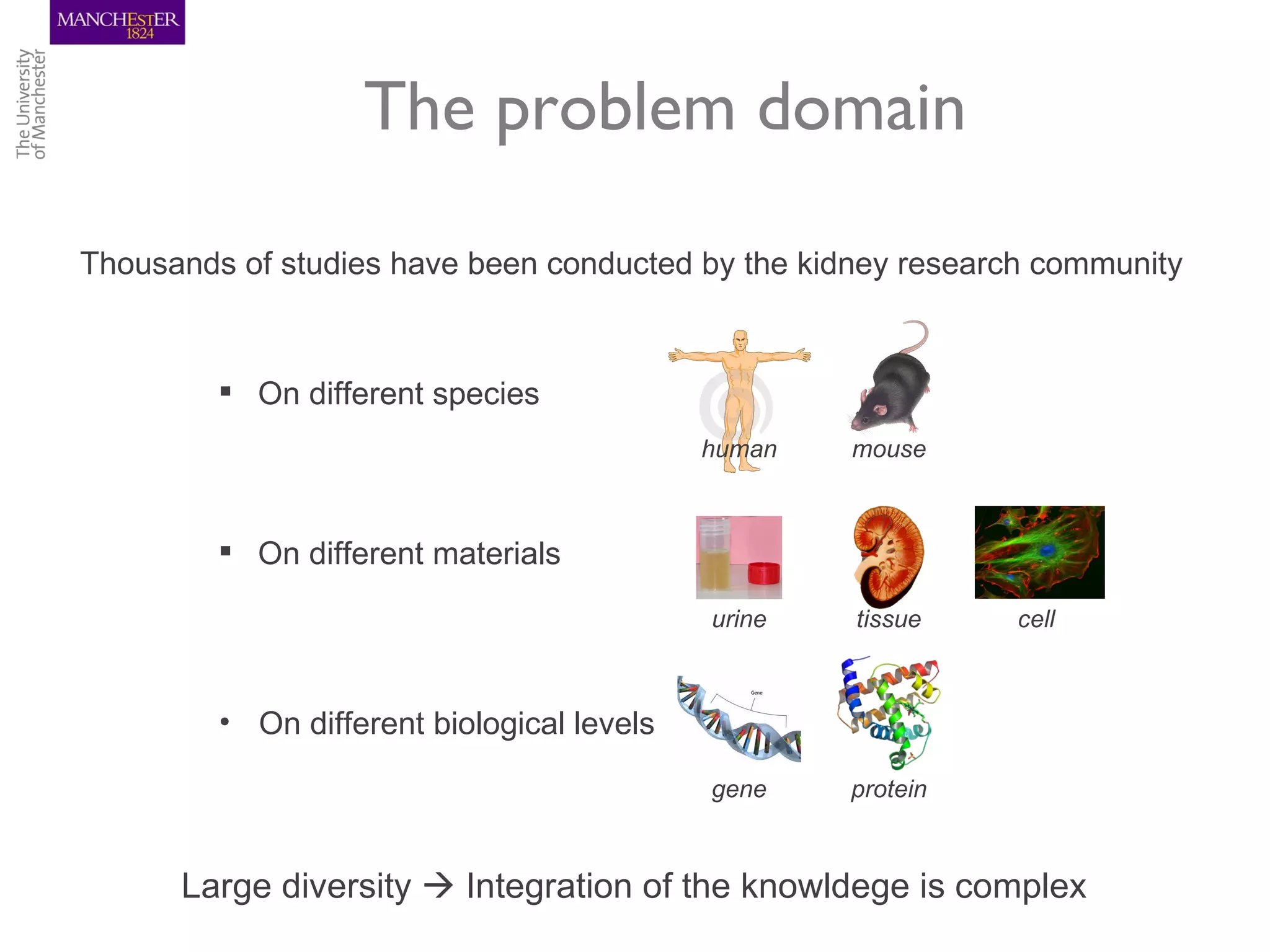
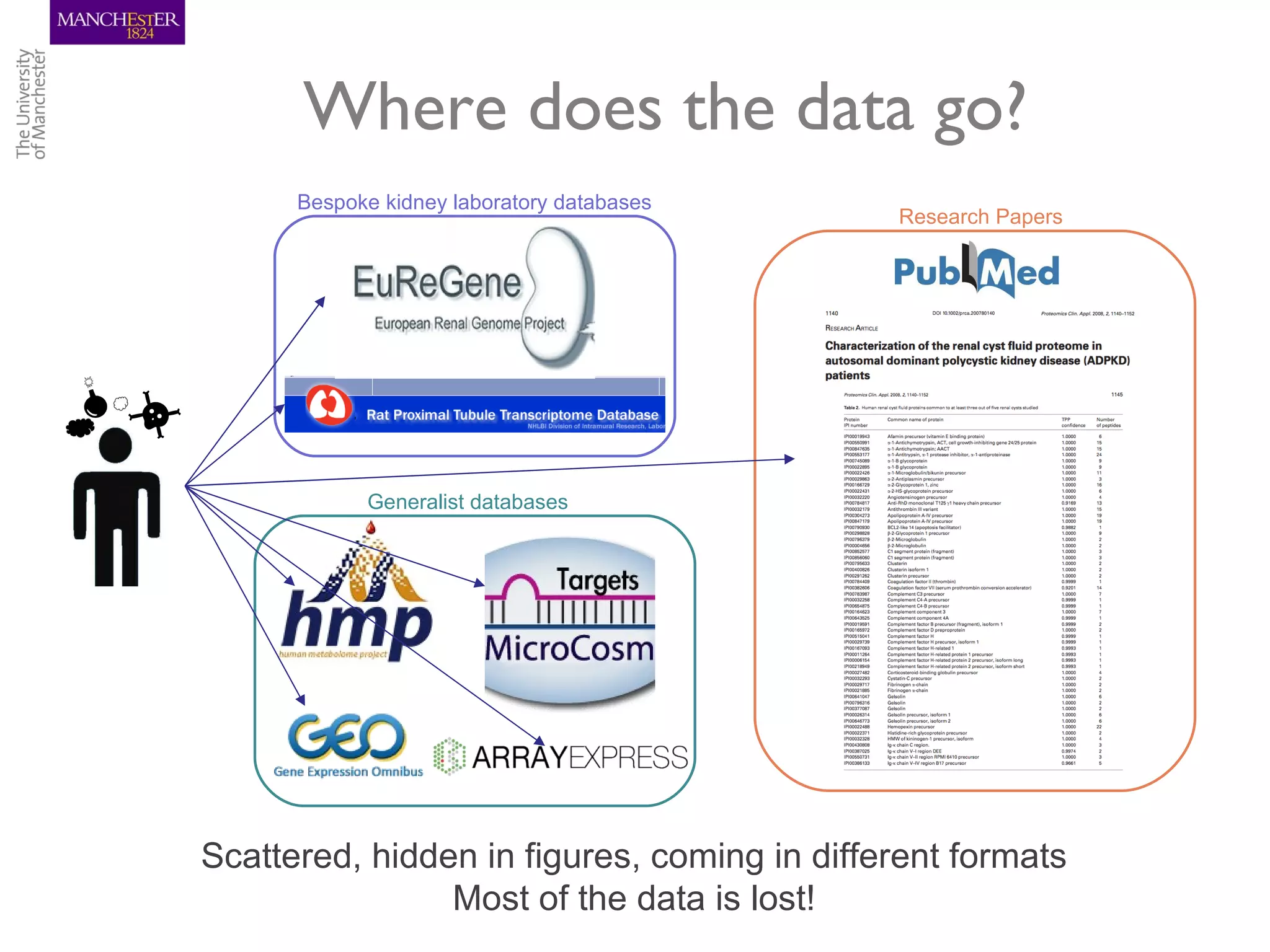
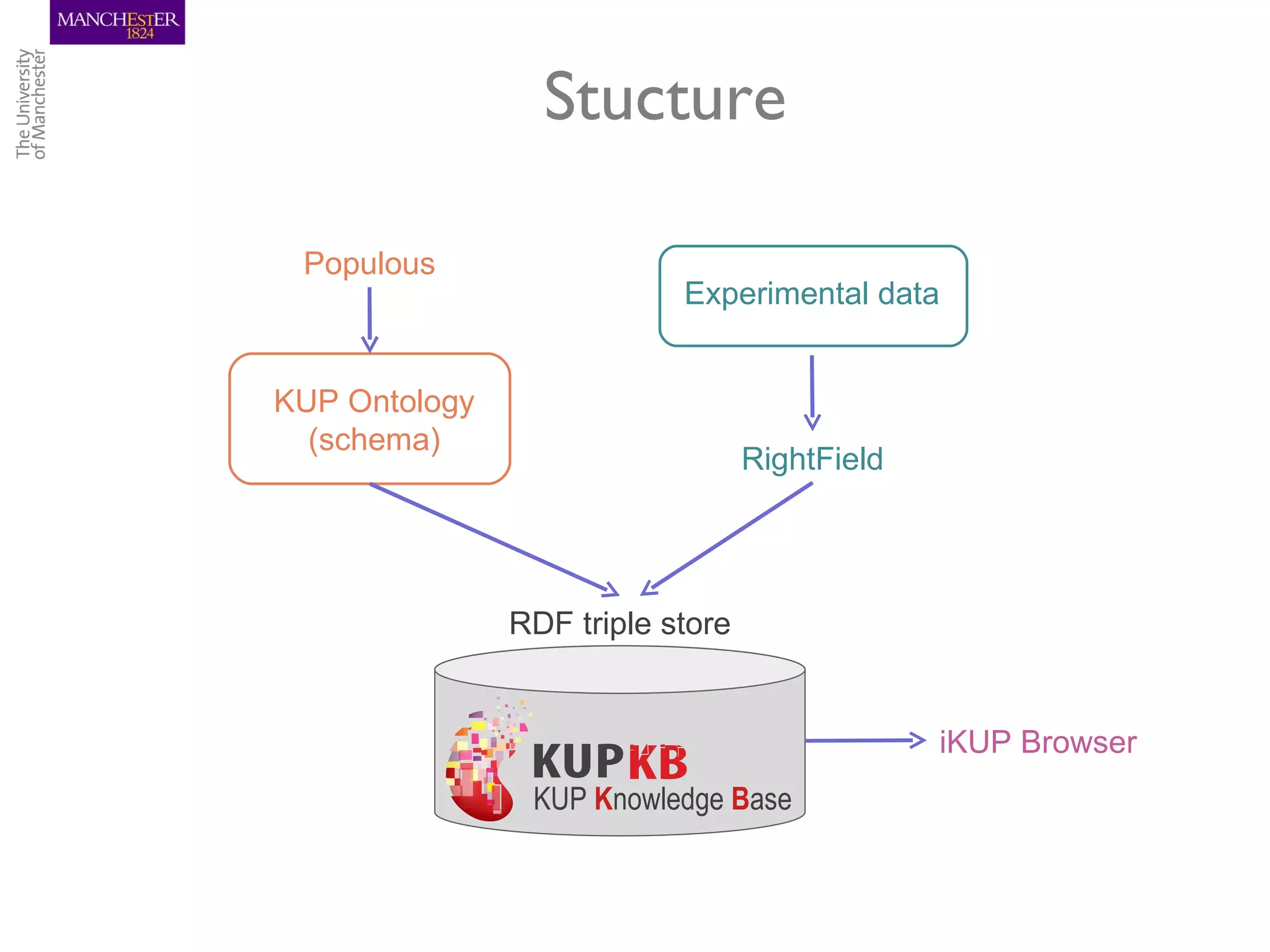
