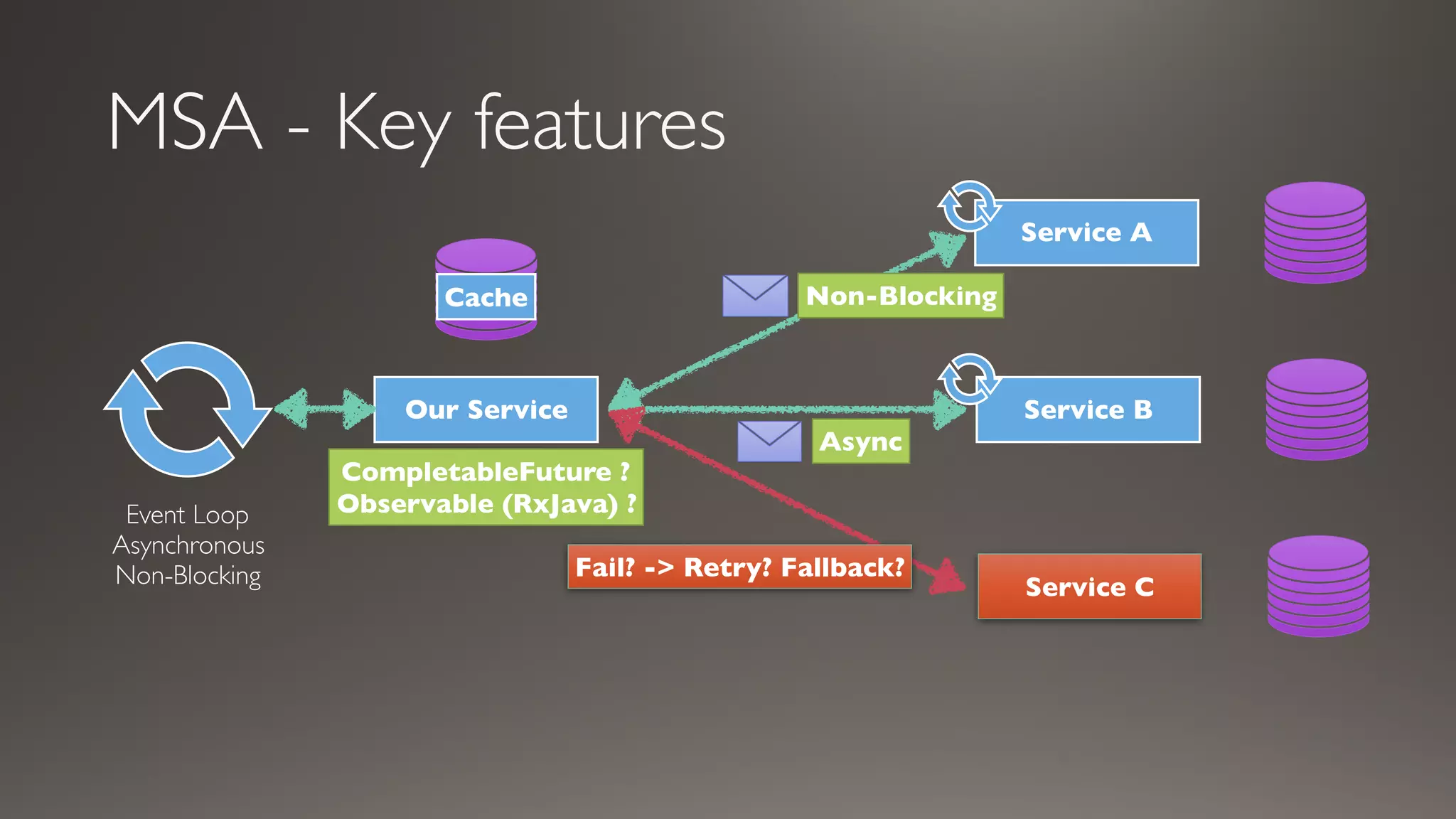
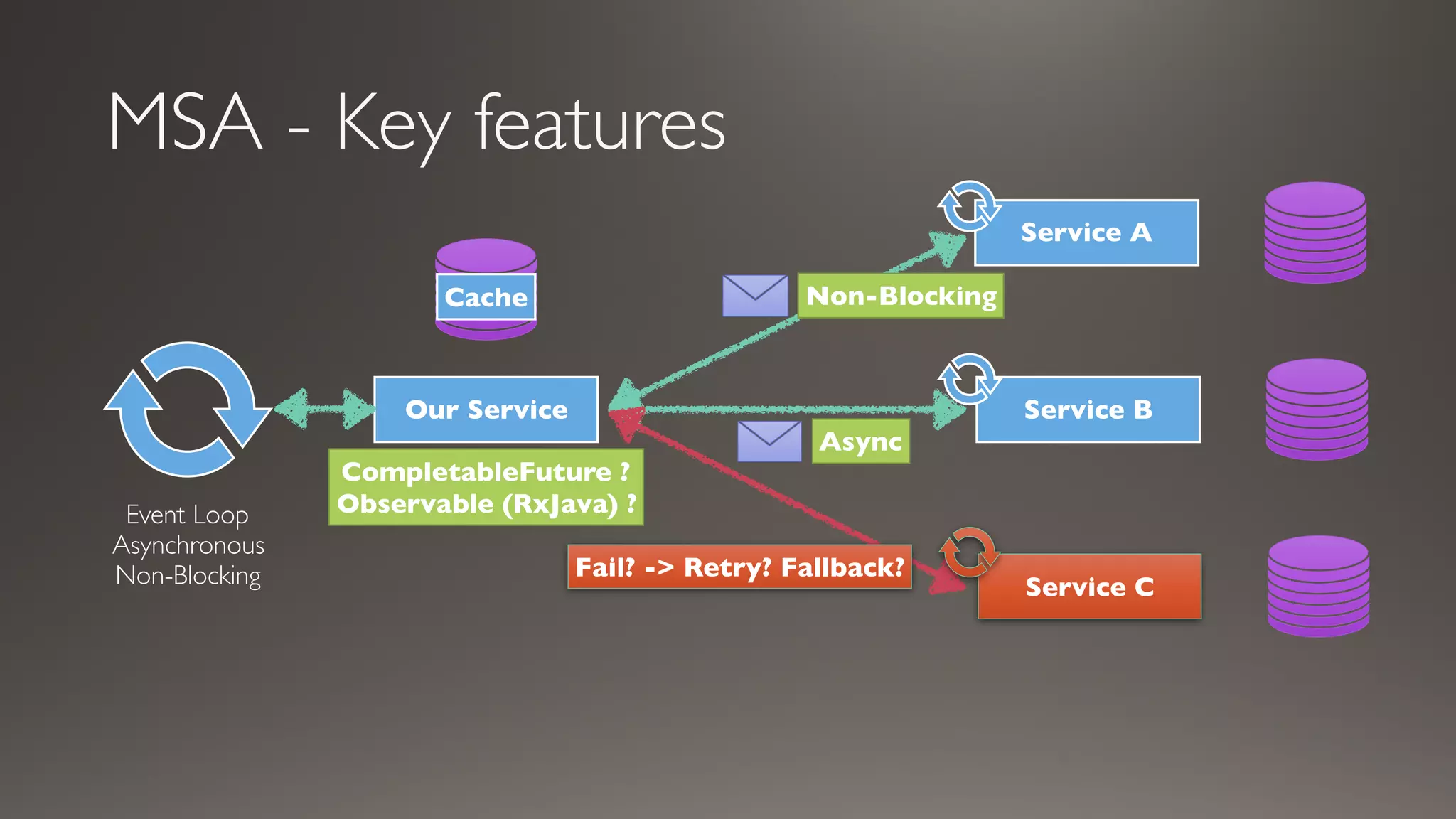
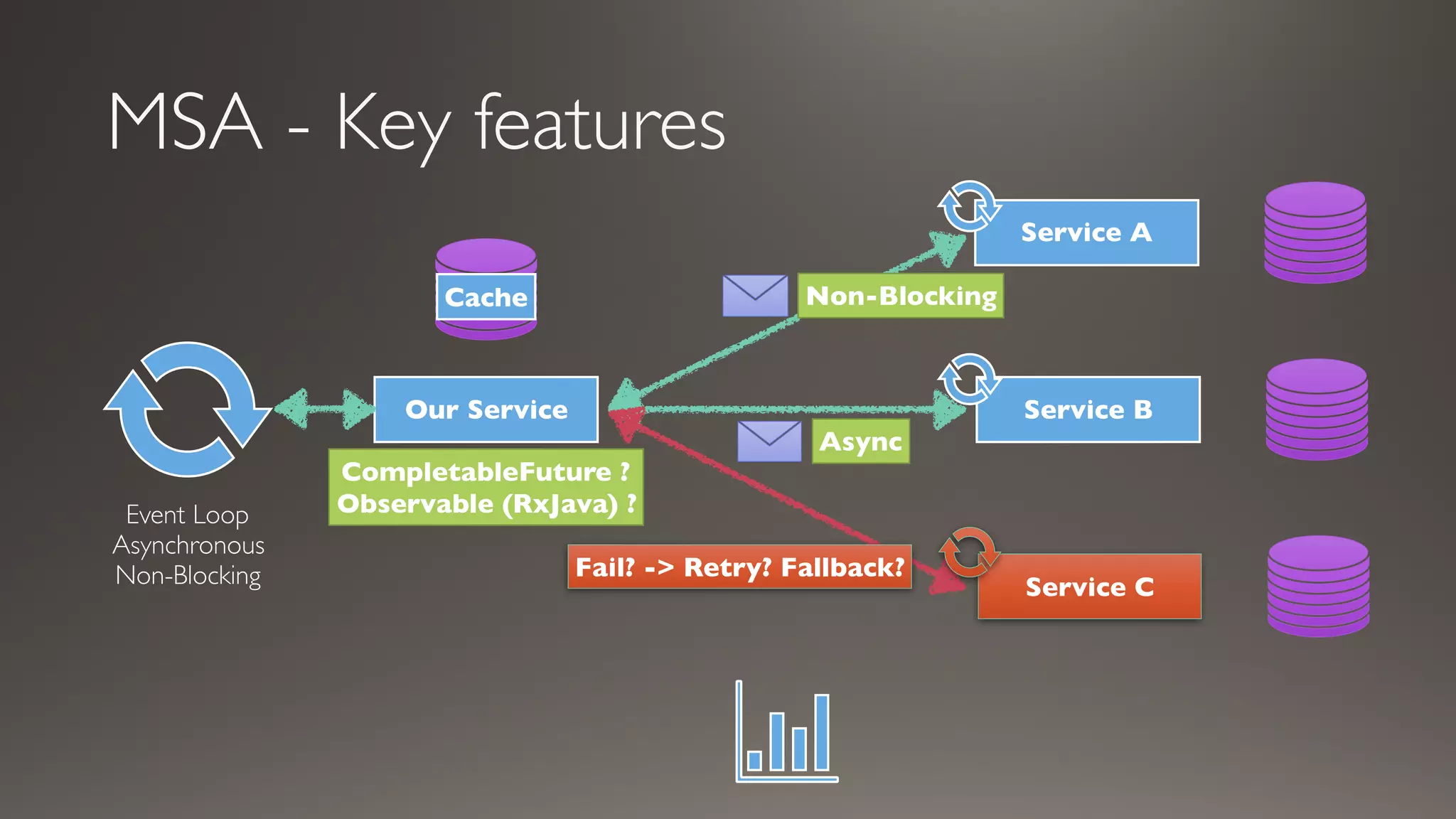
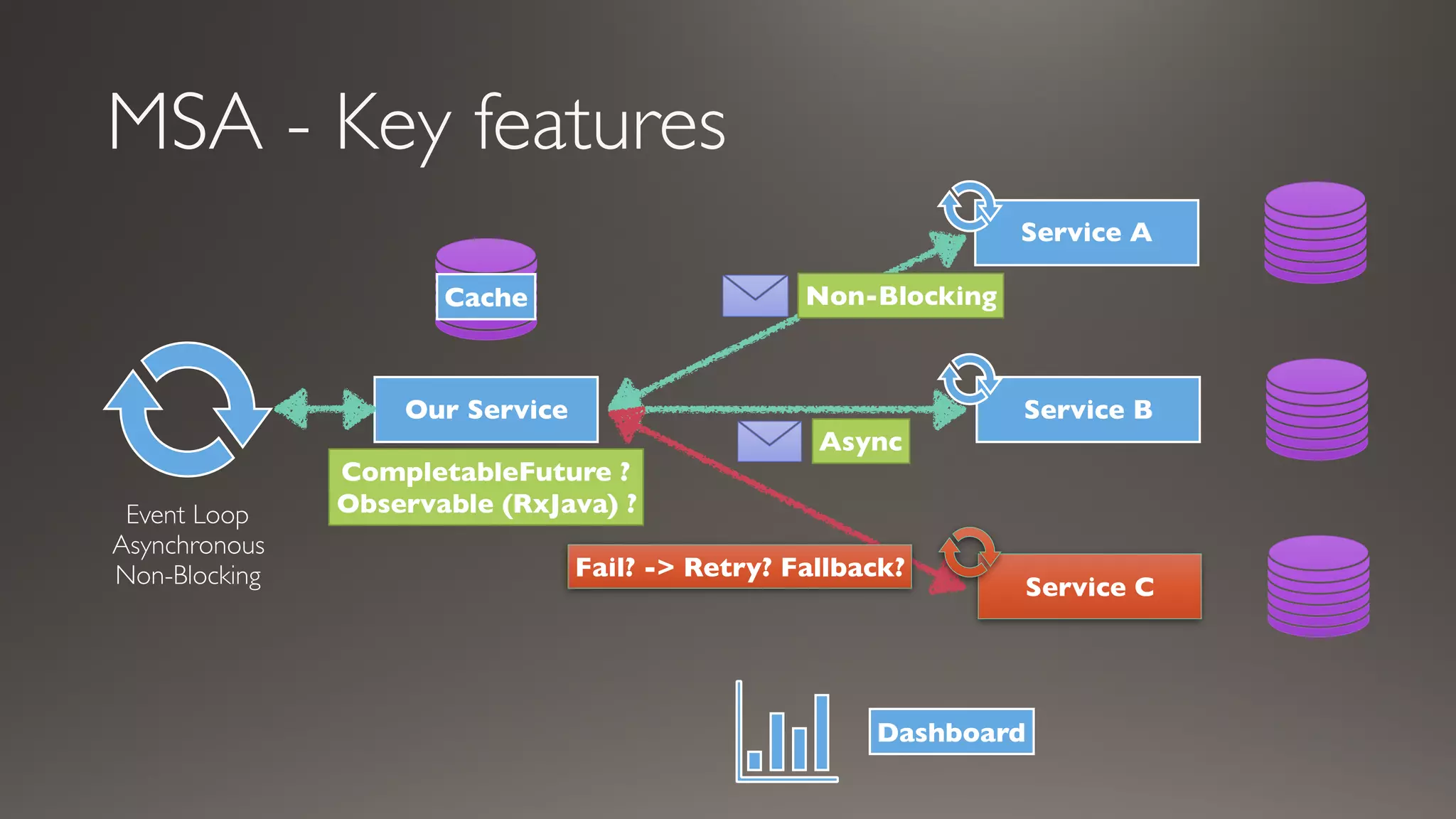
