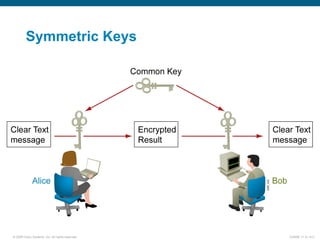
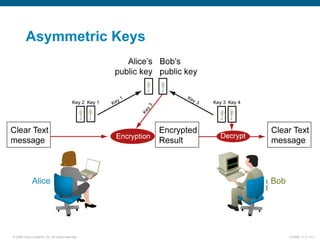
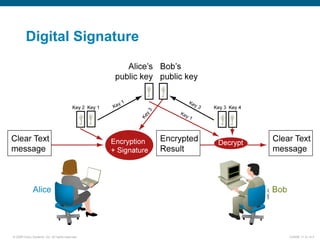
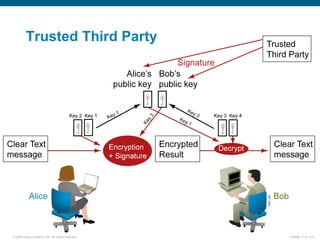
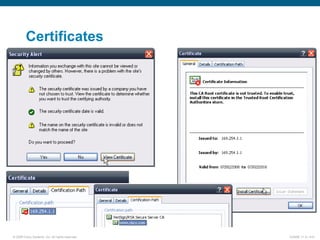
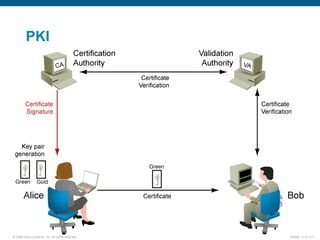
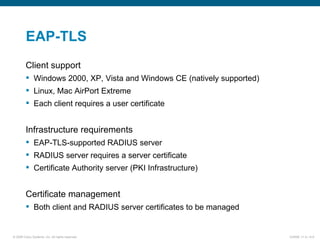
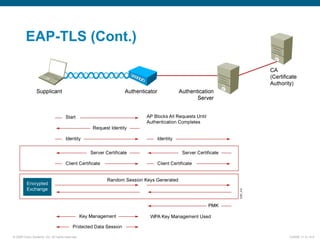
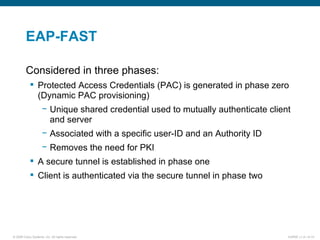
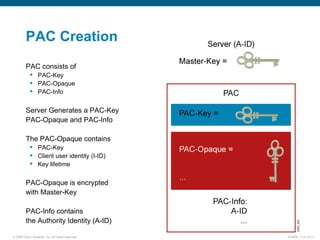
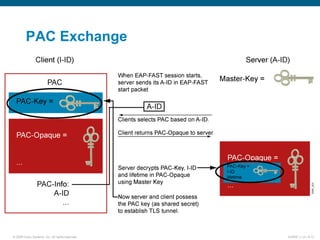
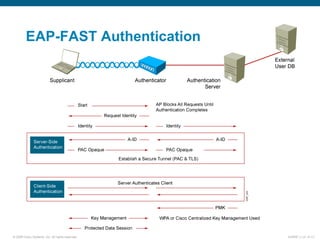
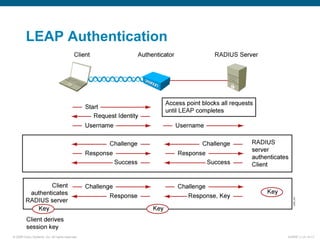
EAP-TLS uses certificates and PKI for mutual authentication between clients and RADIUS servers, requiring client and server certificates that must be managed. EAP-FAST establishes a secure tunnel using dynamically generated PACs instead of certificates. PEAP provides one-way authentication from server to client using a server certificate, allowing different inner authentication methods like EAP-GTC and EAP-MSCHAPv2 without client certificates. Cisco LEAP authenticates users via a username and password with dynamic WEP keys.