1. The document discusses the history and objectives of journal clubs, which began in the 1800s as a way for physicians to critically discuss recent medical literature.
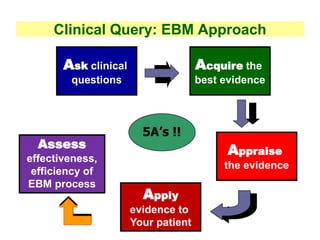
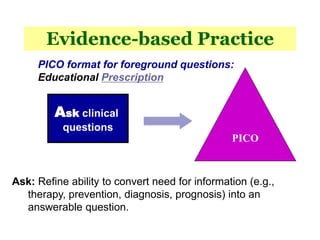
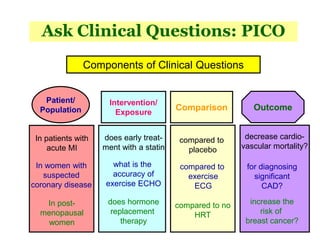
2. Journal clubs aim to improve knowledge and skills in evidence-based medicine, communication, and quality improvement by changing practices based on evidence.
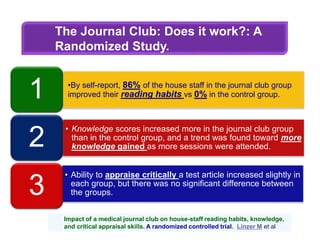
3. Studies have found that journal clubs may be effective in improving reading habits, knowledge of epidemiology and biostatistics, and use of medical literature, though their impact on critical appraisal skills requires more research.