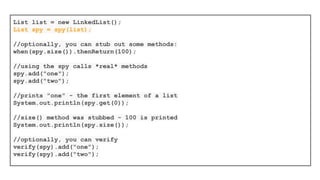
This document provides an introduction to JUnit and Mockito for testing Java code. It discusses how to set up JUnit tests with annotations like @Before, @After, and @Test. It also covers using JUnit assertions and test suites. For Mockito, the document discusses how to create and use mock objects to stub behavior and verify interactions. It provides examples of argument matchers and consecutive stubbing in Mockito.
















![import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import static org.junit.matchers.JUnitMatchers.*;
assertThat("albumen", both(containsString("a")).and
(containsString("b")));
assertThat(Arrays.asList("one", "two", "three"), hasItems
("one", "three"));
assertThat(Arrays.asList(new String[] { "fun", "ban", "net"
}), everyItem(containsString("n")));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/junitmockitofirststeps-140720103803-phpapp01/85/JUnit-Mockito-first-steps-17-320.jpg)








![Use JUnitCore to run tests and see
the results on the console
> java org.junit.runner.JUnitCore TestClass1 [...other
test classes...]
Both your test class and junit must be on the classpath](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/junitmockitofirststeps-140720103803-phpapp01/85/JUnit-Mockito-first-steps-26-320.jpg)