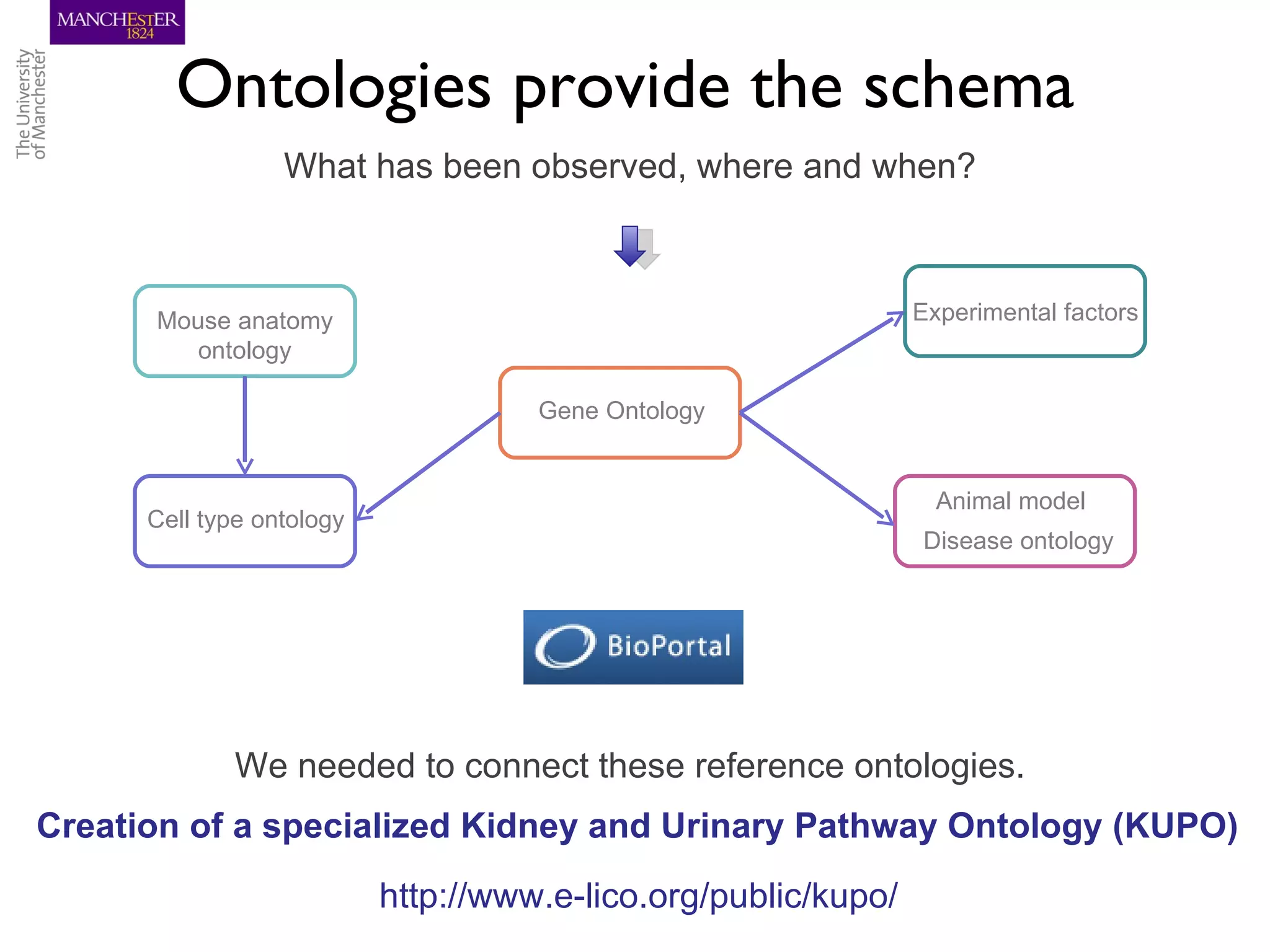
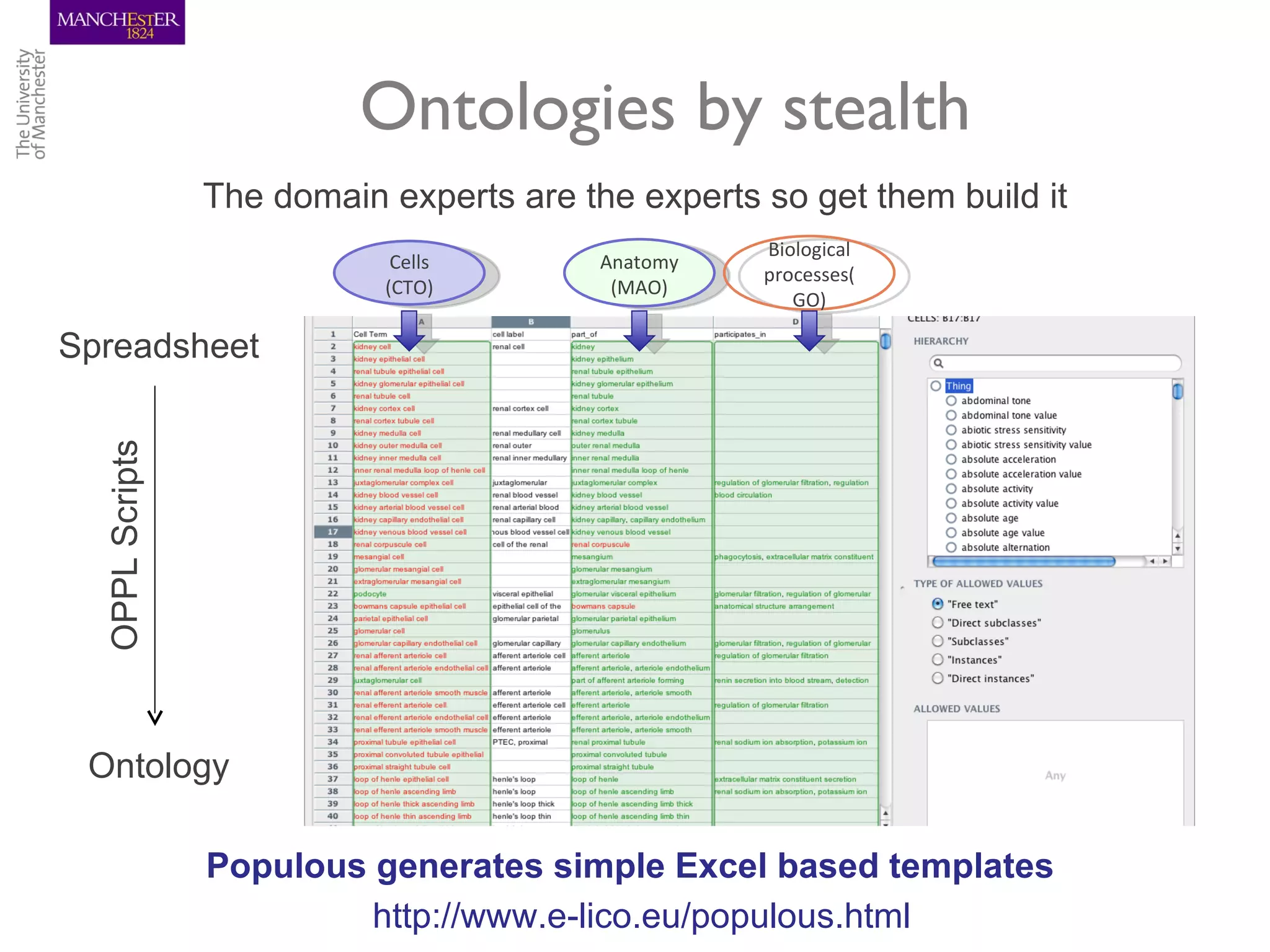
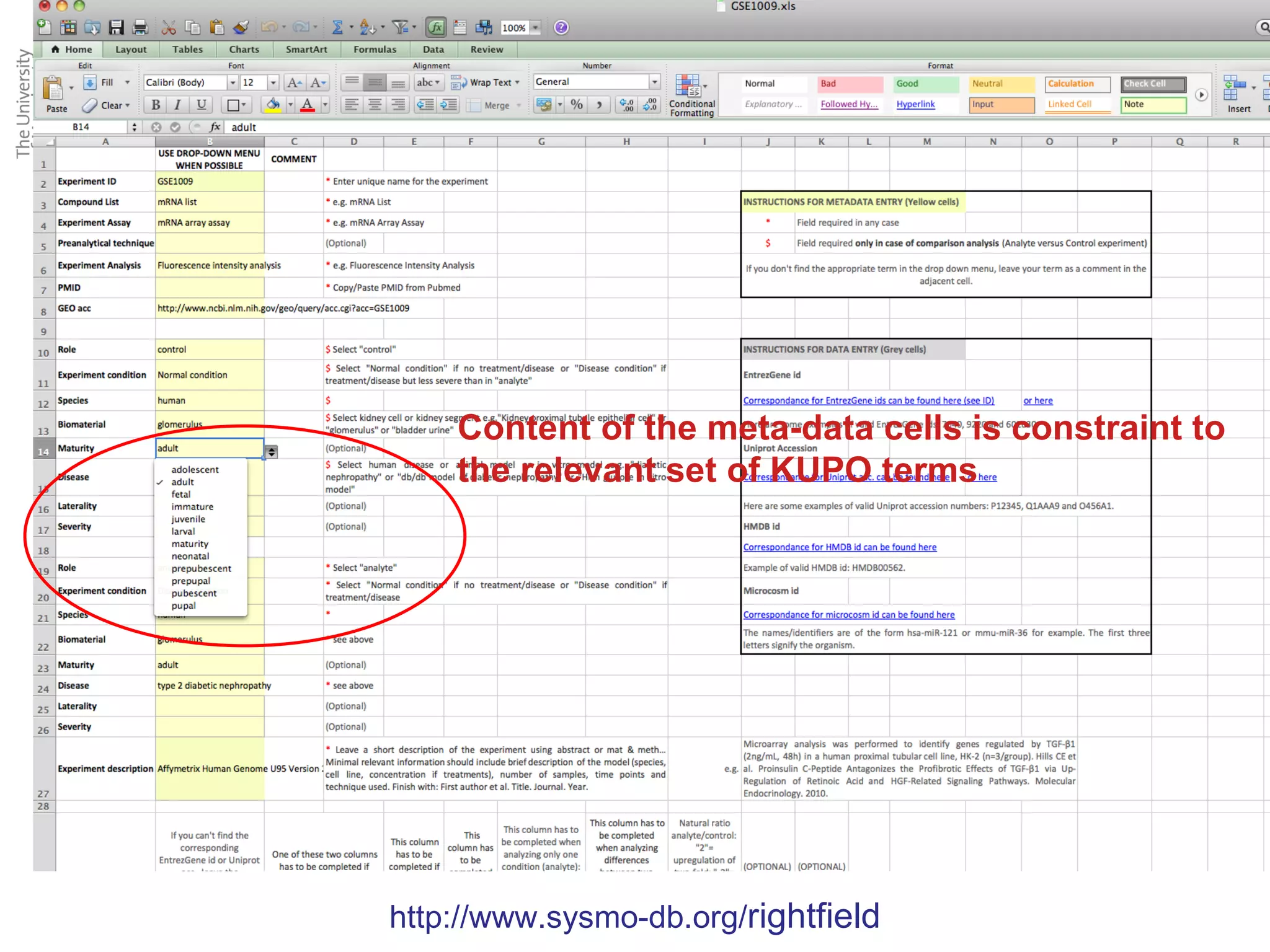