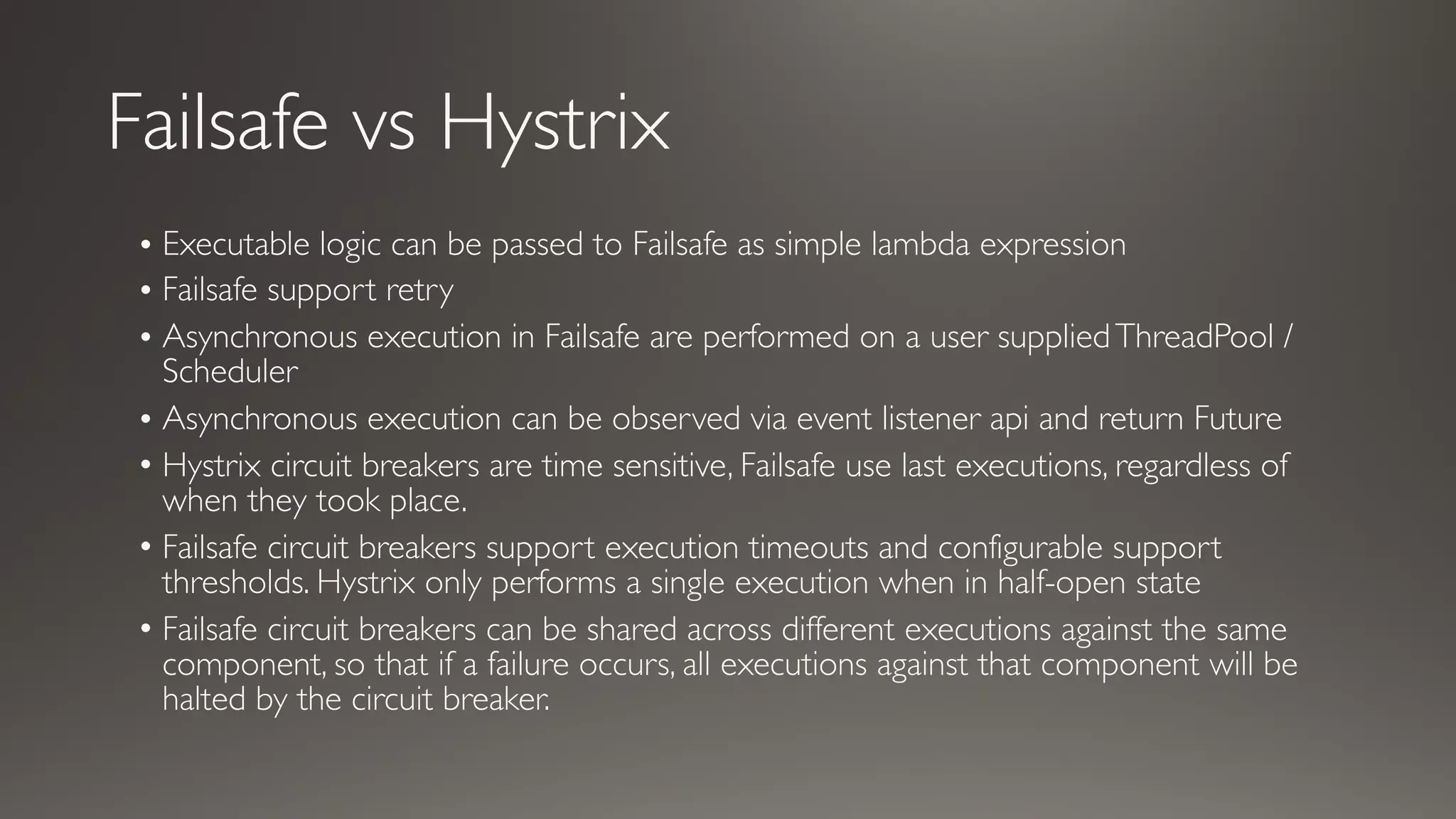
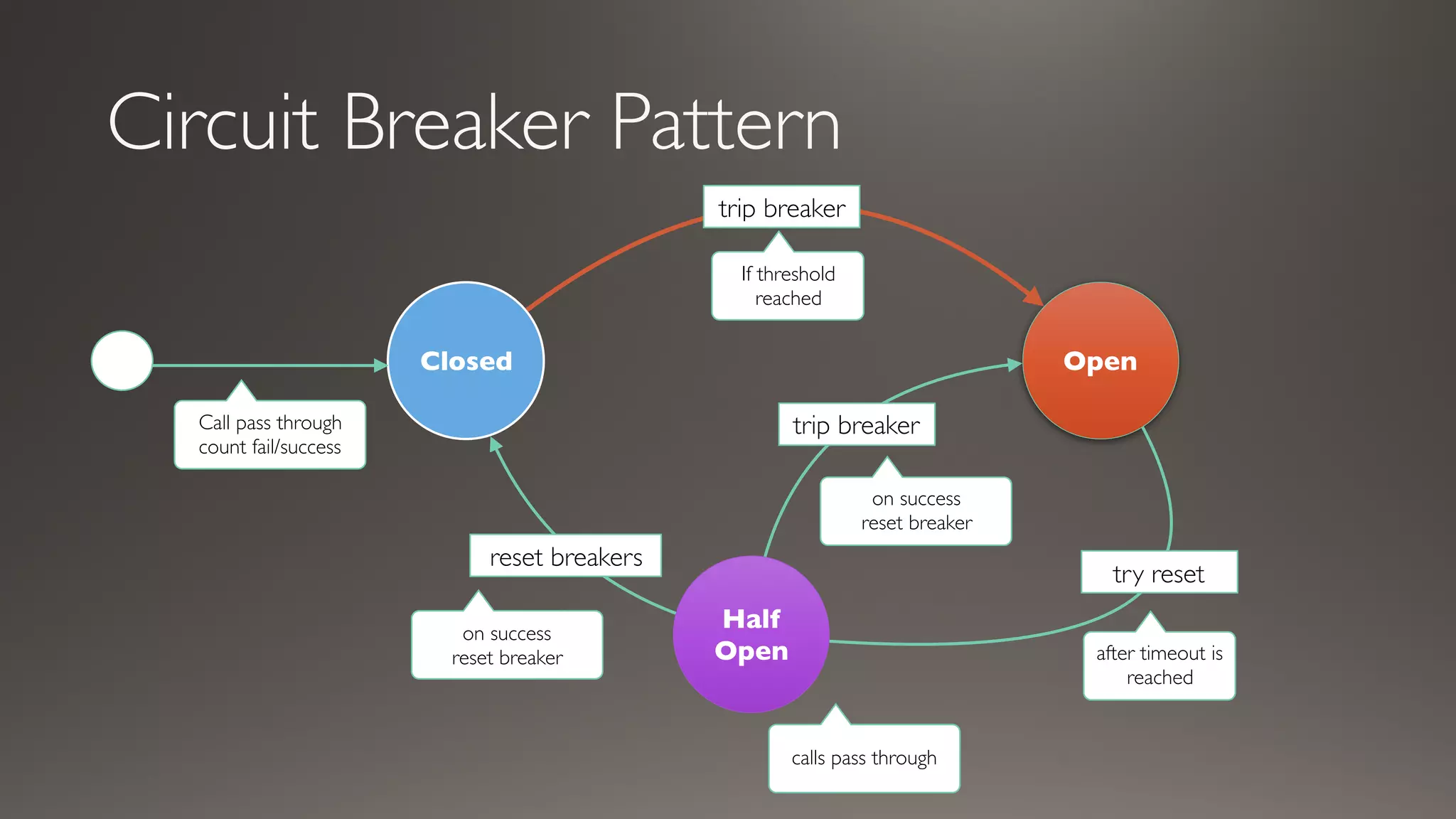
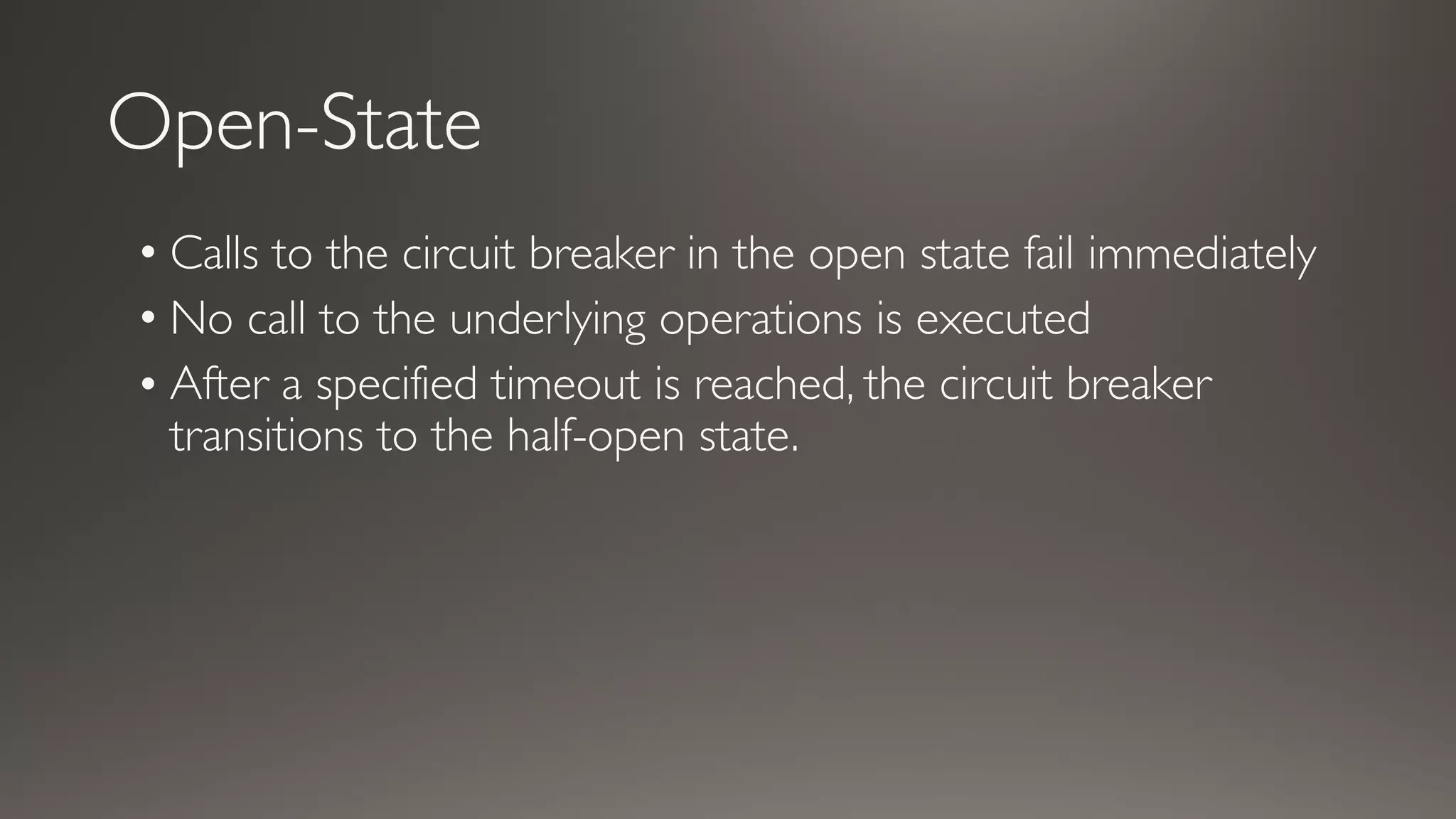
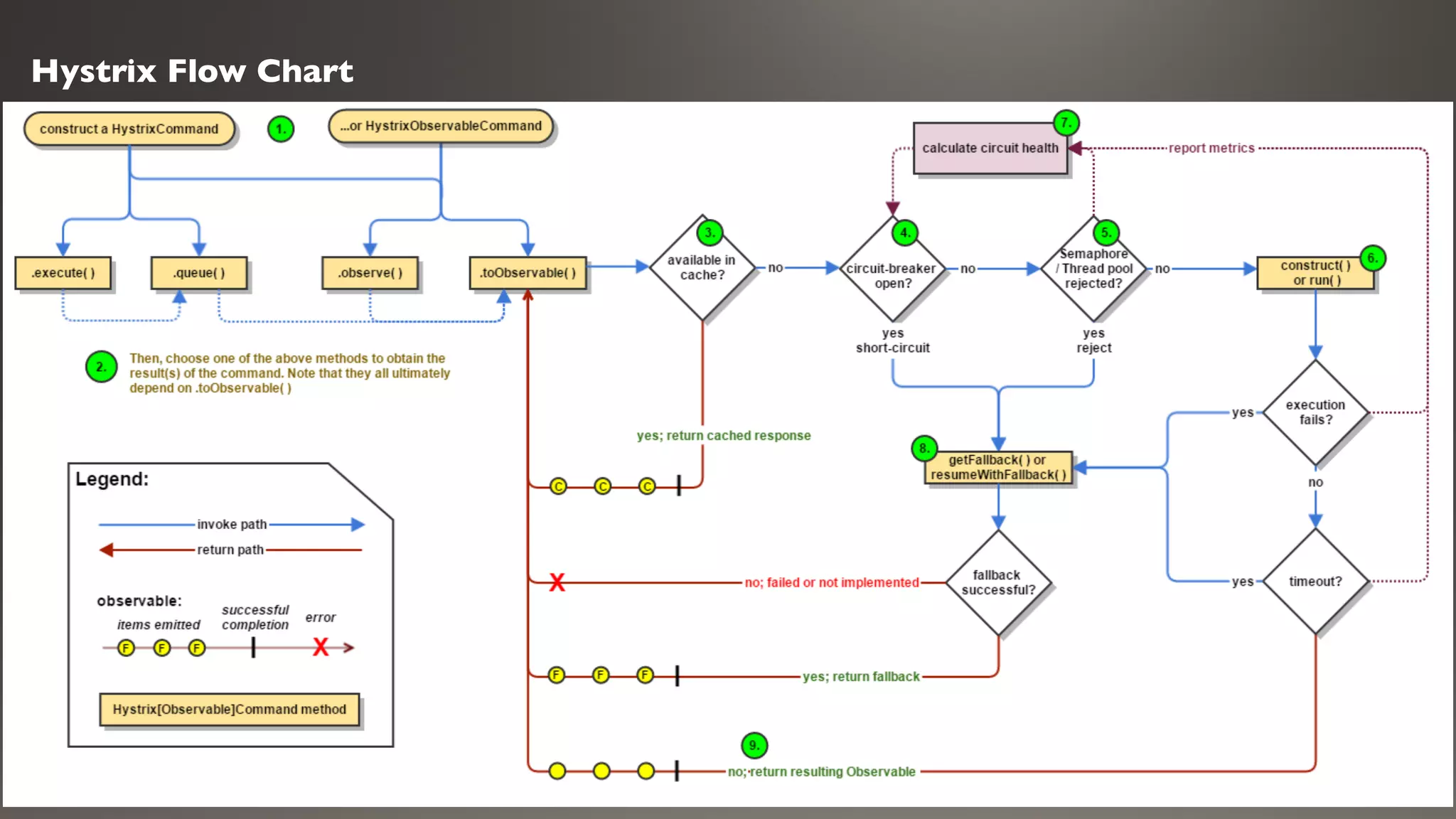
