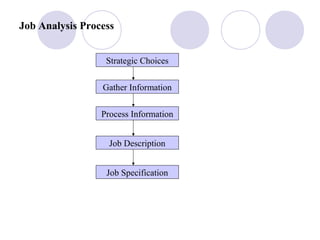
This document discusses job analysis, which involves studying and collecting information about the responsibilities and operations of a specific job. The main goals are to create a job description outlining the key details of the job, and a job specification listing the necessary human qualifications. Job analysis lays the foundation for human resource planning and other functions. It involves strategic choices, gathering job data from various sources, and processing the information to develop the job description and specification.