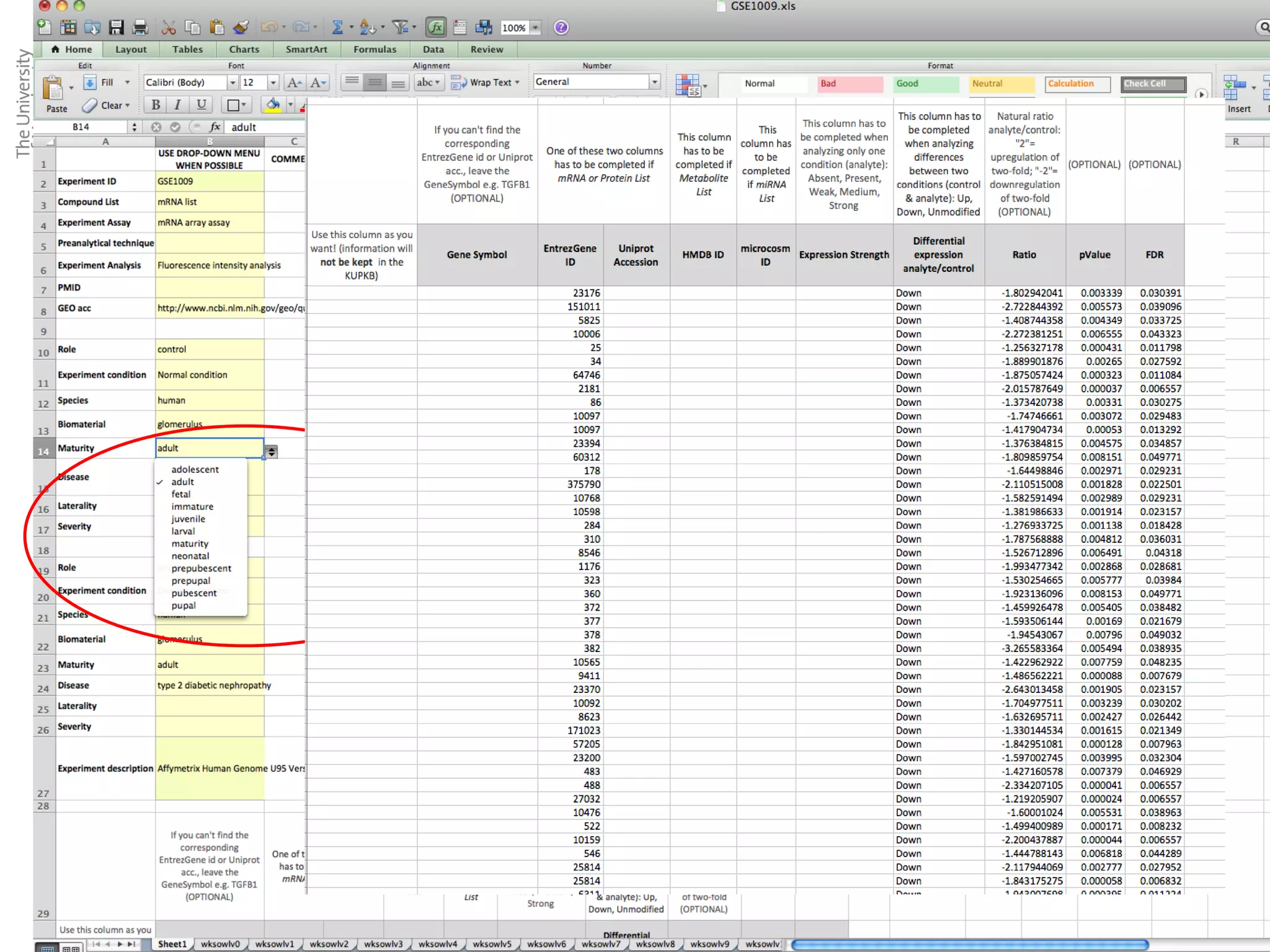
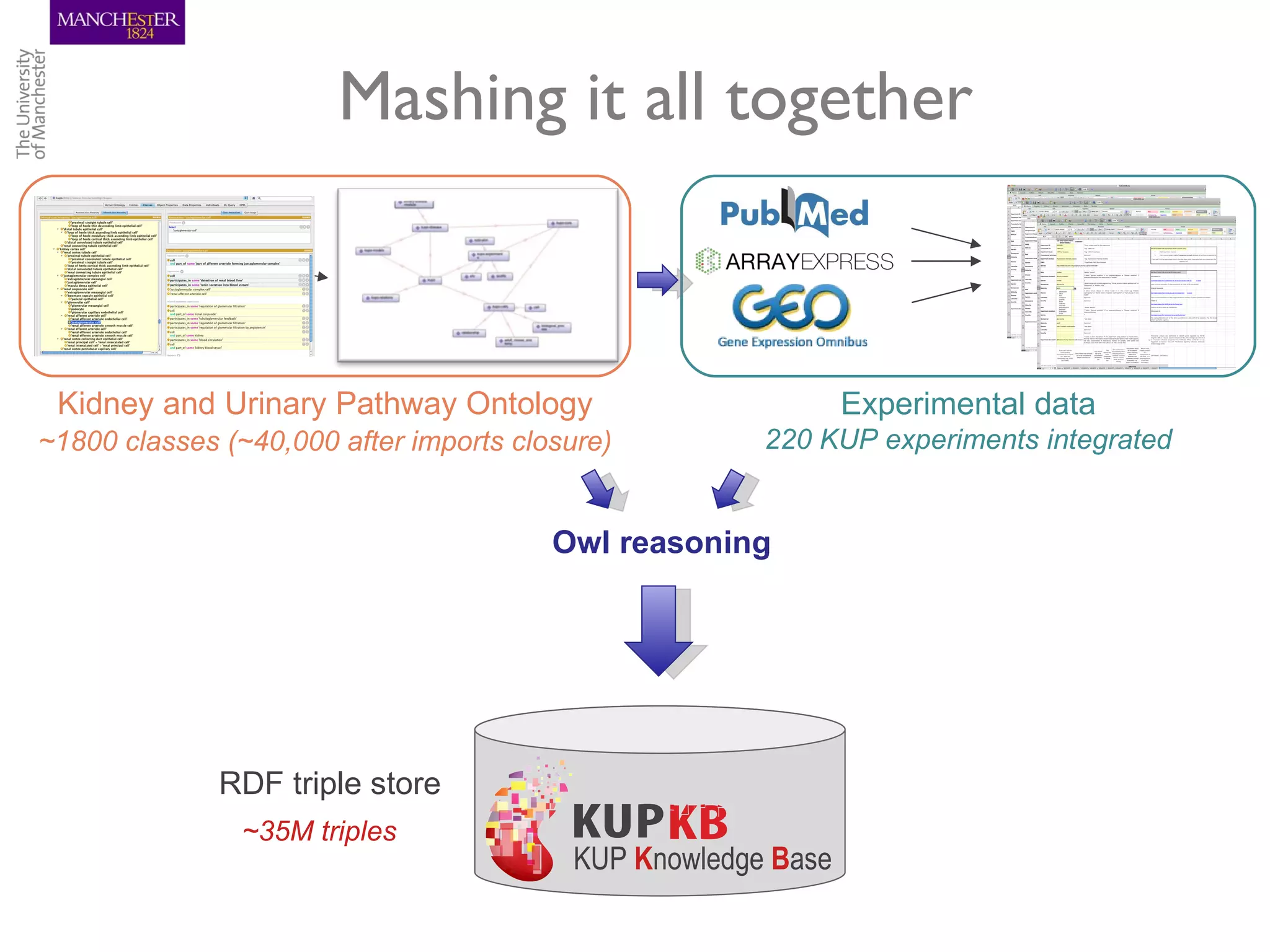
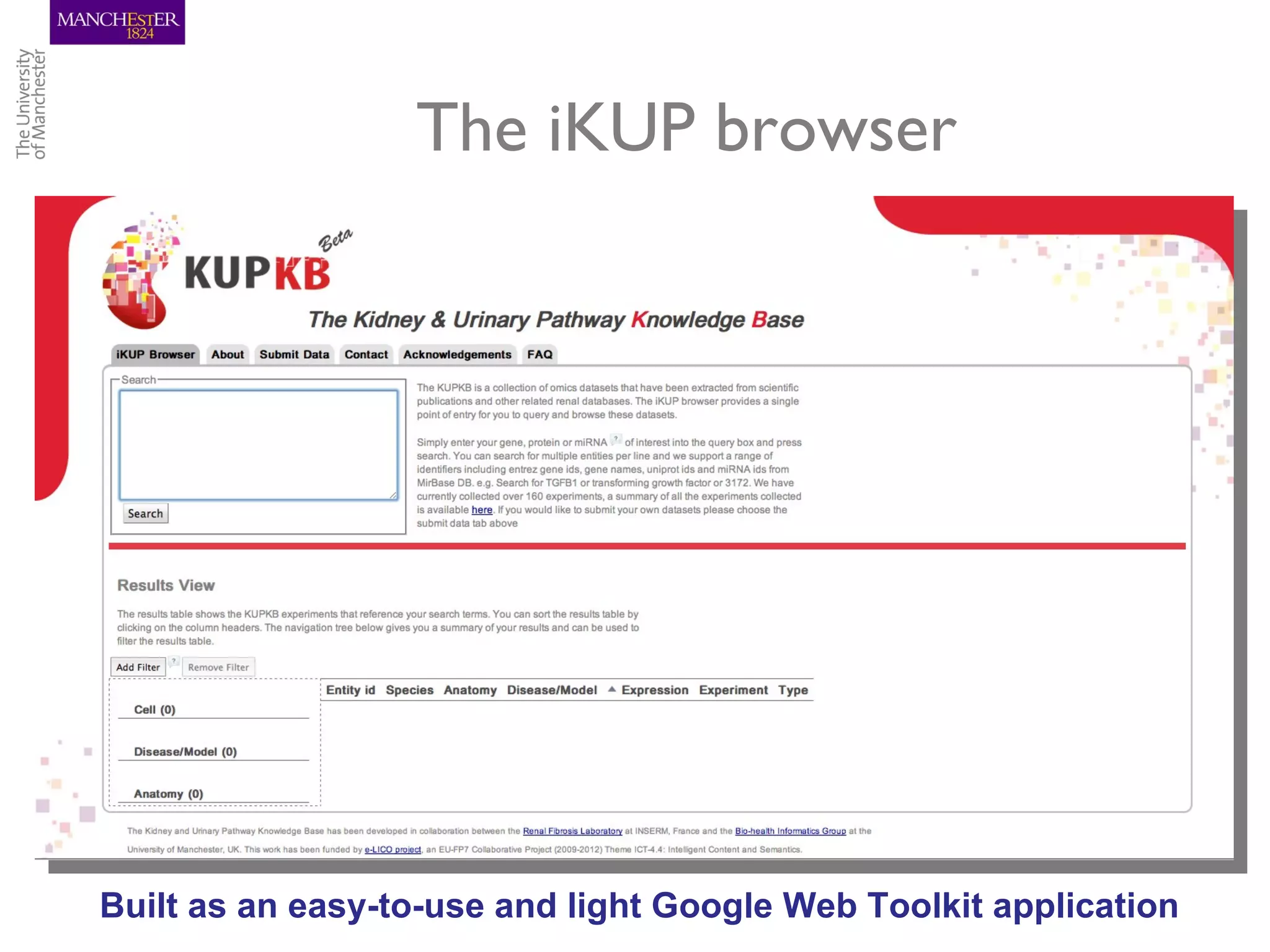