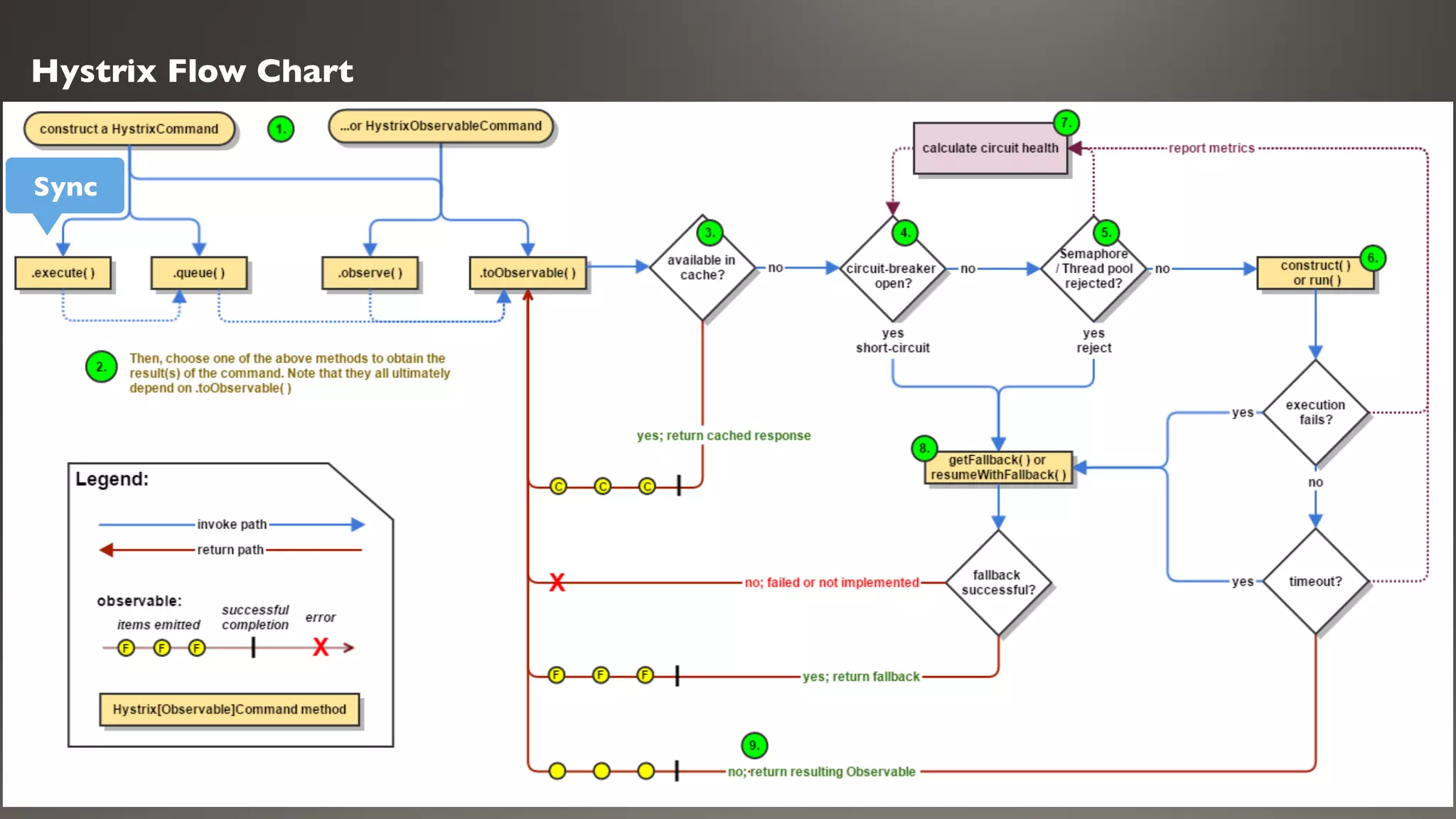
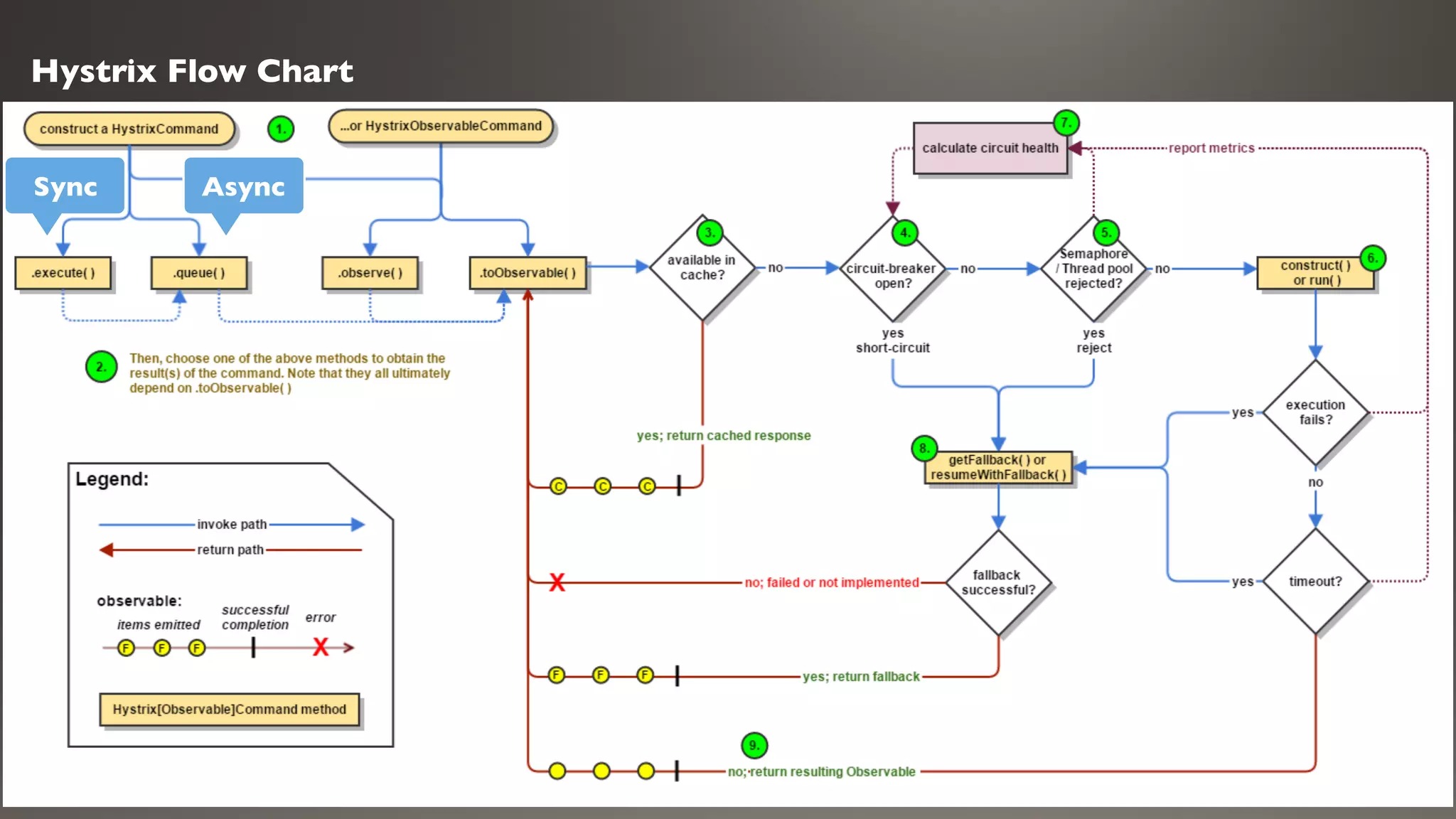
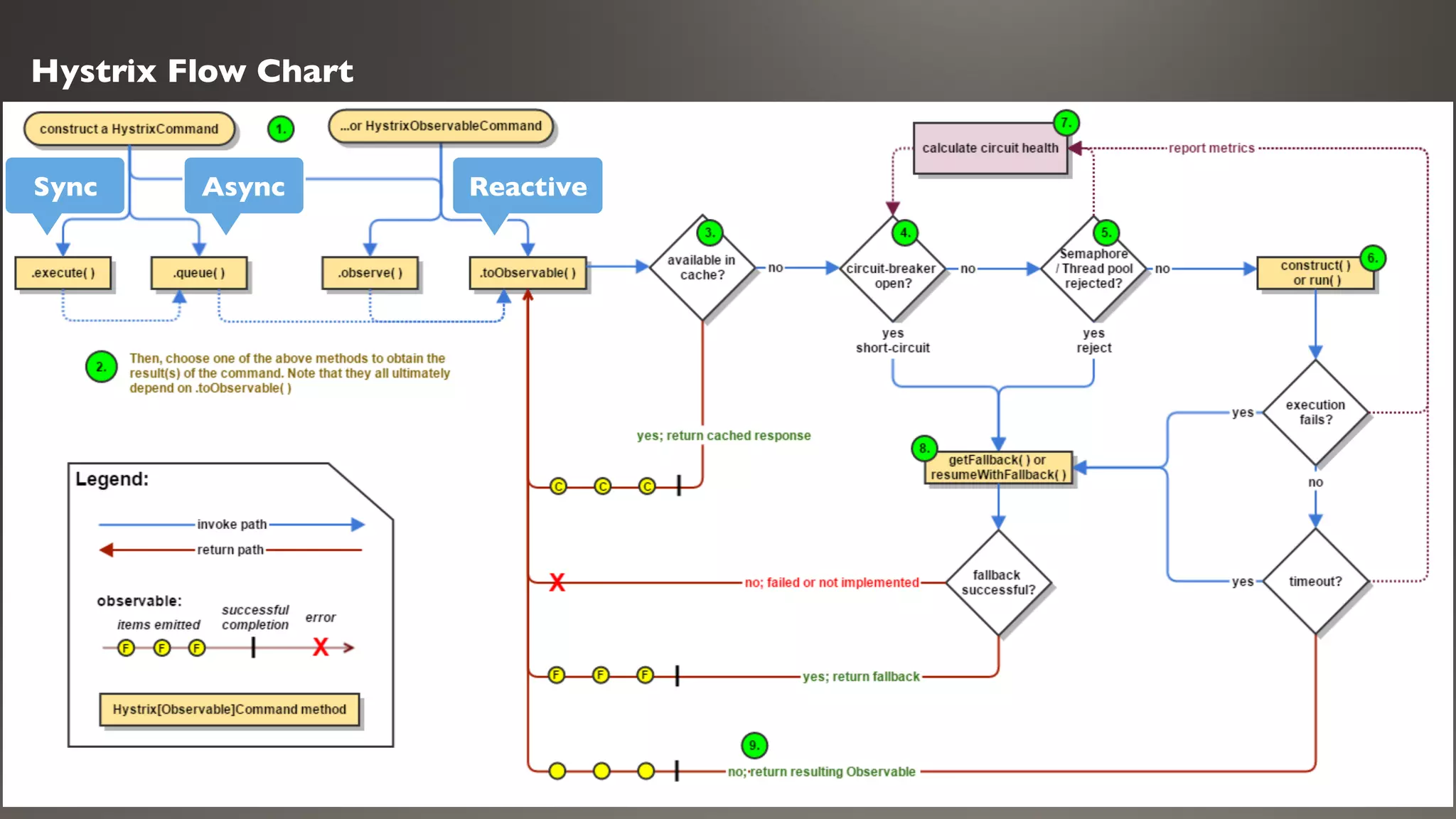
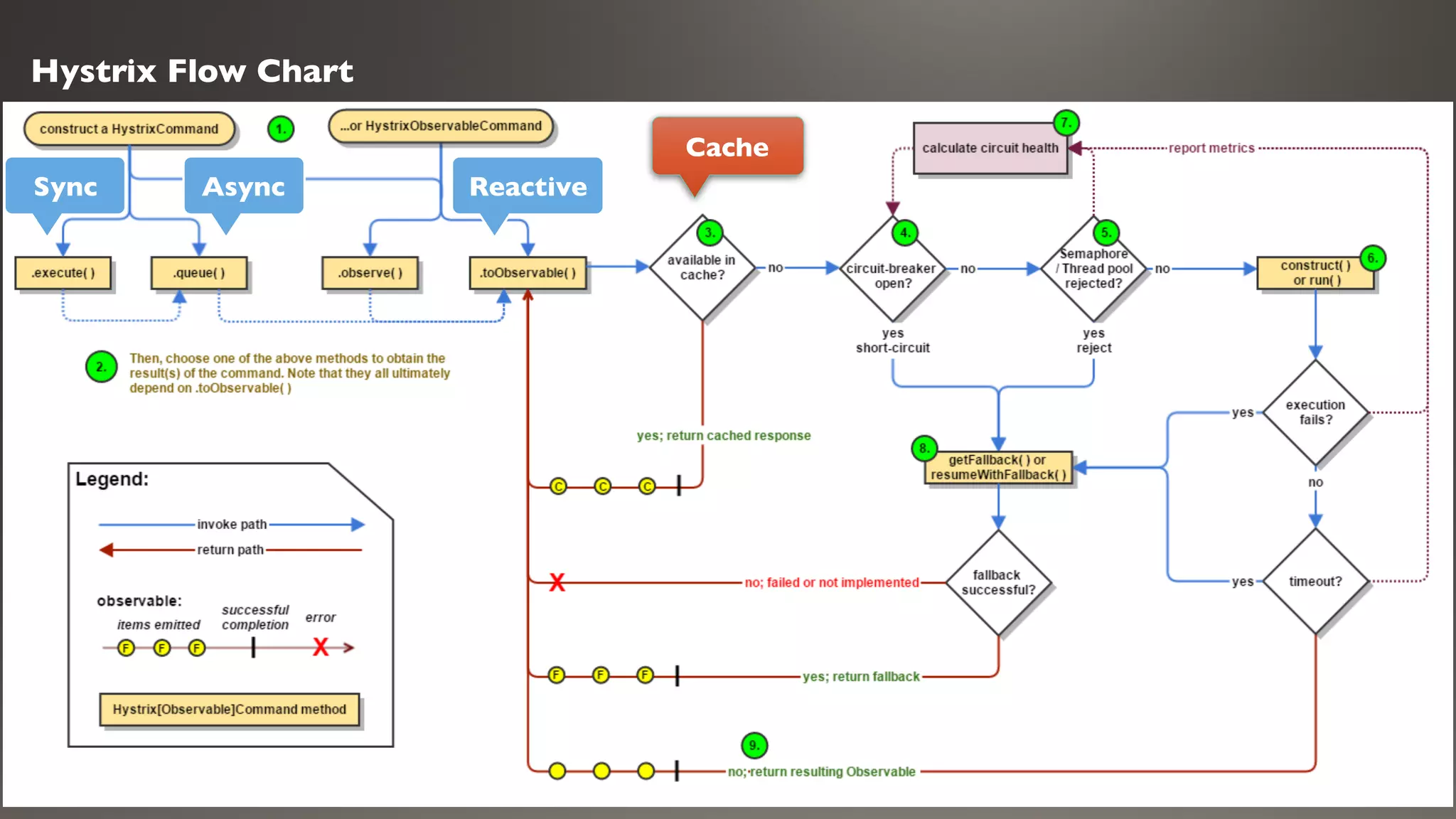
