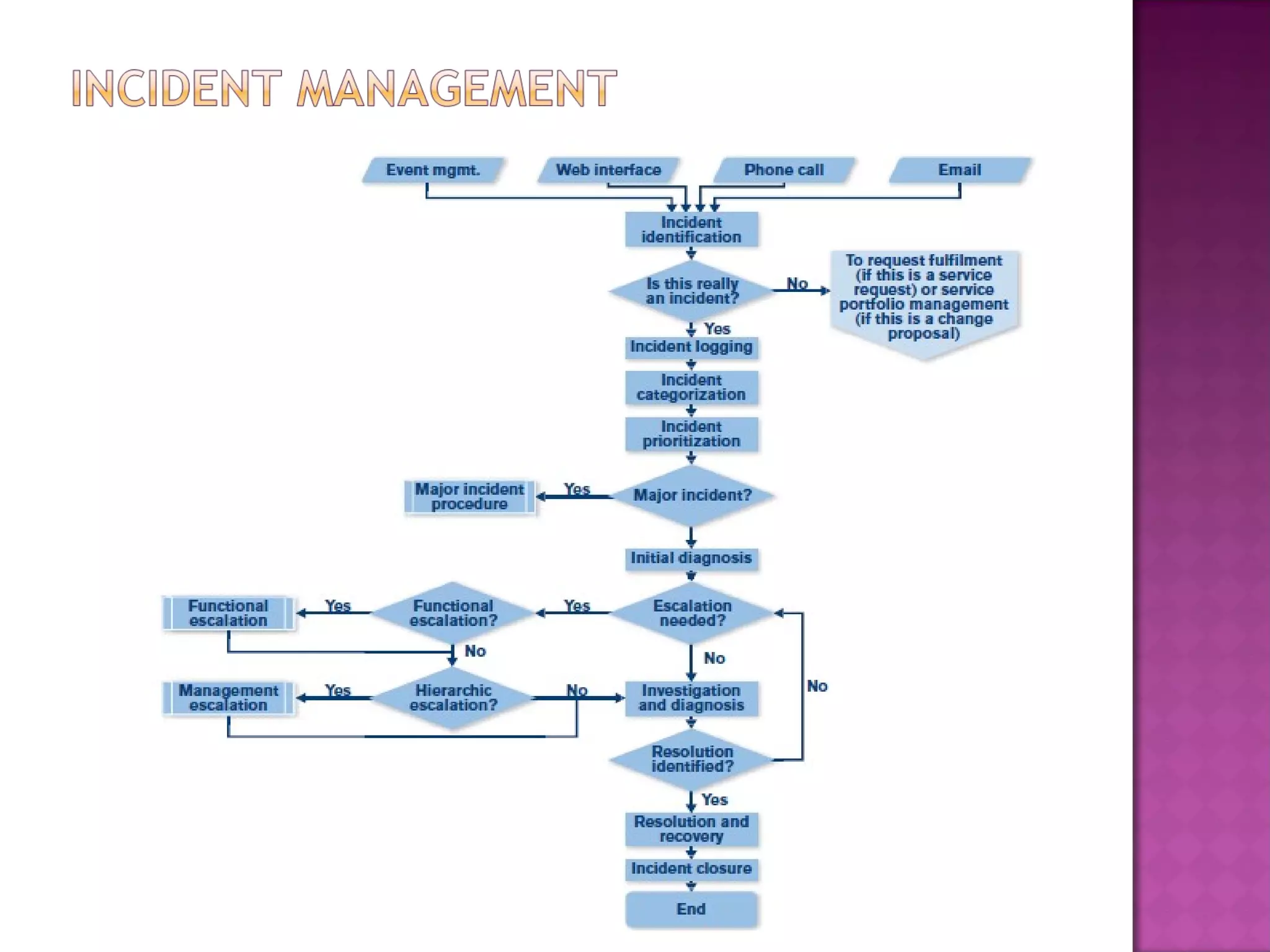
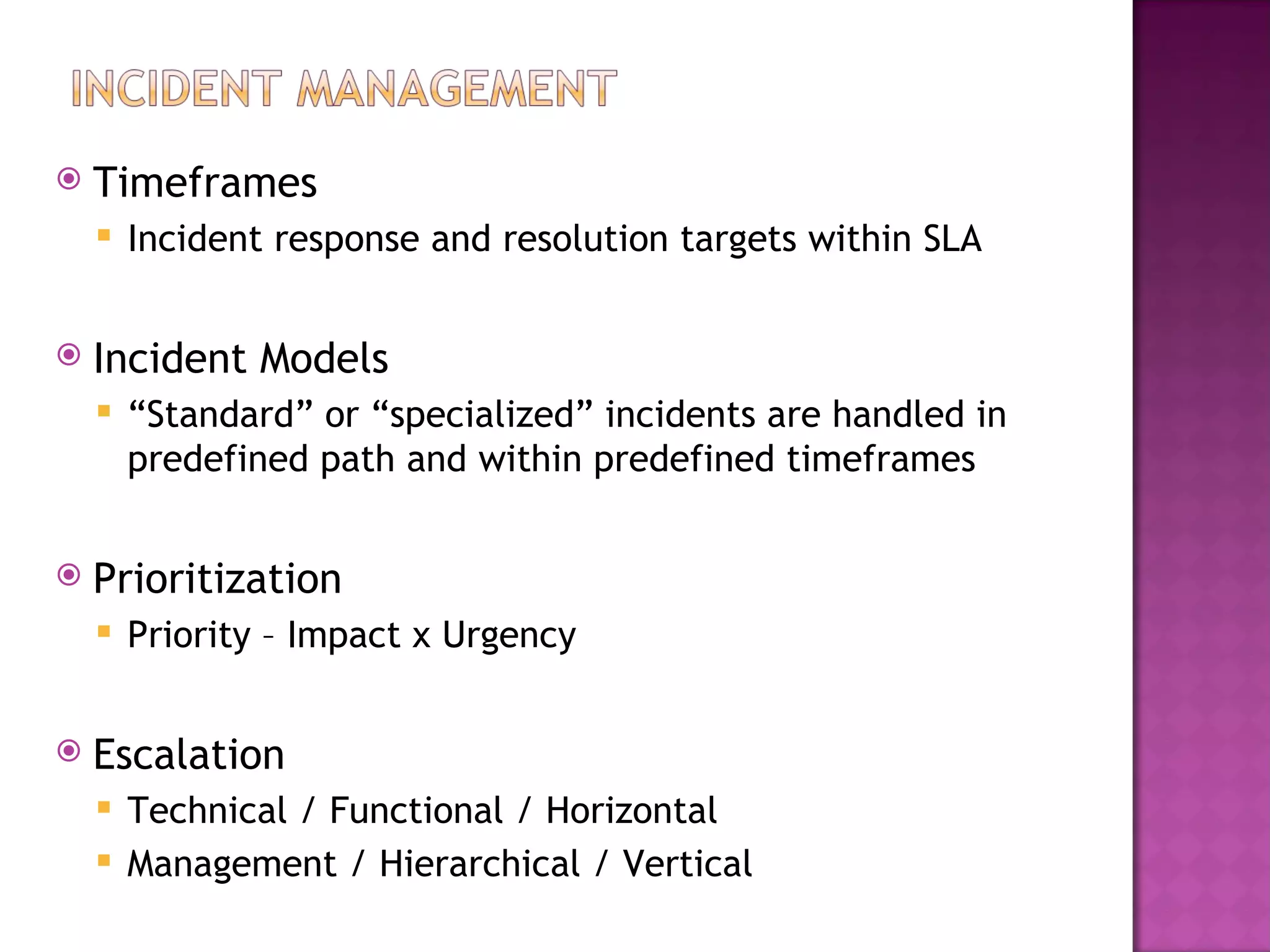
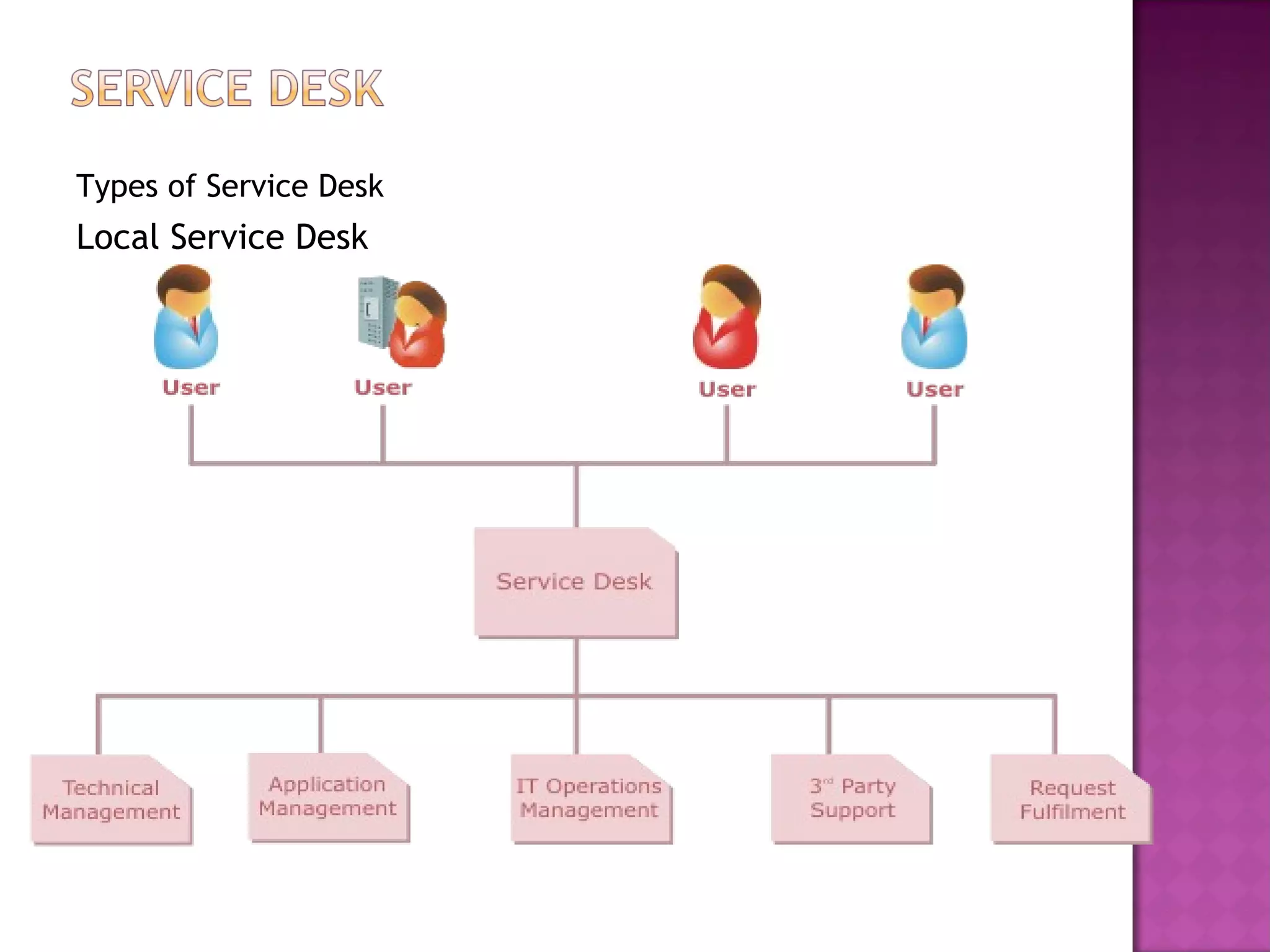