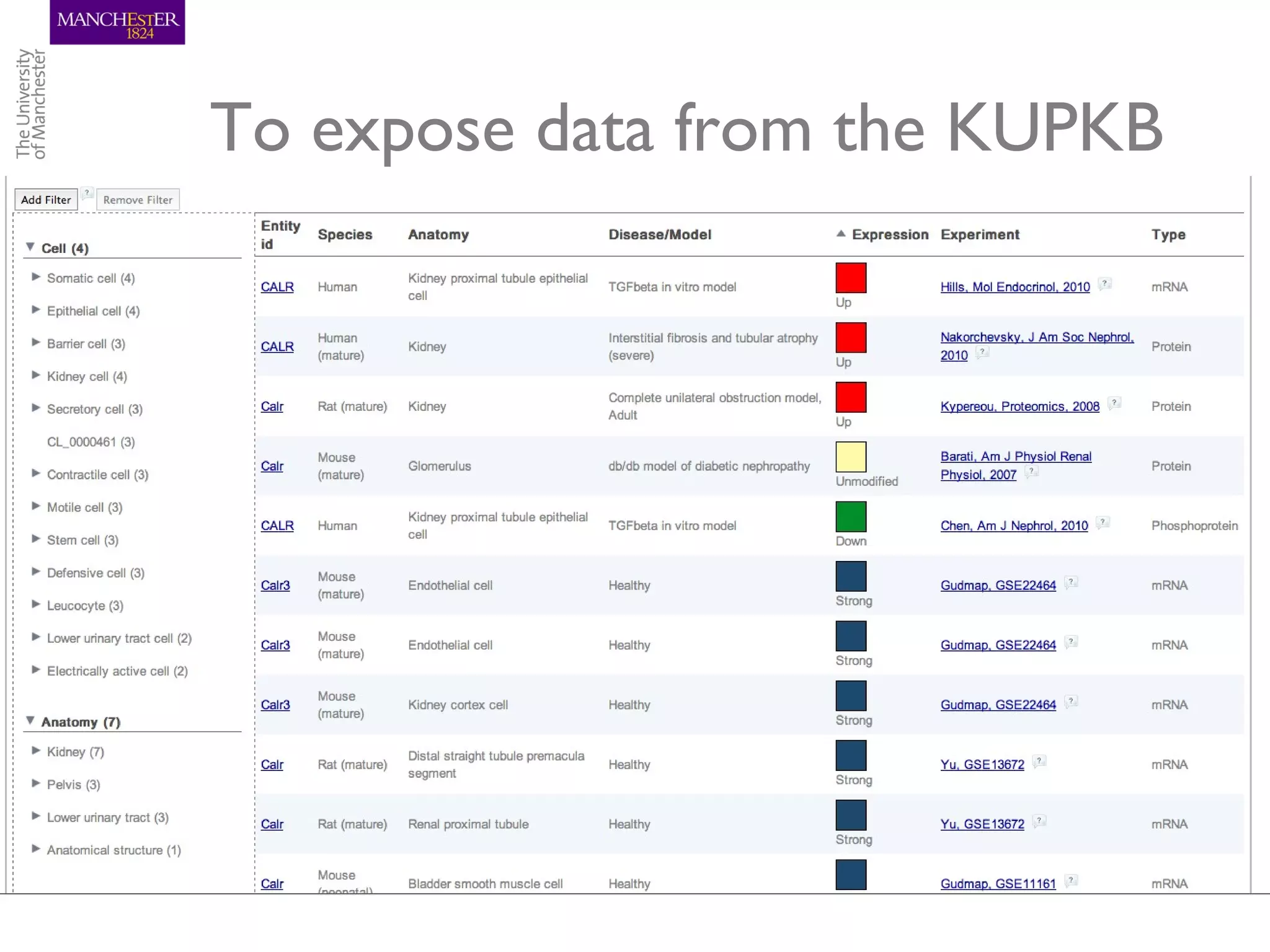
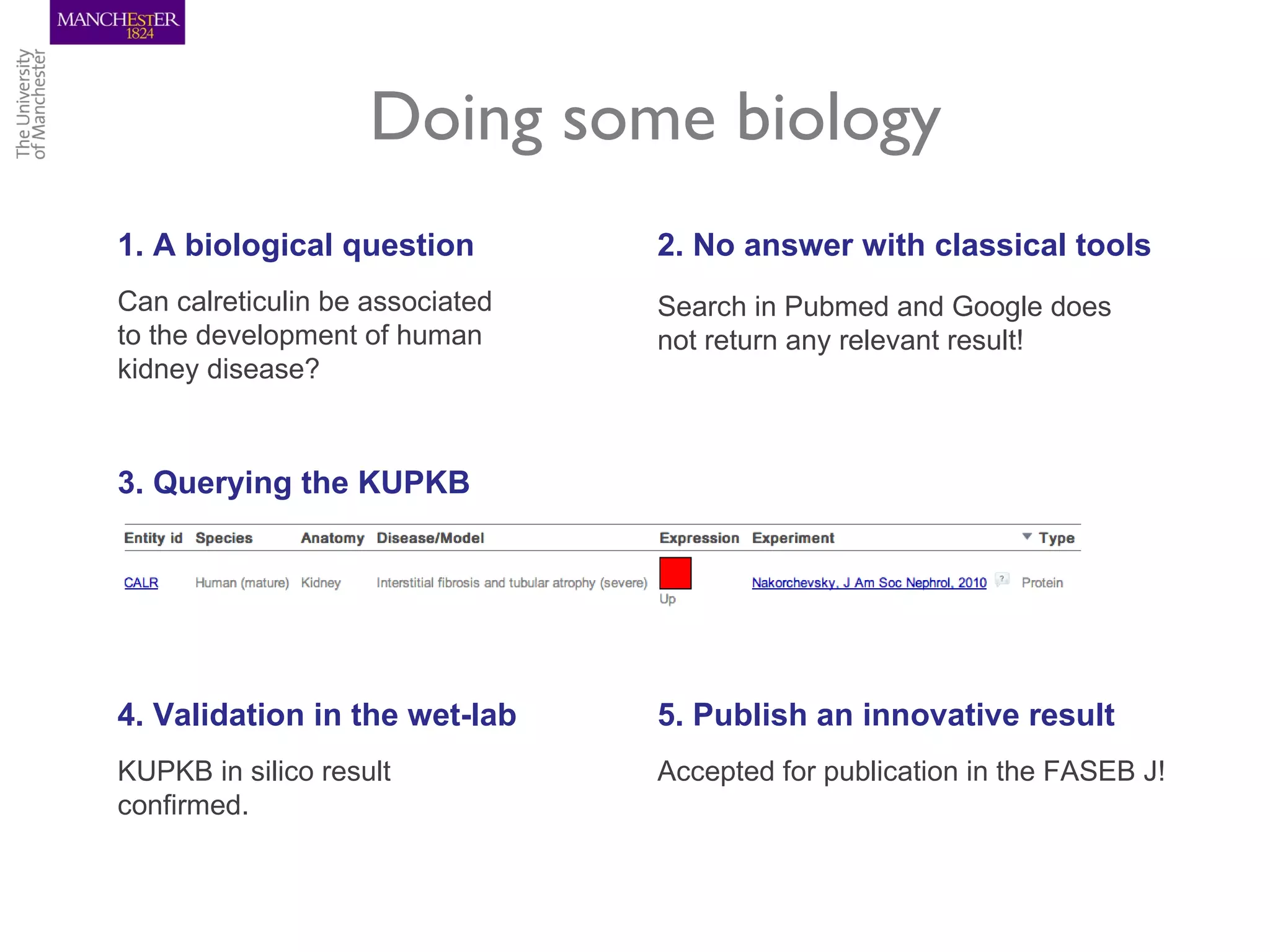
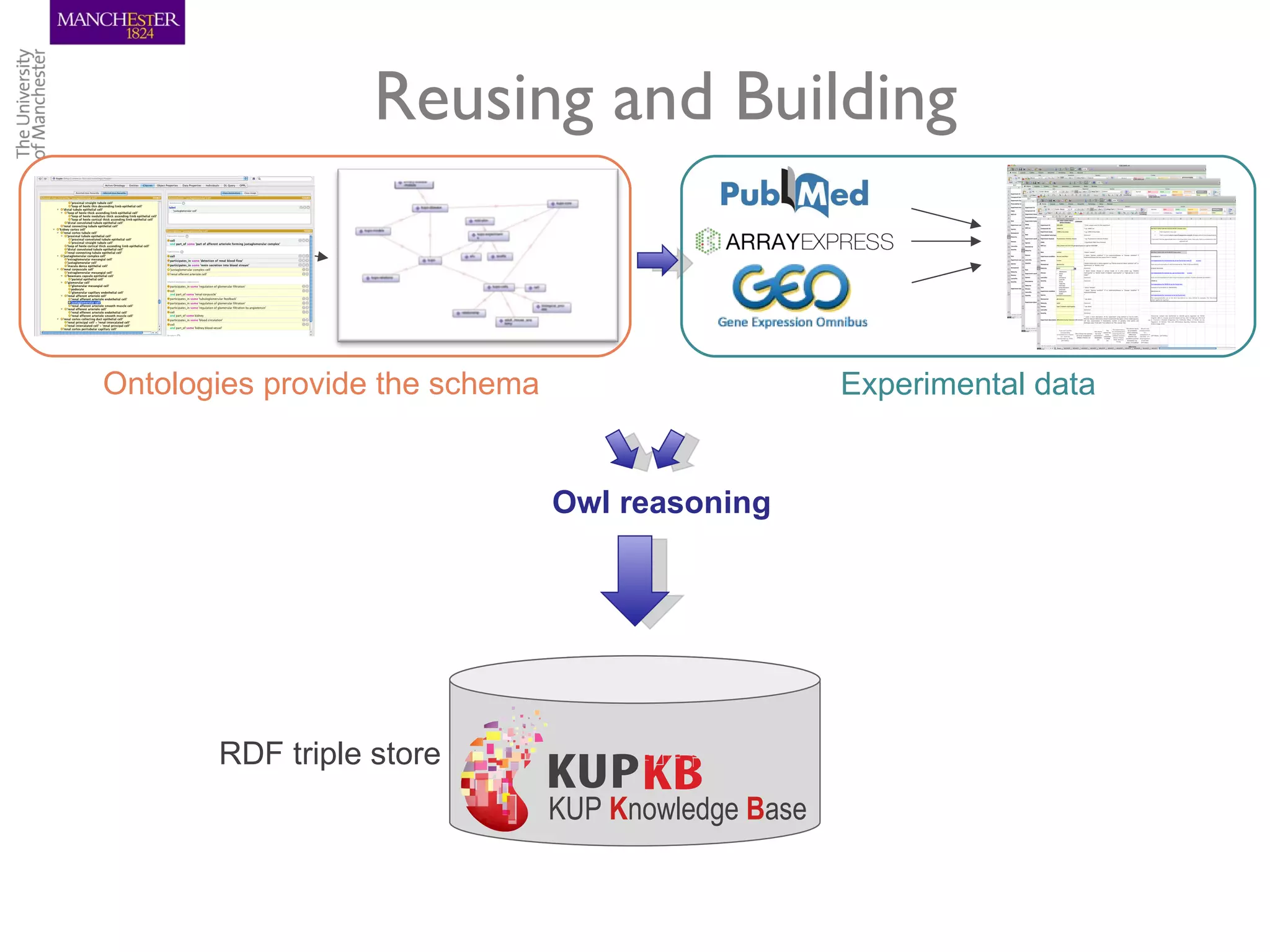