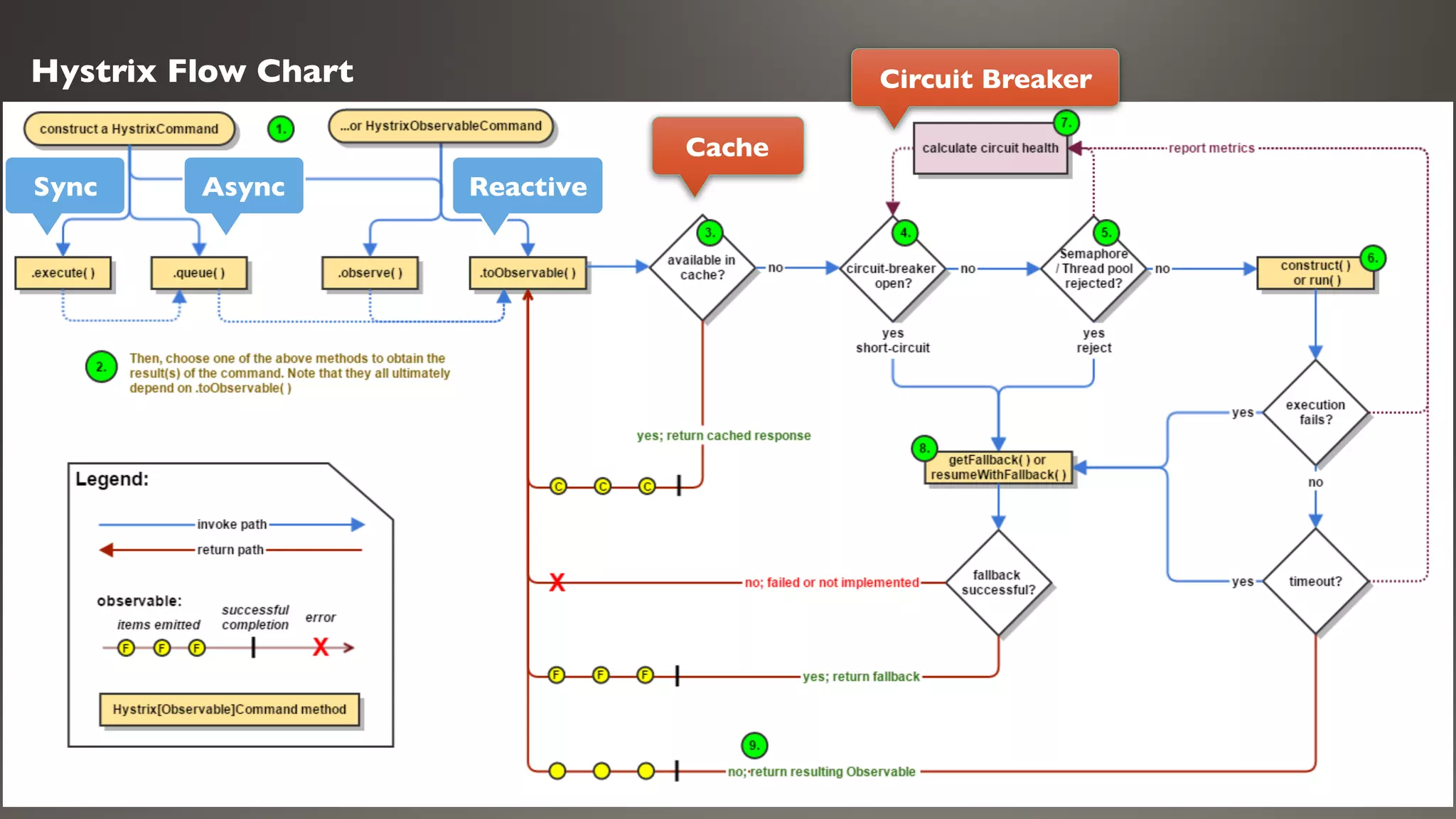
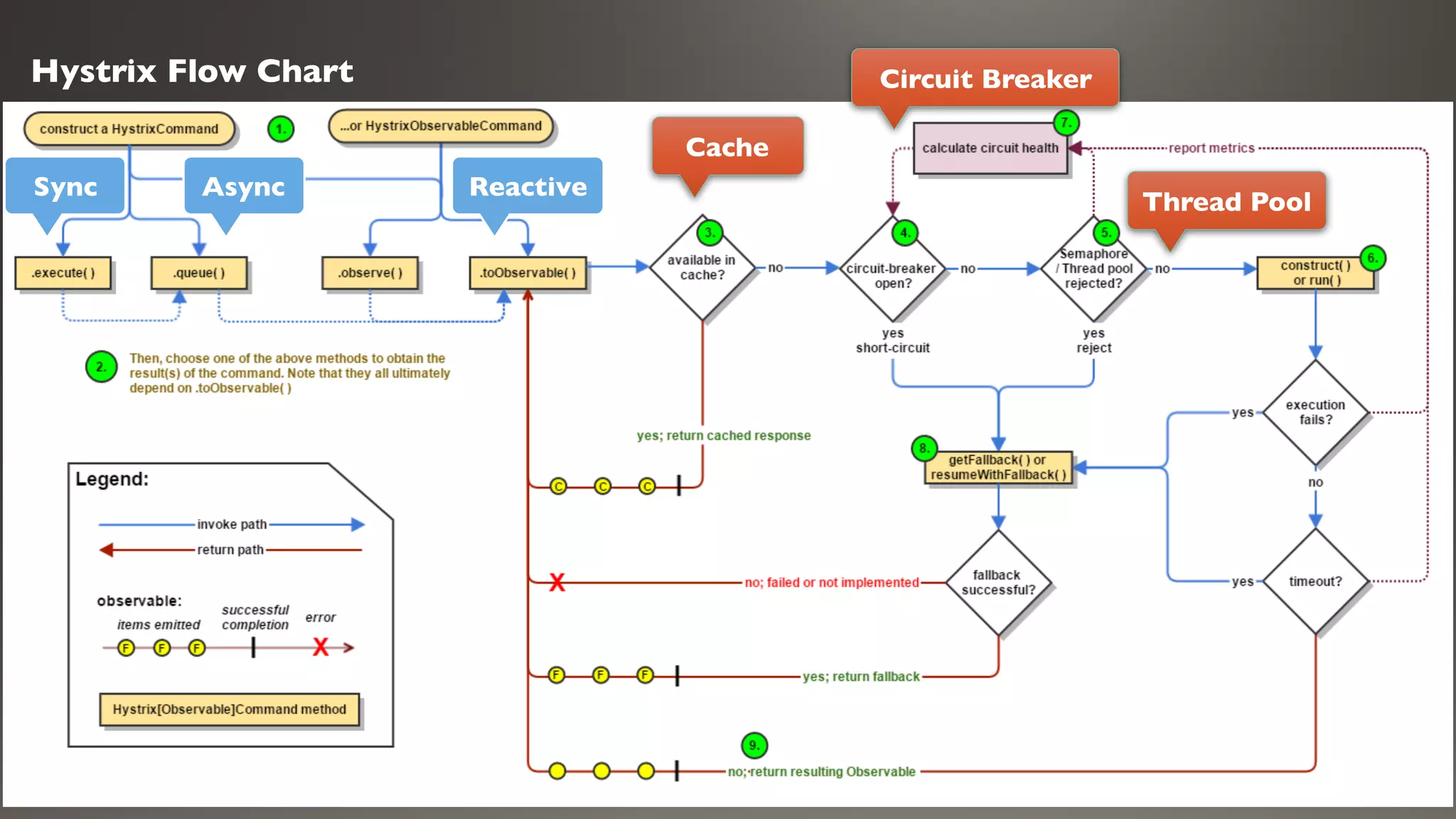
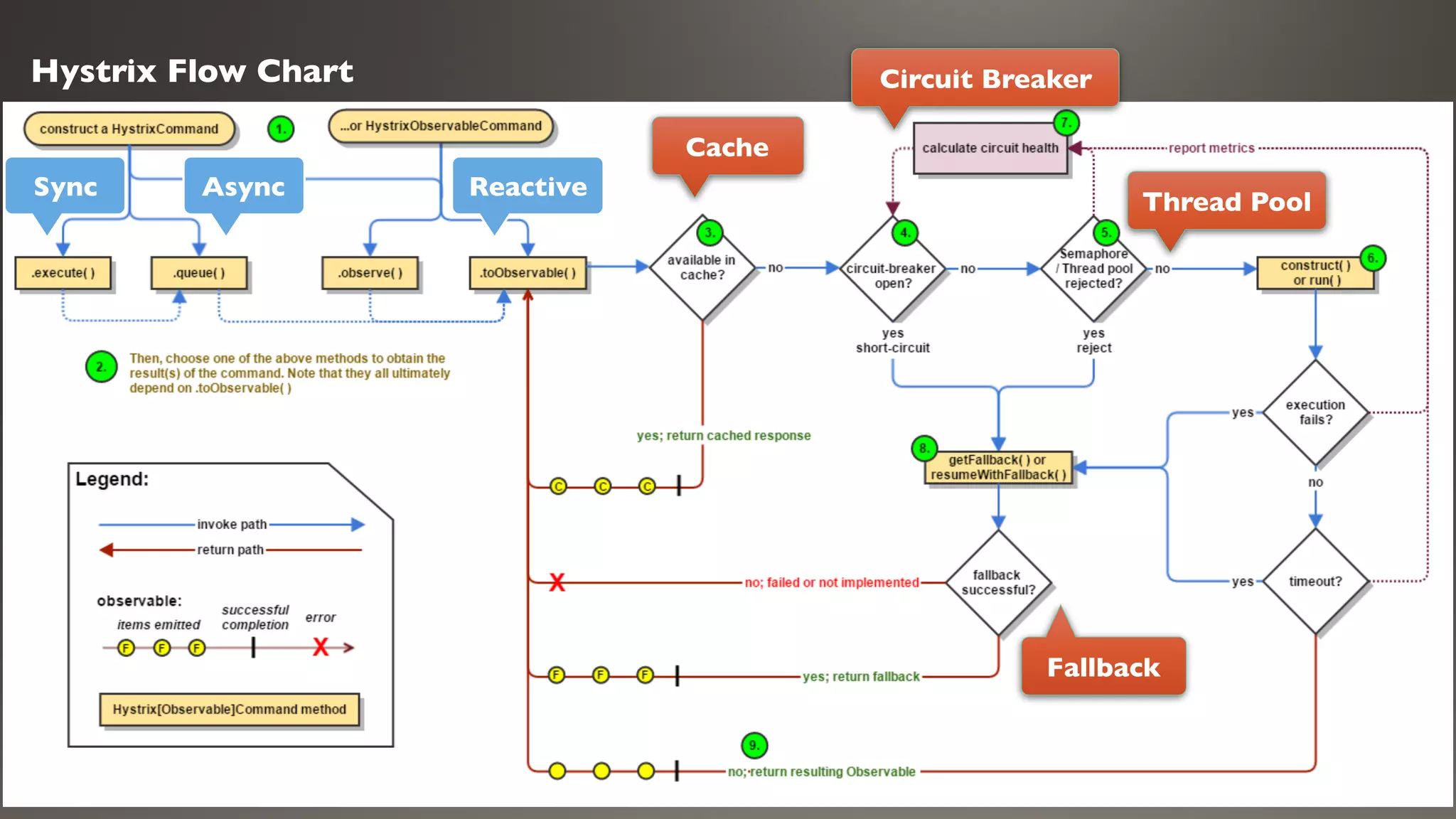
