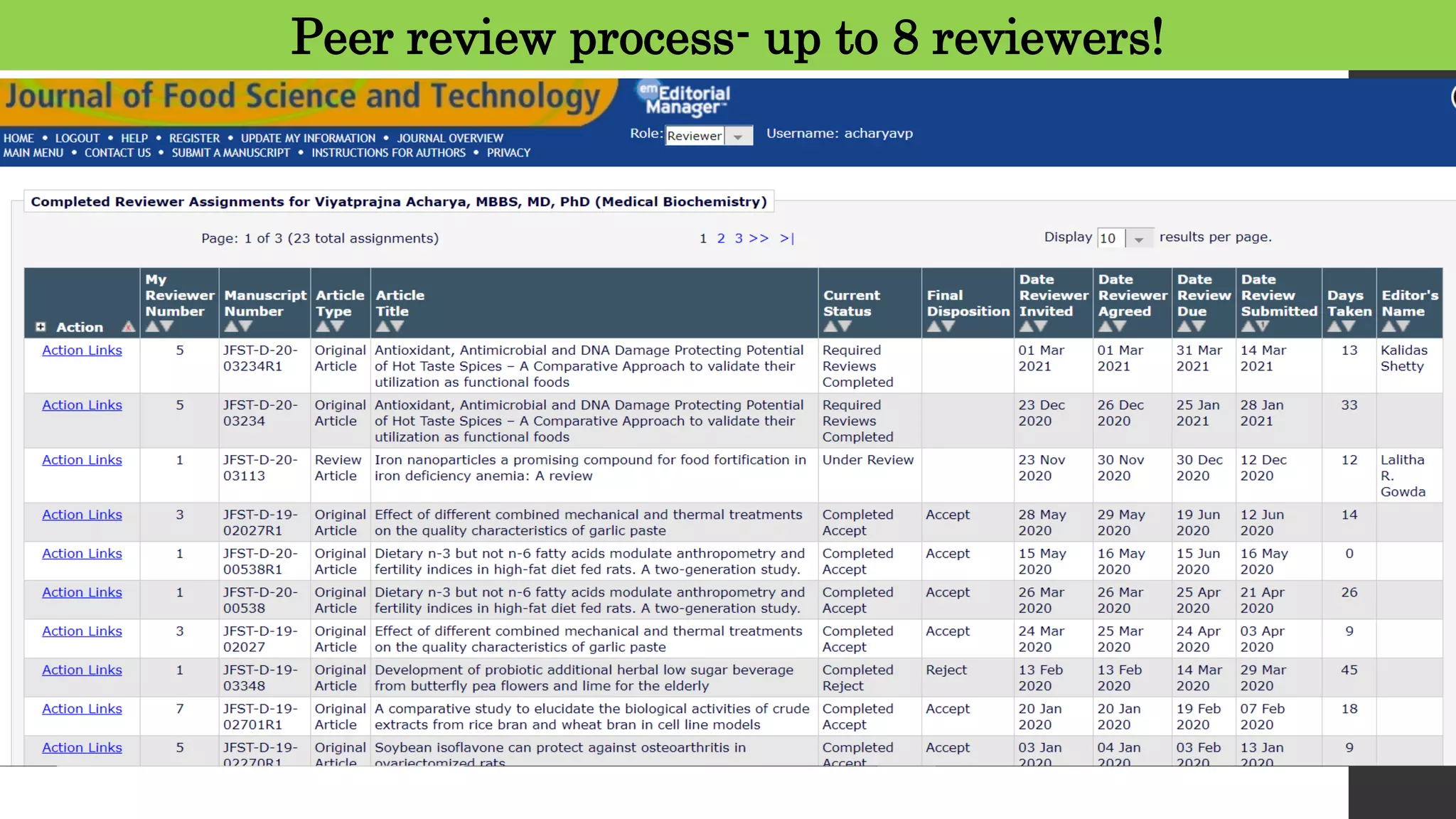
This document provides information about journal clubs and academic journals. It discusses the history of journal clubs, how to select and present articles in a journal club. It also covers different types of academic journals, how they are indexed and ranked. Key metrics for evaluating journals are discussed, including impact factor, eigenfactor score, and SJR. Predatory journals are defined and tips are provided to identify them. Different types of research articles are outlined. The use of impact factor to evaluate individual studies is critiqued. Ways to improve citation of one's own work are suggested.