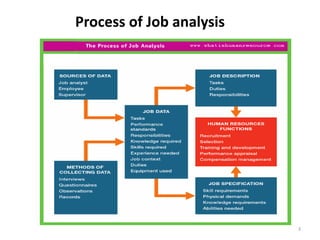
The document discusses job analysis and job design, highlighting the process of job analysis that includes creating job descriptions and specifications. Job descriptions outline duties and working conditions, while job specifications detail the human requirements for the roles. Job design aims to organize tasks effectively to enhance productivity and employee satisfaction, featuring various methods to address issues like employee boredom and turnover.