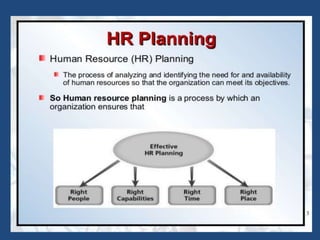
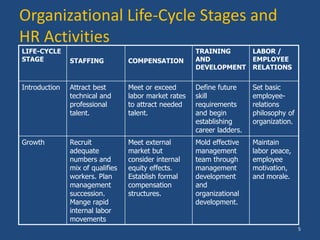
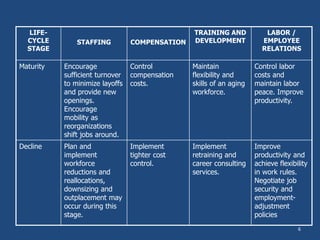
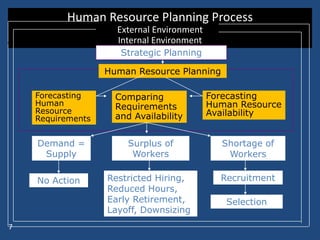
The document outlines the process of human resource (HR) planning, emphasizing its importance at various organizational levels and the factors affecting it. It details the activities and strategies related to staffing, compensation, training, and employee relations across different organizational life-cycle stages. The document also highlights barriers to effective HR planning and prerequisites for successful integration of HR planning into corporate strategy.