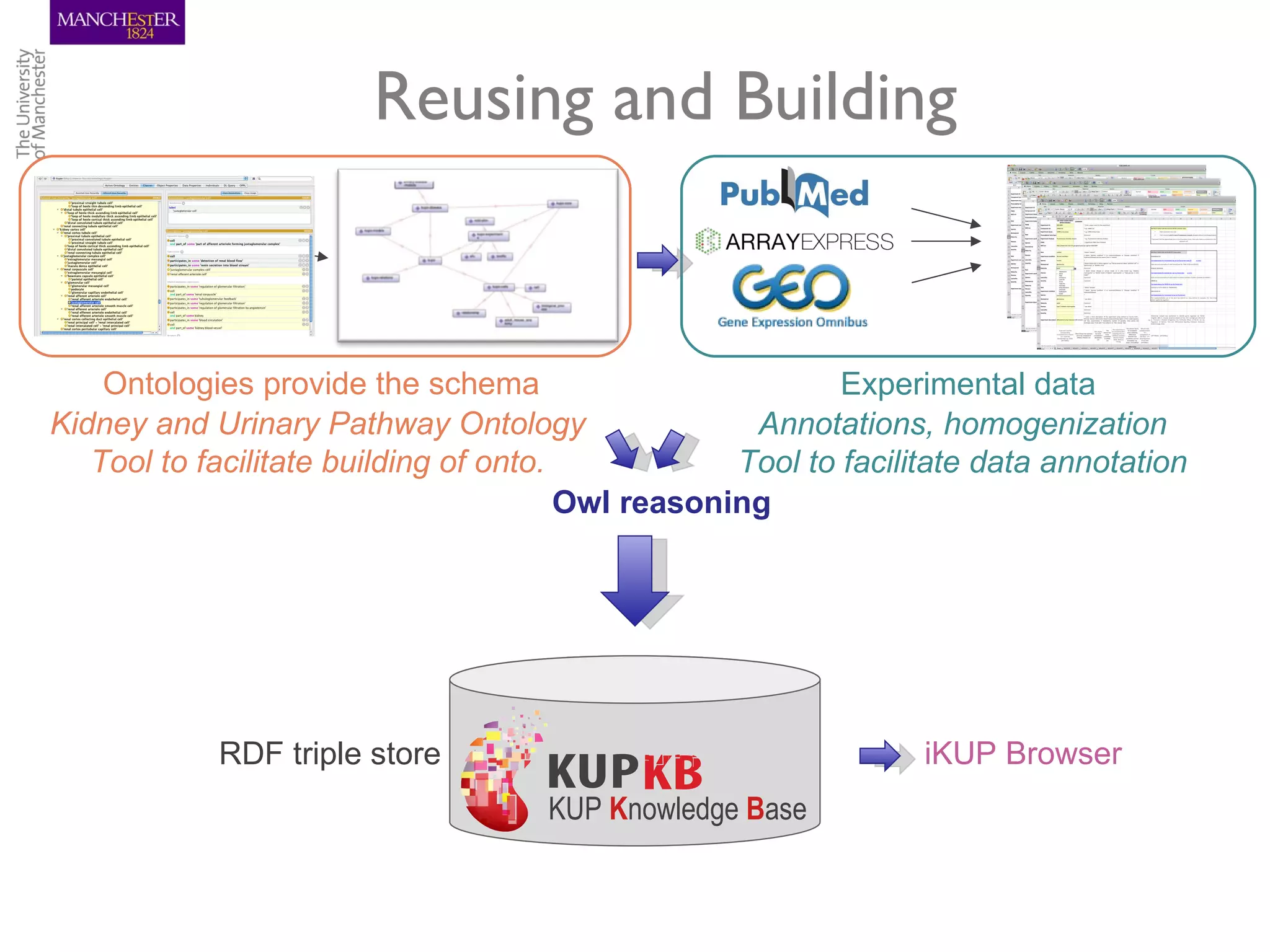
The KUPKB integrates thousands of kidney and urinary pathway studies into an RDF knowledge base using ontologies to provide schema and annotation. The iKUP browser exposes the knowledge in a simple web interface, allowing biologists to more easily survey biological publications and generate hypotheses than traditional literature searches. The tools and APIs used make it possible to build such applications at relatively low cost.