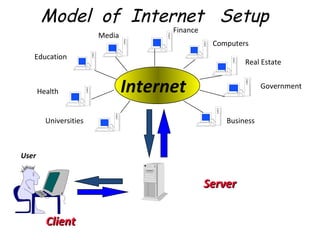
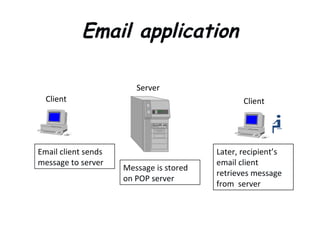
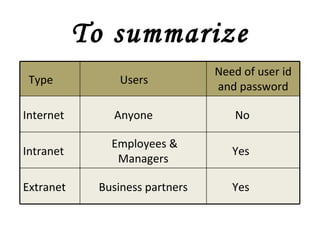
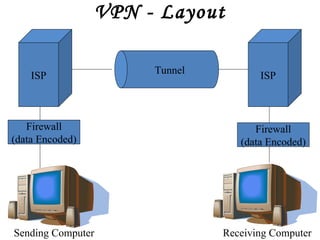
This document provides an overview of basic telecommunications and networking concepts. It defines what a computer network is and common types of networks including local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), and personal area networks (PANs). It also discusses network topologies, standards, the internet, intranets, extranets, and virtual private networks (VPNs).



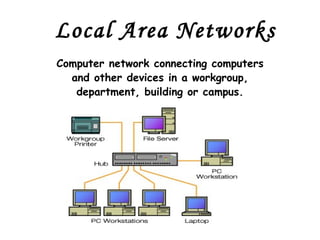
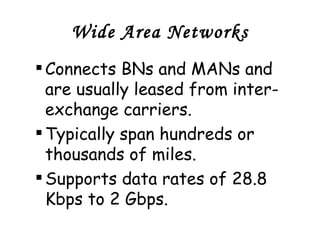
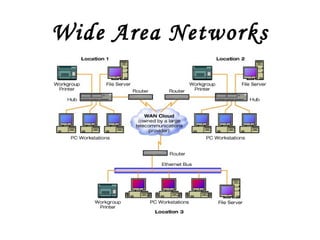




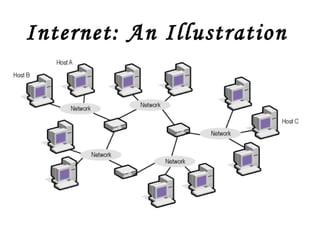






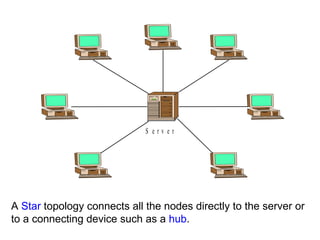
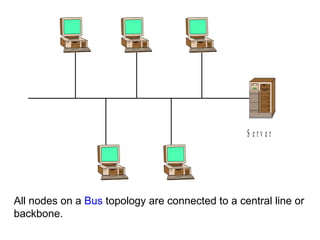
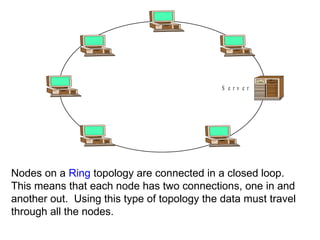
![Local Area Networks- 3 basic topologies These are either the logical or physical way the computers are connected. Each connection on the network is known as a node . These topologies are: Star Bus Ring Mesh [ Partially connected, Fully connected ] Tree](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofnetworking-090902132558-phpapp02/85/Basics-Of-Networking-23-320.jpg)