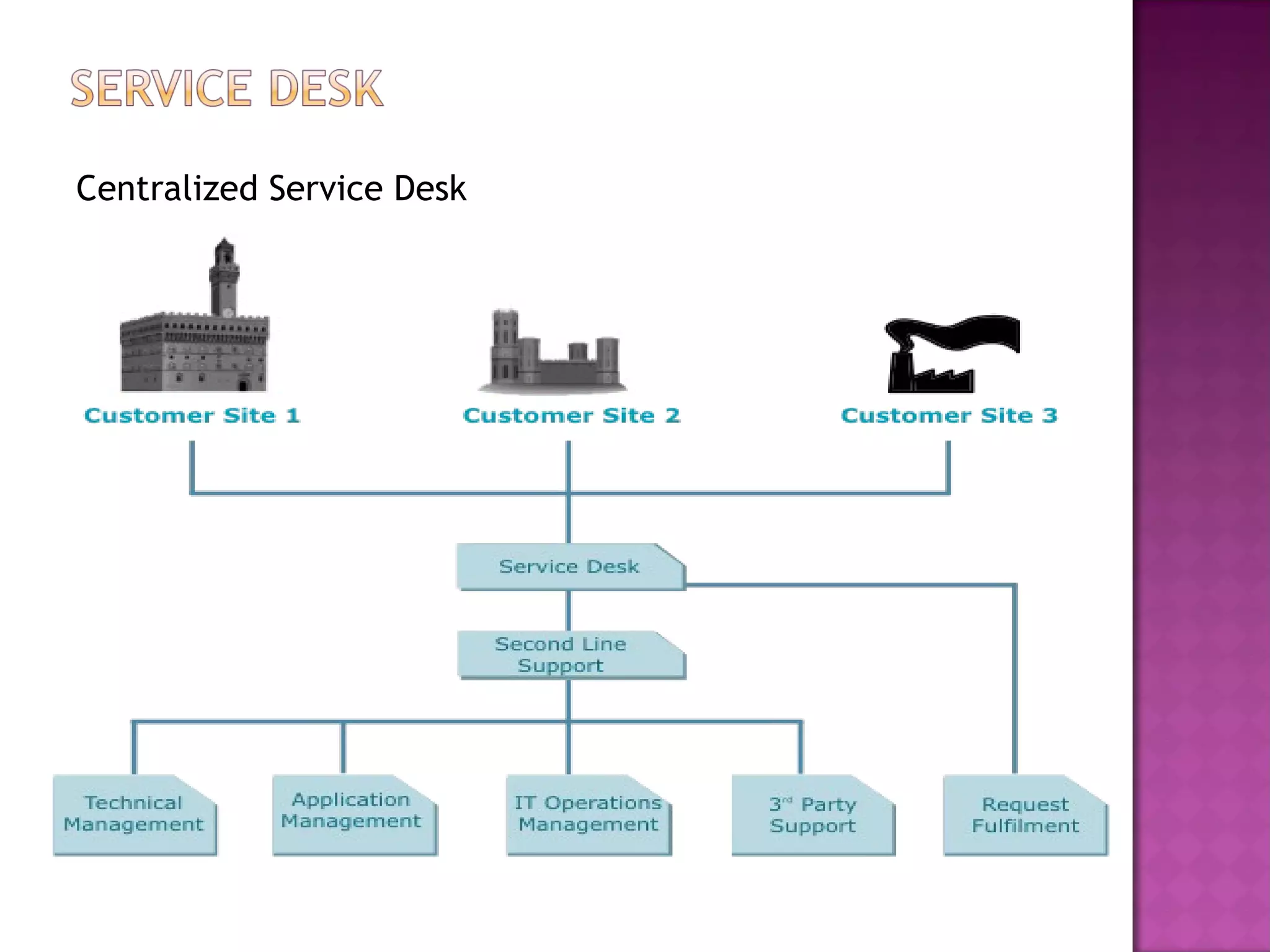
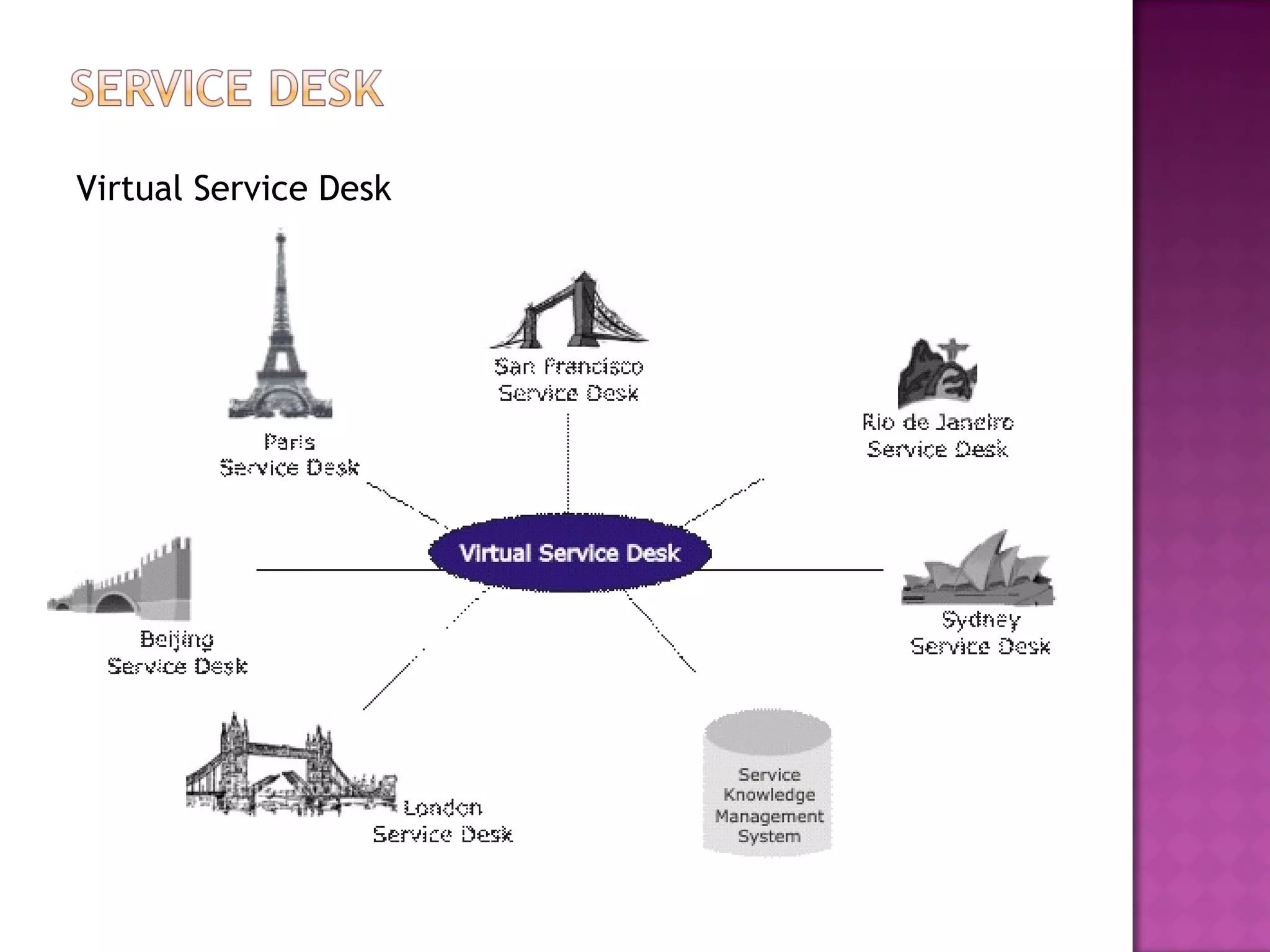
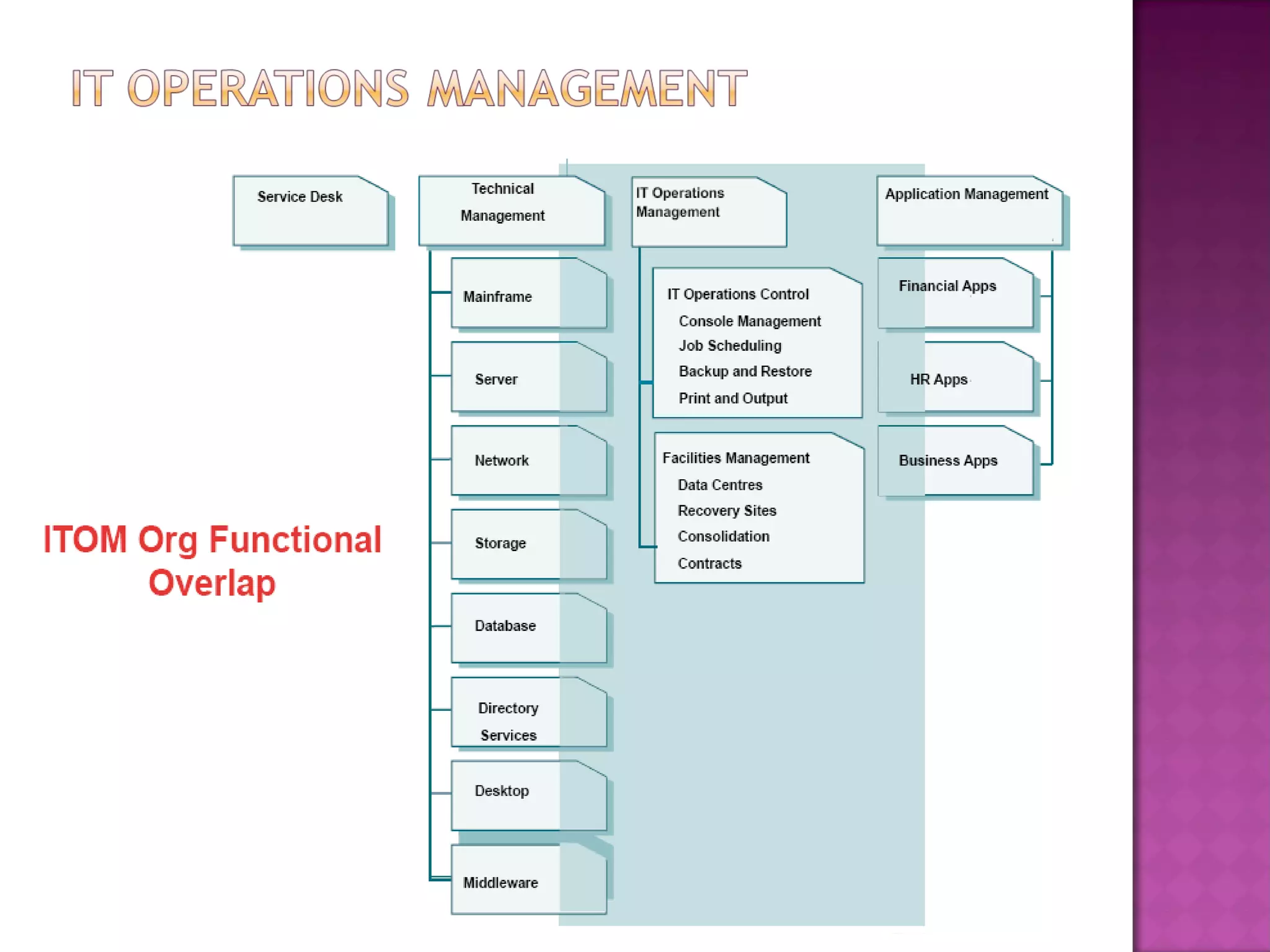
This document discusses several IT service management processes and functions including event management, incident management, request fulfillment, problem management, and access management. It also discusses the purpose, objectives, and scope of processes like monitoring events, incident management, problem management, request fulfillment, and access management. The key roles involved include the service desk, technical management, IT operations management, and application management.