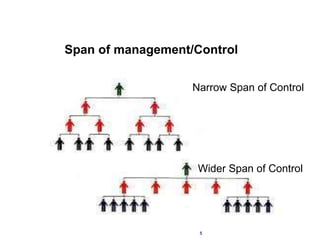
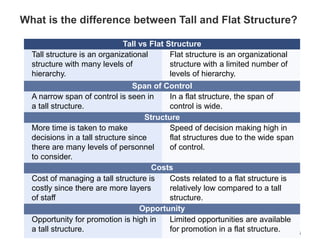
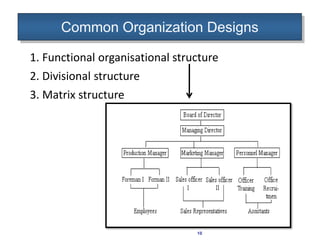
Organizational structure is the framework that specifies relationships between people, work, and resources within an organization. The span of management, or number of subordinates one manager can oversee, largely determines the structure and levels of hierarchy. Tall structures have many levels and a narrow span of control, while flat structures have few levels and a wide span of control. Decision making is faster in flat structures due to their wide span of control, while tall structures provide more opportunities for promotion but involve higher costs and slower decision making across many levels. Delegation of authority and decentralization of decision making can help make structures more effective and motivate employees. Common organization designs include functional, divisional, and matrix structures.