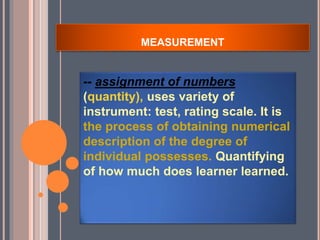
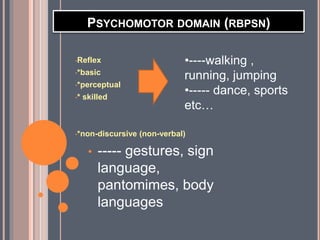
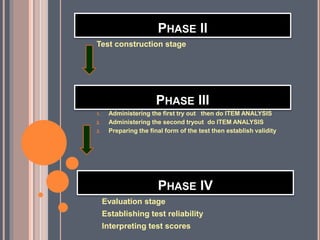
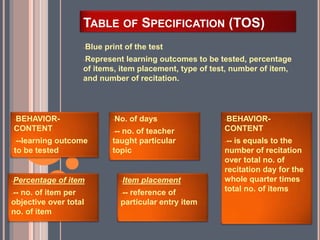
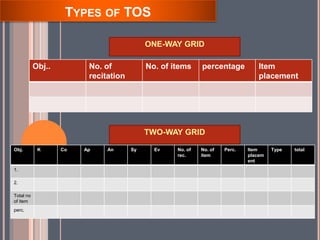
This document discusses key concepts in educational measurement, assessment, and evaluation. It defines tests, measurements, assessment, and evaluation and explains their purposes. It also covers the development of intelligence, achievement, and personality tests. Additionally, it discusses taxonomies of educational objectives, types of tests, steps in developing tests, and characteristics of good tests. The overall document provides an overview of fundamental concepts and principles in educational testing and measurement.