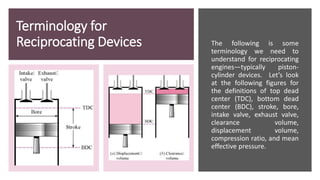
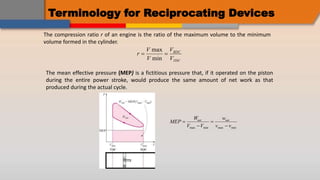
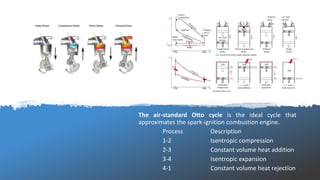
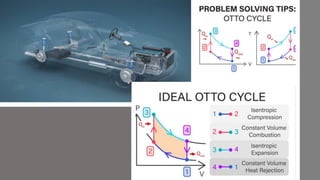
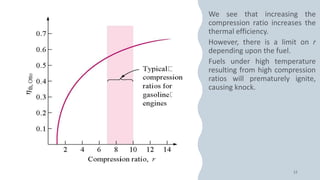
The document discusses the air-standard Otto cycle which is used to model spark ignition engines. It covers the assumptions made in analyzing the cycle including treating air as an ideal gas and approximating the combustion process as a constant volume heat addition process. It then defines key terms related to reciprocating engines. The Otto cycle consists of isentropic compression, constant volume combustion, isentropic expansion, and constant volume heat rejection. An example calculation is provided to determine efficiency, temperatures, pressures, mean effective pressure, and backwork ratio.