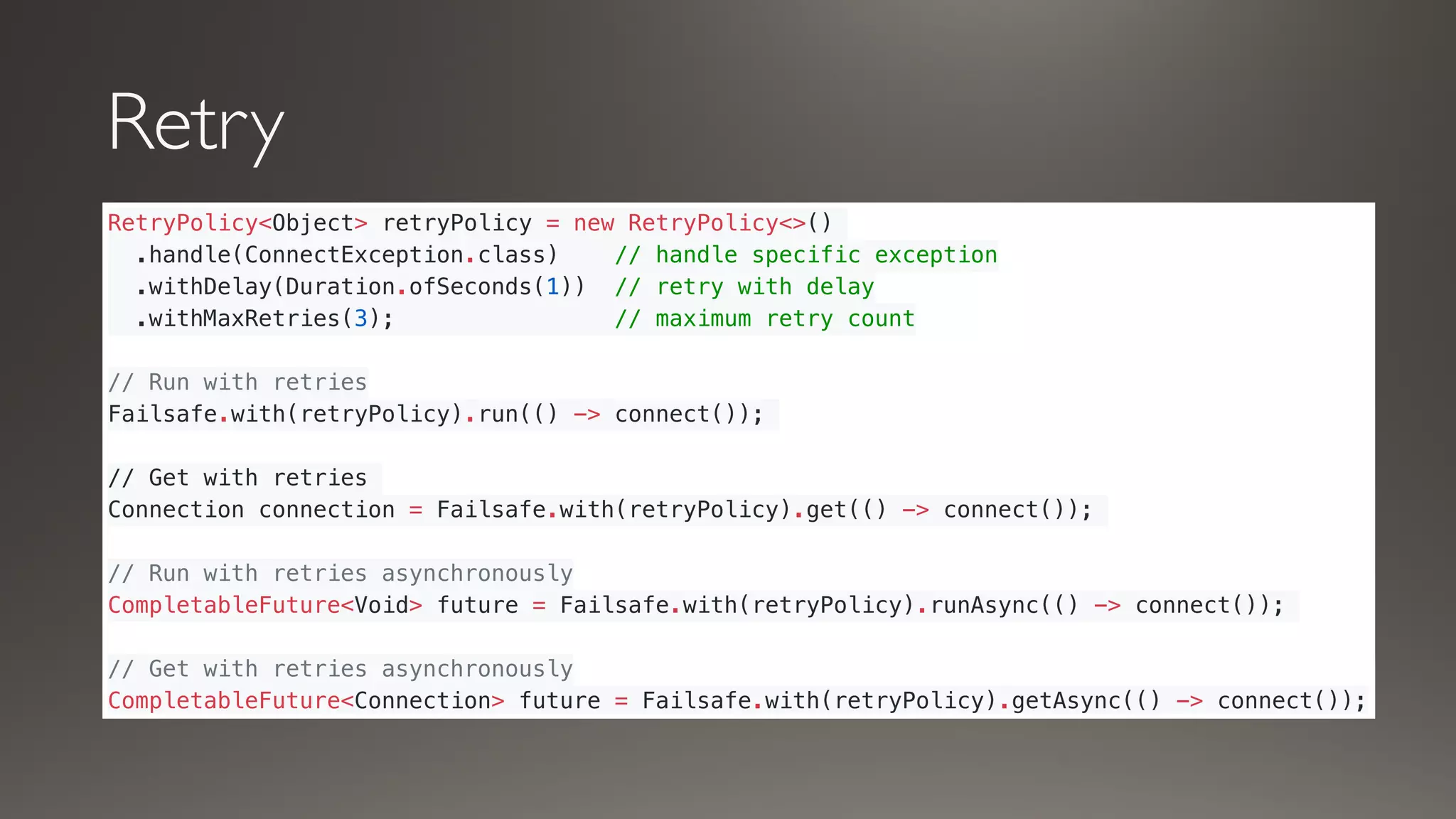
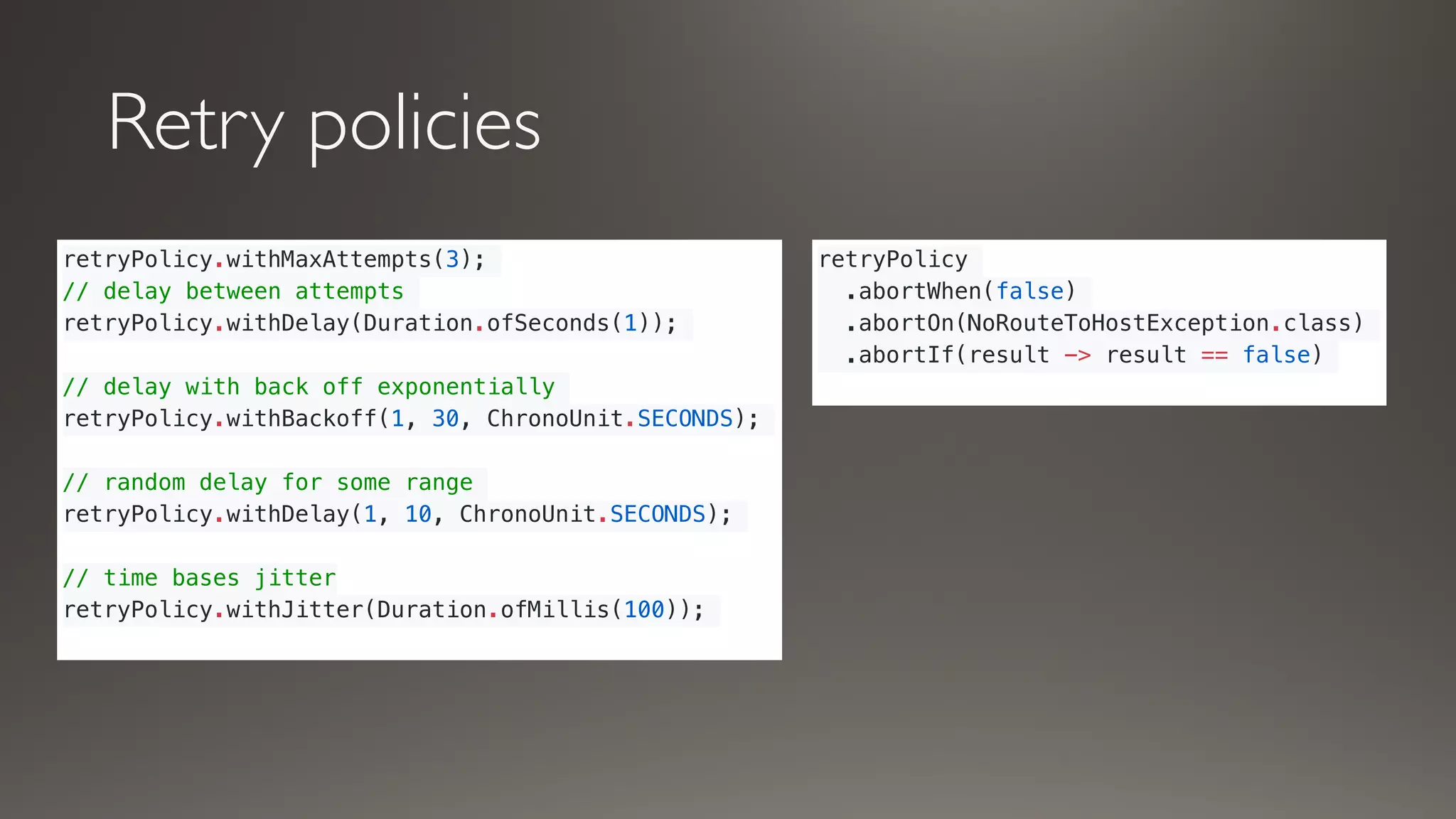
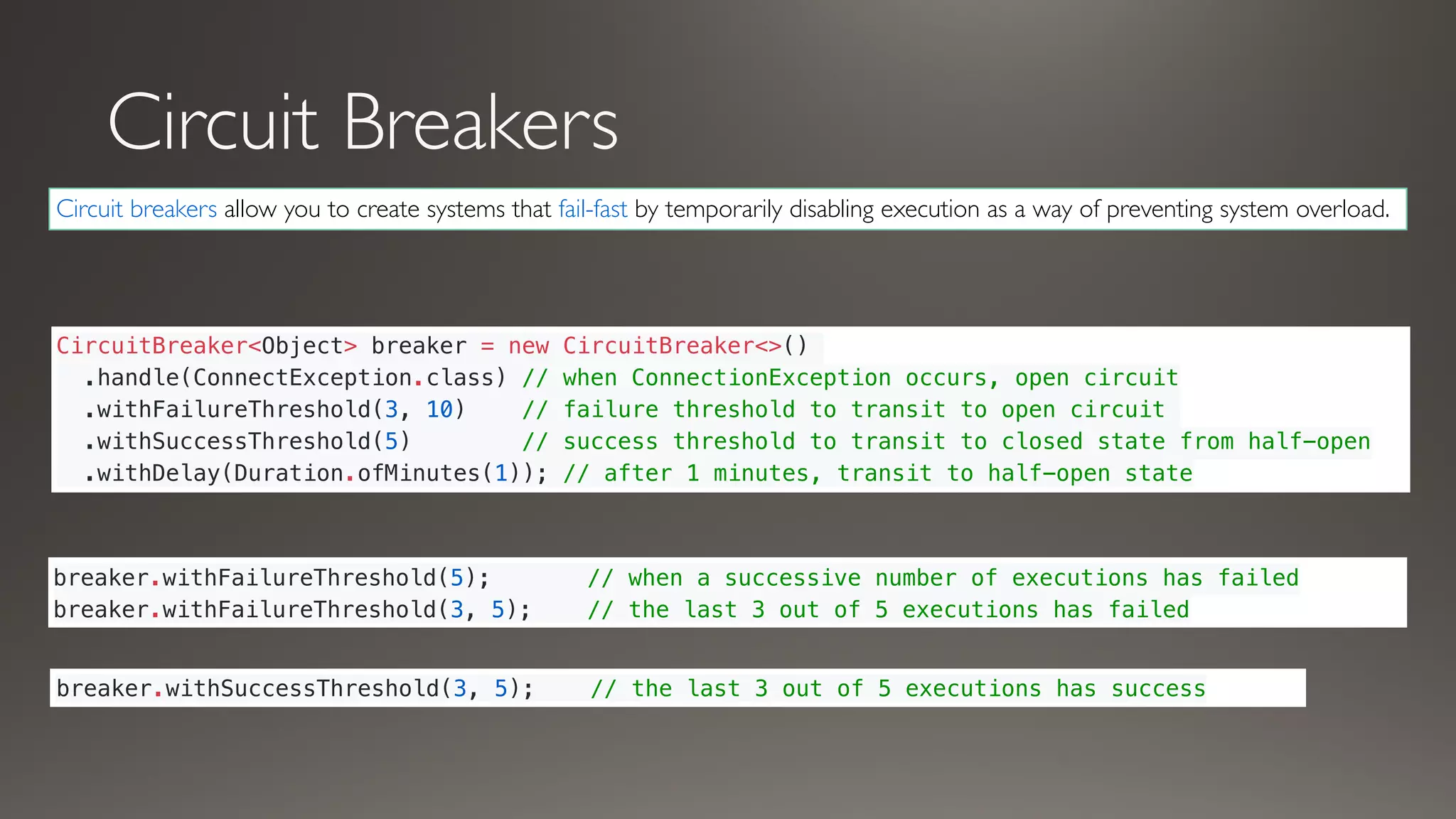
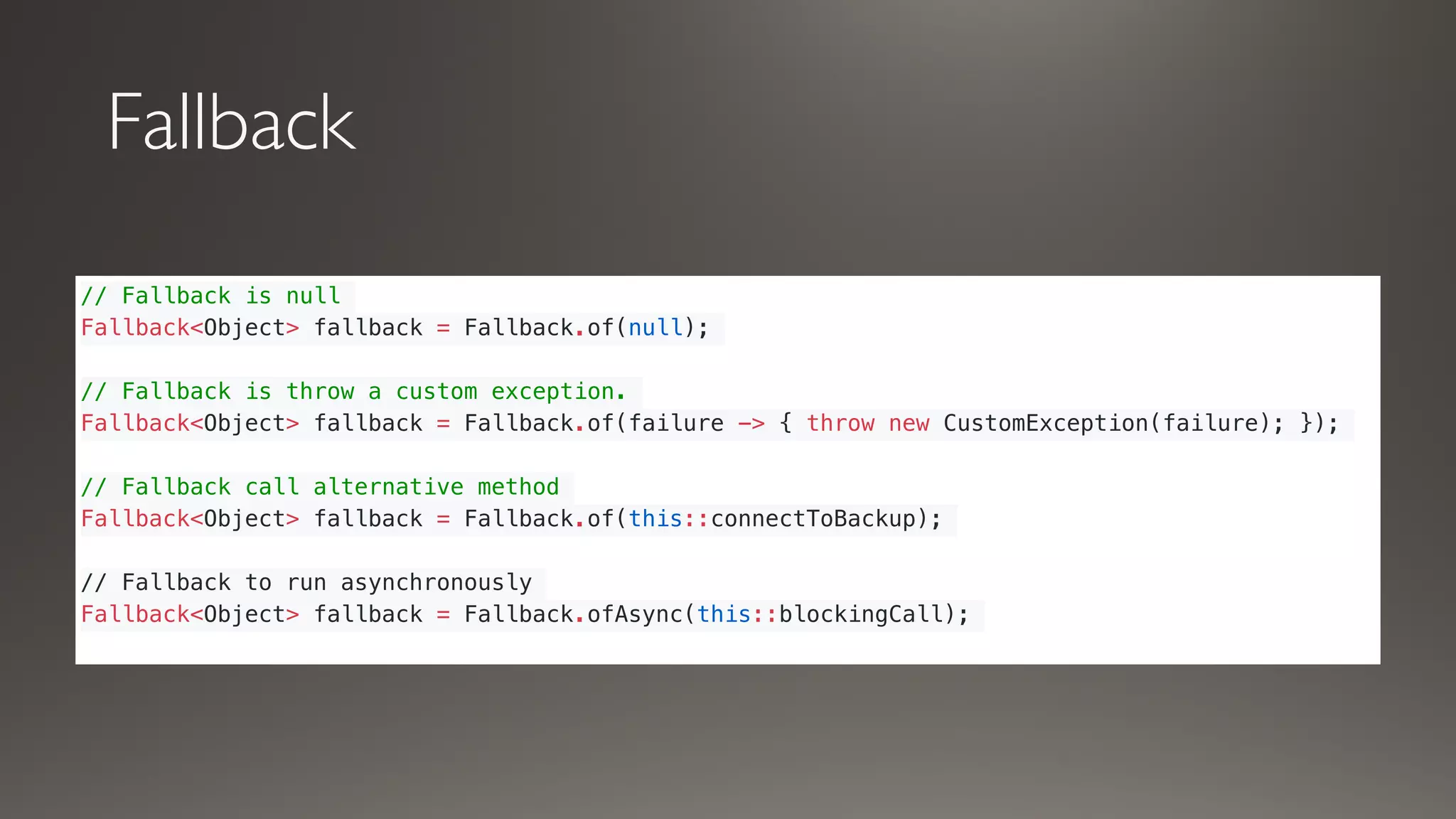
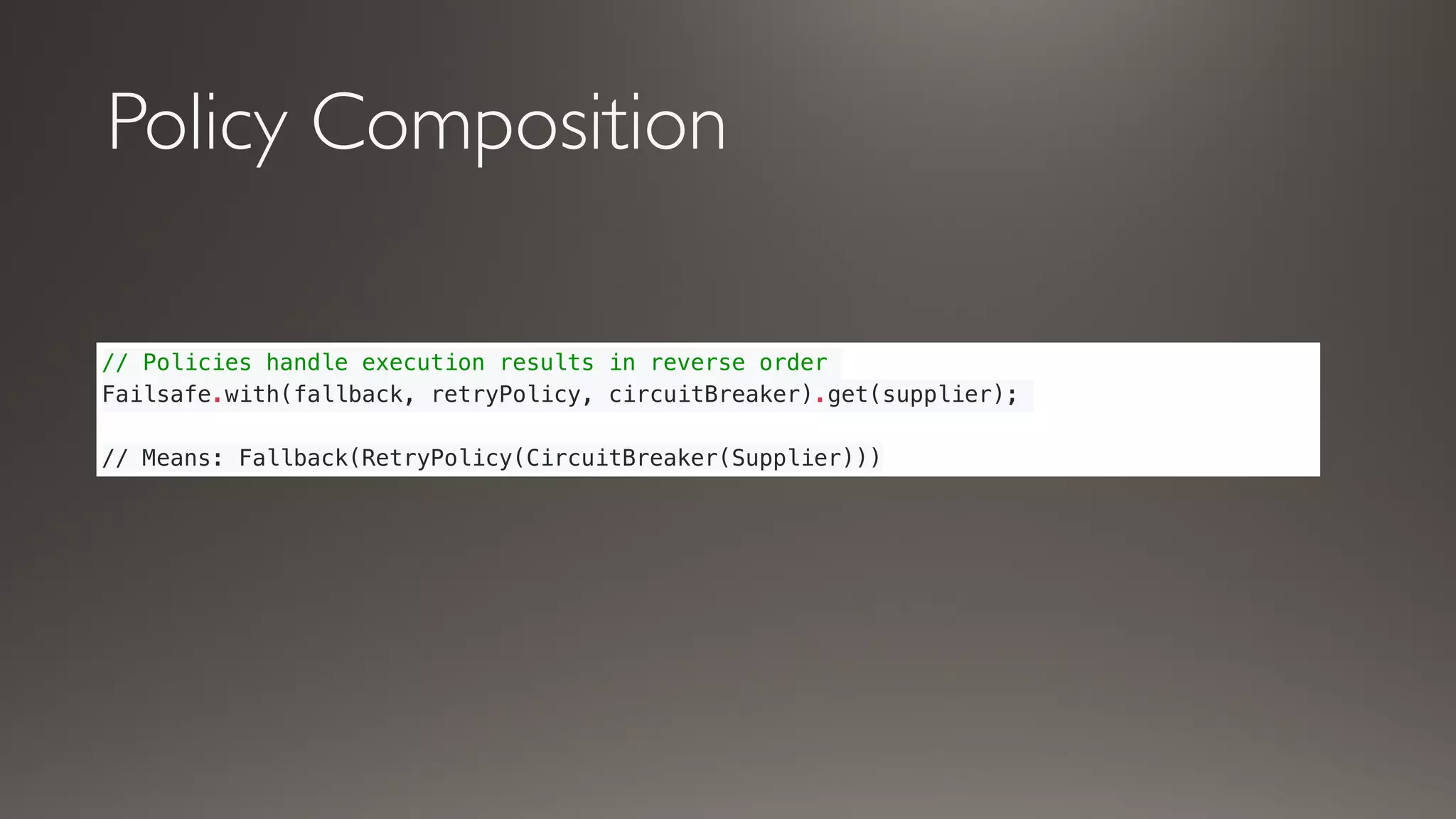
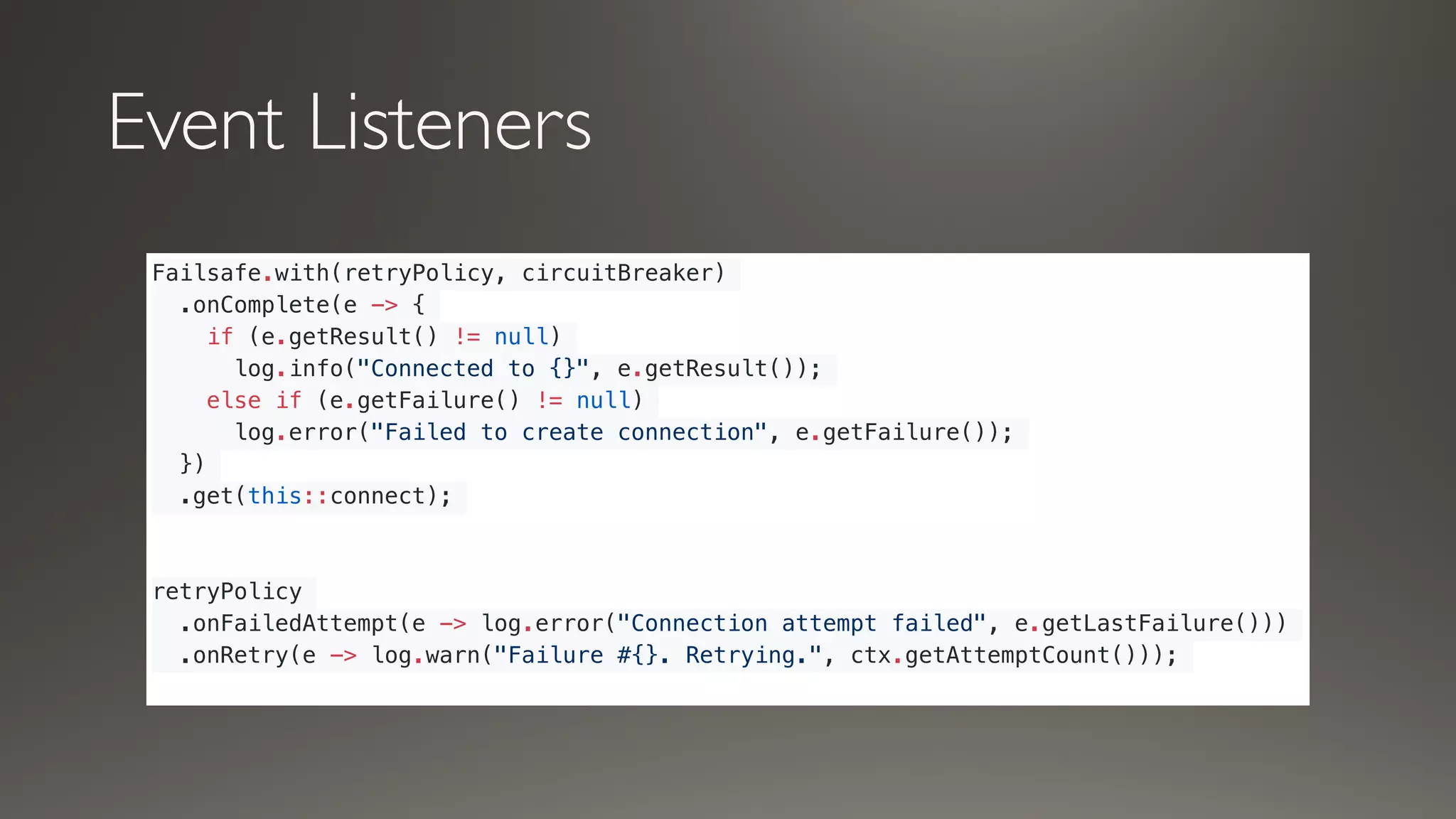
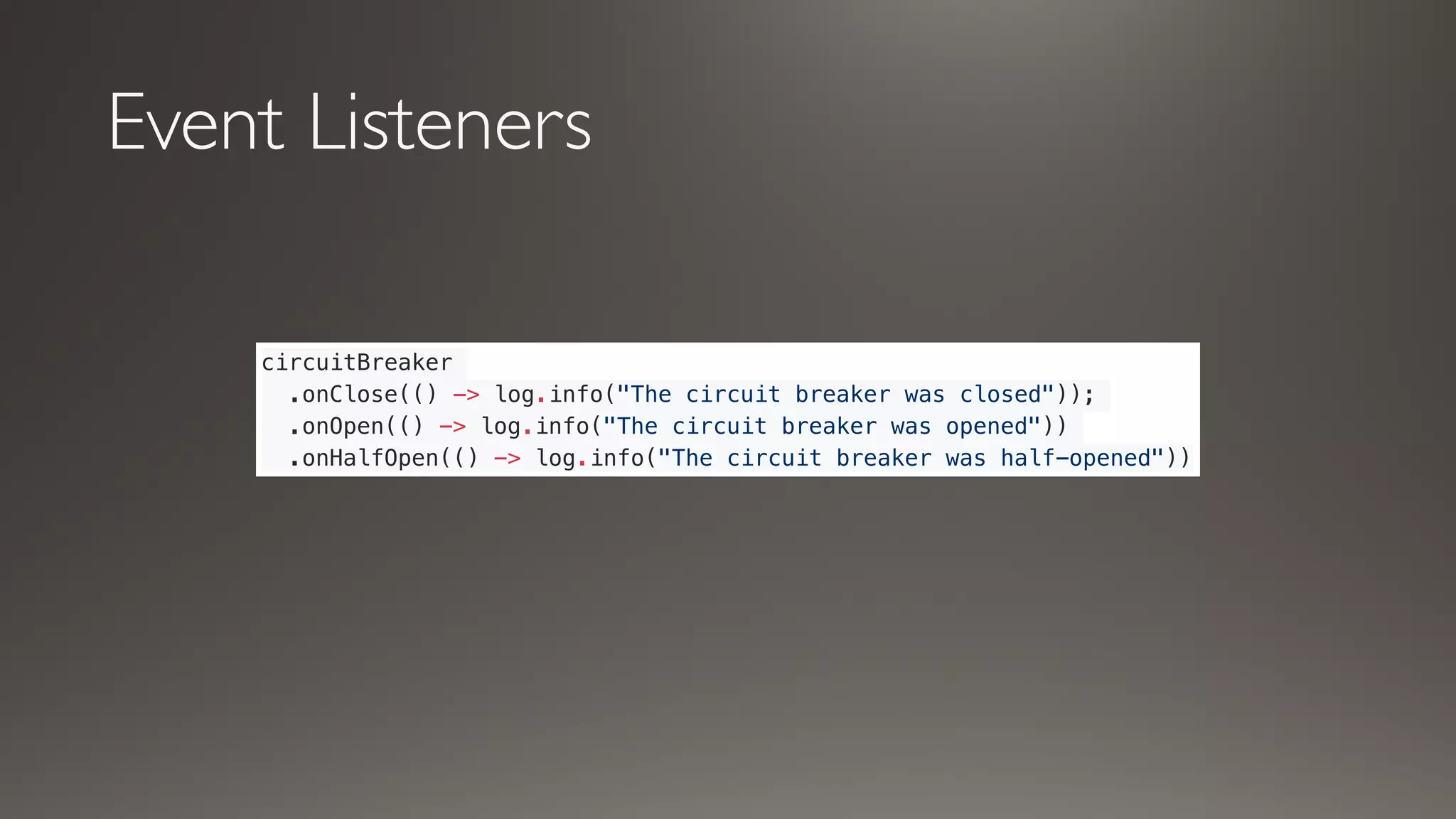
This document introduces Failsafe, which provides latency and fault tolerance capabilities for distributed systems. It discusses how Failsafe compares to Hystrix and how it is used at Coupang. Key features of Failsafe include retry policies, circuit breakers, fallbacks, and asynchronous execution. Event listeners and policy composition patterns are also covered.